Male Reproductive Tract Anatomy in Animal Science
Explore the anatomy of the male reproductive system in animals, focusing on the testis, epididymis, bull reproductive organs, and more. Learn about the functions of the testes, sperm production, testosterone, and the structures involved in sperm delivery and storage. Detailed imagery and descriptions enhance understanding of the intricacies of male reproductive physiology.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Animal/Dairy Science 434 Male Reproductive Tract Anatomy
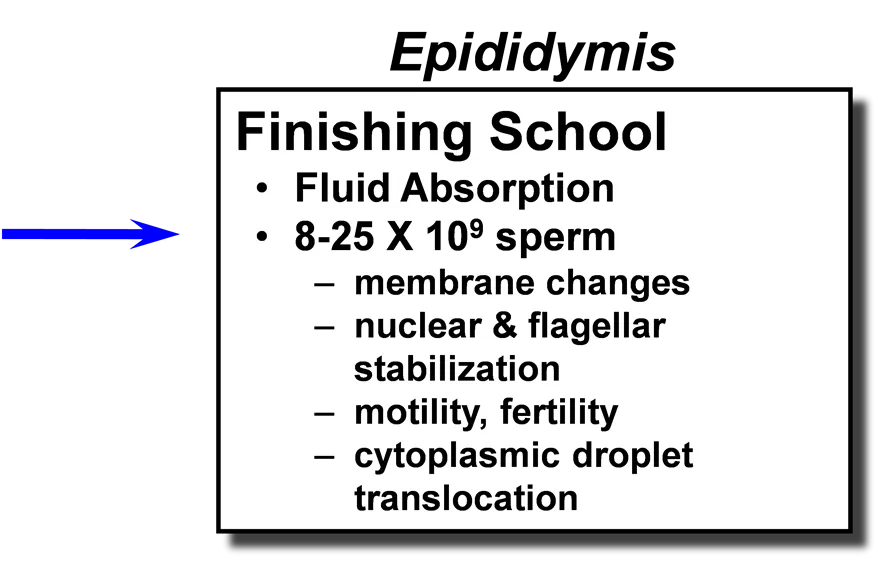
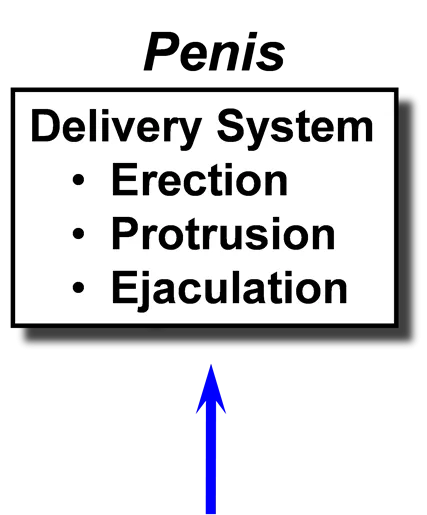
Testis Epididymis Factory 1-25 X 109 sperm/day Plant must be air conditioned Finishing School Fluid Absorption 8-25 X 109 sperm membrane changes nuclear & flagellar stabilization motility, fertility cytoplasmic droplet translocation Penis Delivery System Erection Protrusion Ejaculation Tail of Epididymis Warehouse and Delivery Storage 10-50 X 109 sperm Sperm for 5-10 ejaculates Smooth muscle contractions upon sexual stimulation Accessory Sex Glands Alterations & Packaging Metabolic substrates Surface coatings Transport for sperm
Reproductive Organs of the Bull
Reproductive Organs of the Bull Testosterone Sperm Testis Primary Sex Organ
Quiz 3a What are the 2 major functions of the testes?
Quiz 3a What are the 2 major functions of the testes? The formation of sperm and production of the hormone testosterone.
Bull Tract Thermosensor Radiator Protective sac Scrotum
Bull Tract Longitudinal Section Cross Section
Scrotal Longitudinal Section
Structure of the Testis Seminiferous Tubule Tunica Albuginea Rete Testis (within the mediastinum)
Mediastinum Rete Testis Seminiferous Tubule The Testis
Structure of the Testis Seminiferous Tubule Tunica Albuginea Rete Testis (within the mediastinum)
Structure of the Testis Secondary Sex Organs Spermatic Cord Vas Deferens Vasectomy Caput Epididymis Vas Efferentia 6-12 tubules Corpus Epididymis Cauda Epididymis
Structure of the Testis Spermatic Cord Vas Deferens Vasectomy Caput Epididymis Vas Efferentia 6-12 tubules Seminiferous Tubule Corpus Epididymis Tunica Albuginea Rete Testis (within the mediastinum) Cauda Epididymis
Quiz 3b Sperm are produced in what structure within the testes? Where are sperm stored in the male reproductive tract?
Quiz 3b Sperm are produced in what structure within the testes? Seminiferous Tubules Where are sperm stored in the male reproductive tract? Tail of the Epididymis (Cauda Epididymis).
Spermatic Chord Vascular, lymphatic and nerves Heat exchanger Houses cremaster muscle Pampiniform Plexus Testicular Artery Pampiniform Plexus Counter Current Exchange 39 C - 34 70 ng T/ml - 4.8 ng T/ml C
Spermatic Artery Pampiniform Plexus Testis Arterial Pulse Testicular Artery Testicular Artery
Spermatic Chord Pampiniform Plexus
Bull Tract Tunica Dartos
Contraction of the Tunica Dartos Testis Tunica Dartos Smooth muscle Androgen dependent (Testosterone)
Bull Tract Gubernaculum
Question 3c How is the testis cooled?
Question 3c How is the testis cooled? The blood is cooled by the pampiniform plexus and the testis can be raised or lowered by the tunica dartos. The external cremaster functions in fight or flight events.
Bull Tract Pelvic Genitalia
Pelvic Genitalia of the Bull Pelvic Urethra Muscle
Prostate Rectum Reproductive Organs of the Bull Cowpers Gland Seminal Vesicles Ampulla Bladder Retractor Penis Muscle Vas Deferens Sigmoid Flexure Glans Penis Caput Epididymis Scrotum Testis Cauda Epididymis Gubernaculum
Glans Penis of the Bull Free Part of Penis Urethral Process Raphe Glans Penis Prepuce (Retracted)
Glans Penis Glans Penis Urethral Process Raphe Free Part of Penis Prepuce (Retracted)
Quiz 3d What is a vasectomy and how does this differ from castration?
Quiz 3d What is a vasectomy and how does this differ from castration? Vasectomy is when the vas deferens is cut to prevent a male from getting a female pregnant. Castration is when the testes are removed and will prevent a pregnancy but also eliminates testosterone and therefore male behavior.
Prostate Rectum Reproductive Organs of the Bull Cowpers Gland Seminal Vesicles Ampulla Bladder Retractor Penis Muscle Vas Deferens Sigmoid Flexure Glans Penis Caput Epididymis Scrotum Testis Cauda Epididymis Prepuce Gubernaculum