International Production Management: Location Strategy and Decision Making
International Production Management involves systems, processes, and decisions related to the production of goods and services. Key decisions include plant location, make or buy choices, global sourcing, logistics, and networking. Factors influencing location strategy include customer preferences, product variety, trade barriers, and exchange rates. Centralised and decentralised locations have merits and demerits based on factors like efficiency, cost, and risk. Location choices depend on product nature, raw material availability, market demand, political factors, and organizational considerations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
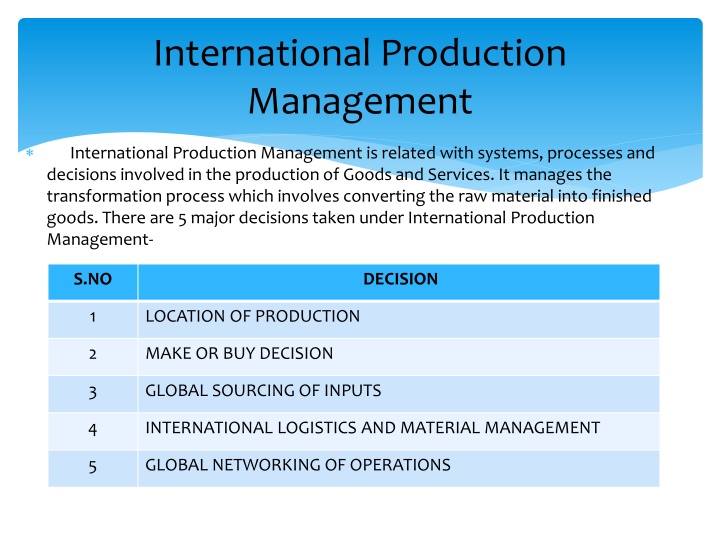
International Production Management International Production Management is related with systems, processes and decisions involved in the production of Goods and Services. It manages the transformation process which involves converting the raw material into finished goods. There are 5 major decisions taken under International Production Management- S.NO DECISION 1 LOCATION OF PRODUCTION 2 MAKE OR BUY DECISION 3 GLOBAL SOURCING OF INPUTS 4 INTERNATIONAL LOGISTICS AND MATERIAL MANAGEMENT 5 GLOBAL NETWORKING OF OPERATIONS
1. PLANT LOCATION DECISION The location of Production facilities the one of the most crucial decisions as it directly impacts the operational efficiency and cost of Production. Also, location is a long term decision which cannot be reversed easily. TWO ALTERNATIVE LOCATION STRATEGY FOR INTERNATIONAL FIRM CENTRALISED LOCATION DECENTRALISED LOCATION There are certain factors which influence the Location Strategy as to whether it will be Centralised or Decentralised like Customer taste & preference, variety of product, trade barriers, exchange rates etc.
Factors influencing the Location Strategy S.NO FACTORS CENTRALISED LOCATION DECENTRALISED LOCATION 1. Taste & Preference in different markets Same Different 2. Type of Product Standardised Global Different Variety 3. Cost of Manufacturing Differs between Countries Does not significantly differ between Countries 4. Trade Barriers Low High 5. Similar enterprise at one place Concentrated No Concentration 6. Exchange Rate Stable Fluctuate Widely 7. BEP w.r.t Global demand High Low 8. Ration between Value and Weight of the product High Low 9. Sources of Input and market Concentrated Dispersed
Merits and Demerits of Centralised and Decentralised Location S.NO CENTRALISED LOCATION DECENTRALISED LOCATION MERITS- Maximum Efficiency Possible Easy to adapt local conditions Standardisation of Product possible Flexibility of Operation Large Economies of Scale Customisation in Production Uniform procedure to simplify administration Less Political and commercial risk. DEMERITS High transportation cost High cost per unit of Production Delay in delivery of products High Administrative Cost
FACTORS AFFECTING LOCATION Once a firm decides whether its going to produce at home or in foreign country, the next step is to decide the exact location and it is dependant on the following factors- Nature of Product- weight, size, perishability etc. Availability of Raw material- skilled labour, power, transport etc. Technology- Product Life Cycle 1. Production Related factors Demand Pattern- Product with decline demand if often produced in developing countries. E.g.- Suzuki produced Maruti 800 in India. Market Size and potential- Customer Feedback- can quickly respond. 2. Market Related factors Political Factors Availability of Inputs- Several IT firms have preferred India due to low cost software professionals. Country of Origin- USA and Japan are known for quality. Social and Cultural factors Cost in logistics 3. Country Related Factors 4. Organisational factors like nature of the firm whether its is a multinational corporation, global corporation of transnational corporation.
2. MAKE OR BUY DECISION Another major decision in International Production is whether to manufacture in- house or procure from third party suppliers. Both the alternatives of making and buying have its advantages and disadvantages. The aim is to get the product of right quality at minimum price. Advantages of Buying Advantages of Making - Lower Cost - Cost Control - Wide Choice - Quality Control - Concentrate on Core activities -Control over Supply - Ease of Exit - Protection of Technology MAKE OR BUY? -Low impact of recession - Specialised Investment Disadvantages of Making Disadvantages of Buying - Higher Investment - No control on cost - Need for expertise - Less control on quality - May be inefficient - Less control on delivery - Difficulty of exit - Less control on technology -High impact of recession - High bargaining power of suppliers
3. GLOBAL SOURCING OF INPUTS (GLOBAL OUTSOURCING) Globalisation gives an opportunity to the firms to source inputs, components and finished products from the best source available anywhere in the world. Companies from countries like USA and Japan ship the components to assembly plants abroad where labour is cheap. China, India, Malaysia have become the global manufacturing hub for companies like Toyota, Nissan, Apple etc. Global outsourcing accounts for about 1/3rdof the world s trade. The main reason for increasing offshore purchase are- 1. Lower Price 2. Better Quality 3. Better technology 4. More cooperative delivery 5. Less Capital and manpower requirements 6. More flexibility to adjust to recession 7. Counter trade requirements are fulfilled
Two main concepts which have emerged out of Outsourcing are- 1. - According to P.F.Drucker, Production sharing means the practice of carrying out different stages of manufacturing of a product in different countries. Here the product is designed in one country, manufactured in another country and assembled in different country. E.g- Apple is designed in California and assembled in China. PRODUCTION SHARING 2. PARTNERING - The buyer supplier partnership is emerging as a strategic issue in International operations due to need for offshoring outsourcing. E.g- When Microsoft develops more powerful software, demand for Intel vhip increases. Similarly, value of Microsoft increases when Intel produce powerful chip.
4. INTERNATIONAL LOGISTICS Logistic is the process of planning, implementing and controlling the efficient, cost effective flow and storage of raw materials, semi finished goods, final products and related information from point of origin to point of consumption. Business Logistics Inbound Logistic Outbound Logistic Sources of Supply Plant/ Customer manufacturing Unit
Management of logistics require concerned decisions Network Design-Number and location of facilities needed. Information system-Information needed for Sales forecasting Transportation- Speedy transportation system improves efficiency Warehousing- how many warehouse, what type of warehouse, where to locate and size of the warehouse is decided. Procurement- Acquiring resources (Raw, Sem finished or finished) Packaging and Labelling Inventory management-Dependant on anticipated demand and time required for replenishment of inventory. Order Processing- It begins when order is placed by a customer till the point it reaches the customer. The order processing affects the customer service significantly so it should be accurate, quick and efficient. In Logistics it is important to create time, place and possession utilities. 1. Time Utility- making product available at right time. 2. Place Utility- making product available at right place. 3. Possession Utility- Transferring ownership of product at right cost.
5. GLOBAL NETWORKING OF OPERATIONS To optimise the efficiency and increase competitiveness, International firms opt for global networking of its operation in different countries. Economic liberalisation and Globalisation have facilitated the movement of inputs and productions across the nations. According to World Investment Report(2002), there are 3 core elementswhich are critical to International production system- Geographic Configuration Governance Global Value Chain There is recent trend towards integration of production specialities spread across nations. Service and support functions are being increasingly Internationalised. Organisation and dispersion of production activities. Can be in various forms such as subsidiary, licensing,etc. It determines linkage with suppliers, producers, marketers. Helps to exercise control over business activities spread over several countries. Maintain co-ordination between functions in various countries. Value chains are becoming fragmented due to Specialisation. An International firm can have its core competitive advantage anywhere along the value chain.