Functions of Reproductive System in Males and Females
The reproductive system plays a crucial role in creating new life, with males producing, maintaining, and transporting sperm, while females support conception and provide a nourishing environment for the fetus. Learn about the distinct functions of both male and female reproductive systems in detail.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
By: Crystal Cerda Clinical Rotation Block 6 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Objective Describe the functions of both male and female. Note taking Fill in the blank diagram Test
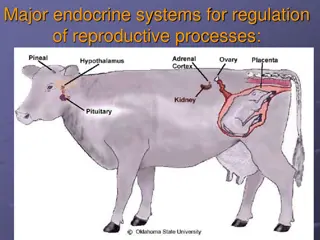
Function The main function for the Reproductive System is the creation of new life. Males: To produce, maintain & transport the sperm, discharge sperm within the female reproductive tract and produce and secret male sex hormones. Female: Production of menstrual cycle, create ovaries for conception, create a nourishing habitat for the fetus when a baby is in the womb and after it s born.
Male Produce about 100 million sperms daily. it is essential to have a lower body temperature to produce the sperm or else high temperature kills the sperm. Sperm lives inside the body about 4-5 days. Organs are located in the outer part of the body. Sperm production starts to diminish as testosterone levels start to decrease later in life. Produce sperm throughout their life time. Their physician specialist are called Urologist.
Female They have about 2 million egg cells when born. Before puberty they are left with 300,000-400,000 egg cells. Ovulation occurs every 28 days. Egg cells last about 12-24 hours after ovulation Organs are located in the inner part of the body. Over a period 5-8 years, menstrual cycles become irregular then infrequent until they stop all together. Their physician specialist are called Gynecologist.
Conception It requires both male and female for the human reproduction to take place. Both male and female requires about and to contribute genetic material. It only takes about one sperm to fertilize an egg. The egg cell gets fertilized in the females fallopian tube then travels down to the uterus where the placenta and baby are formed.
Gender before and after birth The male s genetic chromosome determines the baby s sex. The gender of an embryo can be determined by 20 weeks into pregnancy Characteristics of gender won t be noticeable after childhood.
Additional information The shape of the uterus is pear-shaped. The shape of the prostate gland is doughnut- shaped.
Diagram Answers Answers for male reproductive system: Answers for female reproductive system: A Median section through the male pelvis B Anterior view of the male reproductive tract 1 Vas deferens 2 Seminal vesicle 3 Prostate gland 4 Cowper's glands 5 Epididymis 6 Testis 7 Scrotum 8 Penis 9 Pubic symphysis 10 Bladder 11 Urethra A Median section through the female pelvis B Anterior view of female reproductive tract 1 Ovary 2 Fallopian tube 3 Uterus 3a Cervix 4 Vagina 5 Clitoris 5a Prepuce 6 Labia magora 7 Labia minora 8 Pubic symphysis 9 Bladder 10 Anus 11 Perineum