Insights into the Tourism Industry
Tourism involves traveling to natural areas to study, admire, and enjoy scenery, wildlife, and cultural aspects. The growth of tourism in India has been significant with various initiatives to attract more foreign tourists and promote eco-tourism. Medical tourism is also on the rise, with travelers seeking healthcare services across borders. Explore the opportunities and initiatives driving the tourism industry forward.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PRESENTATION ON- TOURISM INDUSTRY
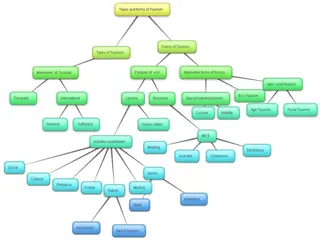
INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION Tourism involves travelling to relatively undisturbed or uncontaminated natural areas with the specific object of studying, admiring and enjoying the scenery and its wild plants and animals, as well as any existing cultural aspects (both past and present) found in these areas. Tourism , for some provides entertainment, for others it serves as a holiday and for yet others it is a means of understanding other peoples ways of life, culture and traditions.
Growth of Tourism in india Organized tourism in India began in 1950s with the genesis of planned development. Over the years, Indian tourism has grown considerably as in indicated by the arrival of foreign tourists. Indian tourism sector has performed well during the last few years with Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs) growing at 9.7% to 8.8 million in 2016.
INITIATIVES TO ATTRACT MORE FOREIGN TOURISTS : Visa-on-arrival (VoA) At present, tourists from 12 countries are able to use this facility which is available at almost all major international imports. E-Tourist Visa (eTV) This facility is available to citizens of 113 countries and 16 airports. Fee for visa has also been reduced considerably to encourage foreign tourist. Niche Tourism Products This initiative has been taken to identify, diversify, development and promotion of such products of tourism industry. Niche products identified so far include cruise, adventure, medical, wellness, golf, polo, meetings, conferences and exhibitions, eco-tourism, film tourism and sustainable tourism. Bed and Breakfast/Homestry Scheme This scheme offers tourists an opportunity to stay with an Indian family and enjoys the warm hospitality and a taste of Indian culture and cuisine in a clean and affordable place. Swadeshi darshan This scheme has been launched for development of theme- based tourist circuits in a way that caters to both mass and niche tourism in a holistic manner.
Eco-Tourism Eco Tourism is defined as responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment , sustains the well-being of the local people and involves interpretation and education. Eco Tourism is promoted in India by evaluating environmental and cultural factors, initiatives by hospitality providers to promote recycling energy efficiency, water reuse and the creation of economic opportunities for local communities.
Medical Tourism Medical Tourism Medical Tourism is a term used to describe the rapidly growing practice of travelling cross international borders to obtain healthcare. Services typically sought by travellers include elective procedure as well as complex specialized surgeries such as joint replacement, cardiac surgery, dental surgery and cosmetic surgeries. To promote medical tourism , the Govt. of India has launched India s Healthcare Portal and Advantage Health Care India.
Domestic Tourism Domestic Tourism is an important segment of the overall tourist scenario although no reliable data are available in this regard. Domestic Tourism is no less pronounced than the foreign tourism. It is domestic tourism which fosters a sense of unity in the otherwise diverse environment of the country and contributes to national integration.
EMPLOYMENT OPPORTUNITIES IN TOURISM Tourism in India has vast employment potential, much of which still awaits exploitation. Another important aspect of employment in tourism is that it employs a large number of women, both educated and uneducated, as well as skilled and unskilled. In fact, women are greater in number than men in hotels, airline services, travel agencies, handicraft making and cultural activities, etc.
Places of Tourist interest in India The Himalayan region Srinagar, Gulmarg, Kullu-Manali, Shimla, Chamba, Haridwar, Mussoorie, Darjeeling, Gangtok, Meghalaya, etc. The Great Plain of North India Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Bihar, West Bengal, Assam,etc. The Peninsular Plateau and the Coastal Plains Gujarat, Goa, Odisha, Karnataka,Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Daman and Diu, Dadra and Nagar Haveli,etc.
PROBLEMS AND PROSPECTS The development of tourism depends upon the development of an integrated infrastructure of national highways, international highways, railways, ports, civil aviation, telecommunication, hotel accommodation and allied services. Inadequacies of such infrastructural facilities adversely affect tourism. Apart from infrastructural development, tourism, requires an environment of peace and stability where the tourist is sure of his safety and security. Political unrest and fear of violence is a death knell to tourists industry. Unfortunately, one part of the country is hit by bandhs, strikes, ethnic clashes and insurgency which adversely affects tourism. Epidemics, such as plague and dengue fever are also detrimental to tourism. It is surprising that some small sized countries like Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, Honkong have been able to attract more tourist and better receipts than India. India Tourism Development Corporation (ITDC) was established in October 1966. The central Department of Tourism is extending financial assistance for improving tourism infrastructural facilities like yatri niwas, tourist lodges, wayside facilities, restaurants, cafeterias, tourist bungalows, etc.
MAIN THRUSTS DURING MAIN THRUSTS DURING EIGHTH FIVE YEAR PLAN EIGHTH FIVE YEAR PLAN Development of selected tourist places. Diversification from culture-oriented tourism to holiday and liesure tourism Development of trekking, winter sports, wildlife and beach resort tourism Exploring new source markets in regions and countries having cultural affinity Restoration of national heritage projects Providing inexpensive accommodation in different tourist centres Improving service efficiency in public sector corporations Streamlining of facilitation procedures of airports
TOURISM AND ENVIRONMENT The origin and growth of tourism in India as elsewhere in the world, is distinctly urban oriented rather than being spread over the country side. This is due to the fact that urban centres provide the necessary infrastructure and wider choice of facilities and price ranges for accommodation, food, entertainment, etc. There is lack of appreciation of the holistic approach to tourism development which takes into account the linkages between environment and pressure of tourists.Theresult is that, almost all the popular tourist centres are groaning under the pressure of annual visitors and quite often facing difficult situation. The unplanned and unchecked growth of tourist centres deprives them of their original charm and ultimately proves disastrous. This is what is happening to some of the famous tourist centreslike Shimla, Mussoorie, Darjeeling, etc. where sometimes even drinking water is not available to cater to the needs of the tourists. The Taj Mahal at Agra, the MeenakshiTemple at Madurai, the Lingaraja temple in Bhubaneshwar and the palace in Udaipur are examples of this nature where much of the original beauty and charm is lost due to unplanned constructions around them. With the view to improve tourism and at the same time taking care of the environment, the central and the state governments are coming forward with new development plans.