Aromatic compounds
Aromatic compounds are chemical compounds containing a ring with delocalized pi electrons. Learn about the definition, naming conventions, and reactions of aromatic compounds such as benzene. Explore topics like aryl groups, halogenation reactions, and the mechanism for bromination of benzene.
0 views • 19 slides
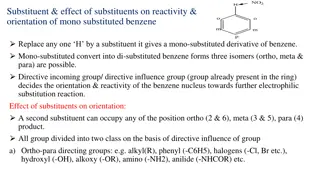
Substituent Effects on Benzene Reactivity and Orientation
Substituents in benzene derivatives influence reactivity and orientation in electrophilic substitution reactions. They can be classified as ortho-para directing or meta directing based on their effect. Ortho-para directing groups increase electron density and activate the ring, while meta directing
7 views • 14 slides
Mono Chloro Benzene Manufacturer in Gujarat
Discover excellence in chemical manufacturing with Modi Chemical, a premier Mono Chloro Benzene Manufacturer in Gujarat. Experience top-quality products and unmatched service, meticulously crafted to meet your industrial needs. Partner with us to access cutting-edge solutions and unparalleled expert
2 views • 1 slides
Understanding Aromatic Compounds: Benzene and Its Structures
Aromatic compounds, specifically benzene and its derivatives, are central to organic chemistry. This summary delves into the resonance structures of benzene proposed by Kekulé, the orbital model for benzene, symbols representing benzene, and the aromatic character rules based on electron count. Thi
2 views • 25 slides
Understanding Benzene and its Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions
Aromatic compounds like benzene undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions (EAS). This process involves the reaction of an electrophile with the aromatic ring, leading to the formation of various derivatives. Examples include halogenation, nitration, and sulphonation of benzene, each with
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Effects of Substituents on Benzene Reactivity
Substituents on an aromatic ring impact reactivity and substitution orientation. Activating groups make benzene more reactive, while deactivating groups reduce reactivity. Ortho-para and meta directors guide future substitutions to specific positions. Examples of activating and deactivating groups a
0 views • 10 slides
Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Structure, Aromaticity, and Nomenclature
Aromatic hydrocarbons, with benzene as a key example, possess unique properties due to their highly unsaturated structures. The molecular formula of benzene is C6H6, and it exhibits resonance through a planar structure with sp2-hybridized carbons. To be classified as aromatic, a compound must have a
0 views • 19 slides
Overview of Air Emissions and Quality Assessment in Shale Gas Development
The presentation discusses the estimation of air emissions from shale gas development and production in North Carolina, highlighting the importance of analyzing emissions from oil and gas activities and associated truck traffic. The process involves building emissions inventory, photochemical modeli
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Tie Lines in Ternary Systems
Ternary systems involve three components where partial miscibility can lead to phase separation. Adding alcohol to a benzene-water mixture can promote miscibility by acting as an intermediary solvent. By breaking cohesive bonds and increasing heat, the system can transition to a single phase. The pr
0 views • 15 slides
Criteria for Solvent-Related Hearing Loss and Compensation Claims
The Department of Labor (DOL) has specific criteria for accepting claims related to solvent-induced hearing loss in employees. If an employee has sensorineural hearing loss in both ears, was exposed to certain chemical solvents, and worked in particular job categories for a concurrent 10-year period
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Benzene and Its Derivatives: Methods, Properties, and Reactions
Explore the methods for preparing benzene, understand its chemical properties and reactions including halogenation, nitration, sulfonation, Friedel-Crafts alkylation, and acylation. Dive into carbon-carbon bond formations and substitution reactions in aromatic compounds.
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Anthracene: A Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon
Anthracene, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, is composed of three fused benzene rings and exhibits unique properties such as a blue fluorescence when crystallized with benzene. It is commonly found in coal tar and has various industrial applications, including dye production, smoke screens, wood p
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Petroleum Hydrocarbons and Their Properties
Petroleum is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons, including paraffins, olefins, naphthenes, and aromatics. Paraffins are fully saturated and stable, olefins are unsaturated with double bonds, naphthenes are cyclic saturated hydrocarbons, and aromatics are cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons containing ben
0 views • 19 slides
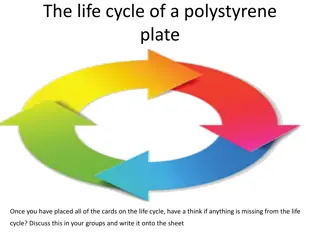
The Life Cycle of Polystyrene Plates: Environmental Impact Analysis
The life cycle of a polystyrene plate involves the manufacture of chemical components, such as benzene and styrene, leading to the production of polystyrene through the use of blowing agents. The extraction and use of these components have environmental implications, highlighting the need for sustai
0 views • 14 slides
Introduction to Aromatic Compounds and Benzene Nomenclature
Learn about aromatic compounds, their resonance in benzene, orbital structure, nomenclature for benzenes, and different types of substituents like monosubstituted and disubstituted benzenes. Explore the stability of aromatic compounds compared to aliphatic ones and understand the nomenclature for va
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Colligative Properties and Vapor Pressure in Solutions
Colligative properties are solution properties dependent only on solute concentration, not solute identity. The Van't Hoff factor helps in such equations, especially for ionic compounds. Vapor pressure lowering is a key colligative property where a solute decreases vapor pressure. Raoult's Law expla
0 views • 23 slides