Energy Changes and Light Behavior
Explore the concept of energy changes with a focus on kinetic and potential energy. Learn about different forms of energy like electrical, chemical, and thermal. Discover how light behaves through reflection, refraction, and properties of light waves.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 14 Energy Changes
Lesson 1: Energy Key Vocabulary
1. Kinetic energy- The energy that an object has because of its motion
2. Potential energy- Energy that is stored in an object
Lesson 14.1 Notes 1. Energy that is stored in an object is potential energy. 2. The energy of motion is kinetic energy. 3. Electrical energy can be used to run appliances. 4. Chemical energy is energy that is stored inside matter (a form of potential energy). 5. Mechanical energy is energy an object has due to its motion (a form of kinetic energy). 6. Light energy is energy that can be seen. 7. Sound energy is energy that can be heard. 8. Thermal energy is energy from heat.
Lesson 2: How Light Behaves Key Vocabulary
3. reflection- Occurs when light waves bounce off a surface
4. refraction- Occurs when light waves bend as they pass from one material to another
2. prism- A substance that separates white light into colors
1. light- A form a energy that can be seen and travels in waves
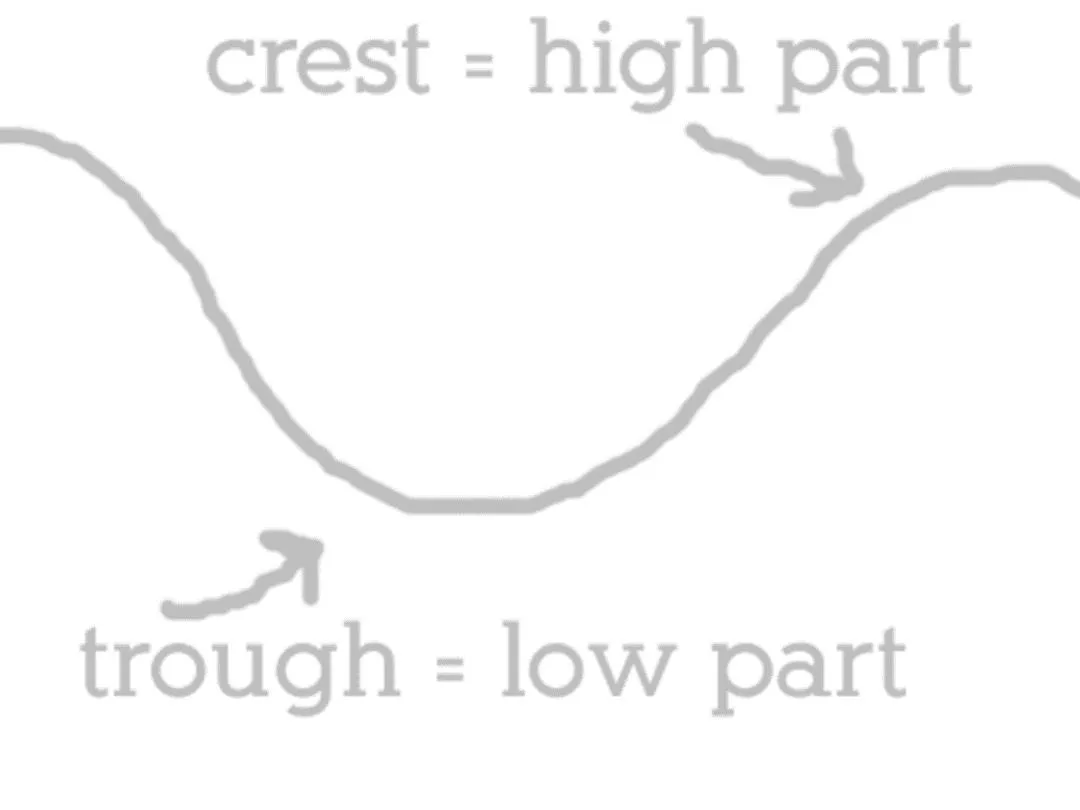
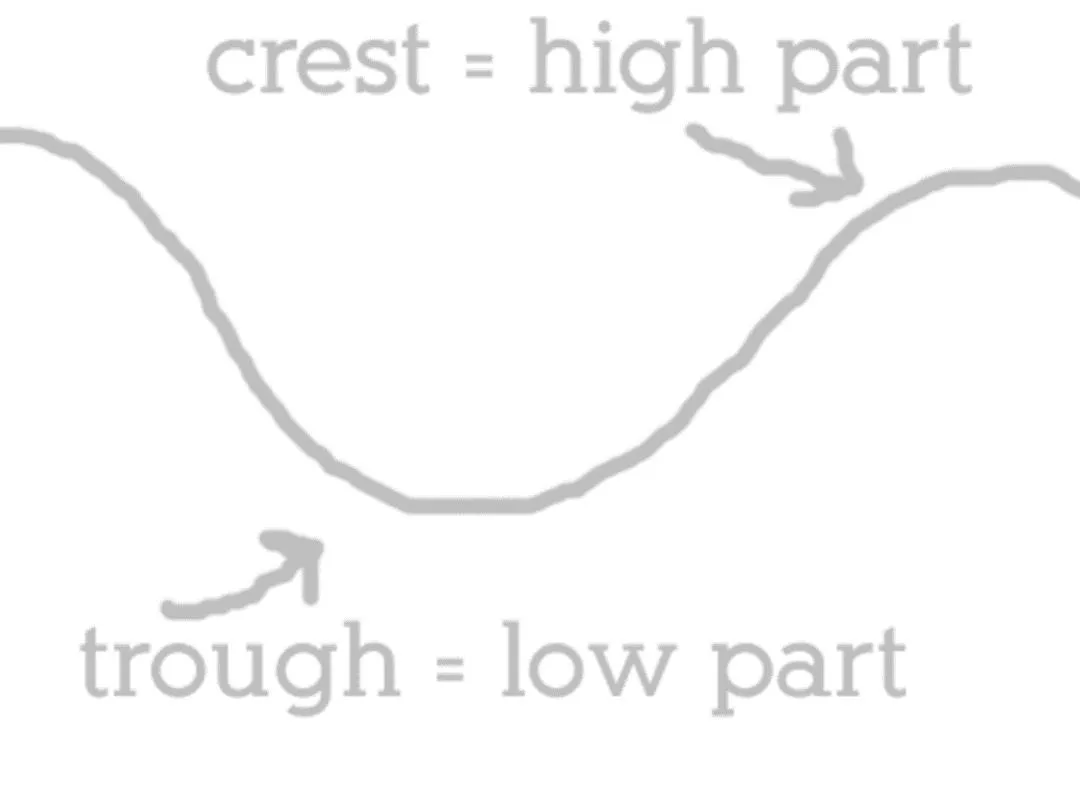
Lesson 14.2 Notes: Properties of Light 1. Light is a form of energy that you can see and travels in waves. 2. The high point of a wave is called a crest. 3. The low point of a wave is called a trough. 4. The distance from one crest to the next crest is called the wavelength.
Lesson 14.2 Notes: Behavior of Light 1. Reflection- when light waves bounce off a surface 2. Refraction- when light waves pass through an object and are bent as they go through 3. Absorption-when light waves are taken into an object 4. Transmission- when light waves pass through an object
Lesson 14.2 Notes: Colors of Light 1. The color of an object depends on the color of light that it reflects. 2. White light is made up of all the colors of the rainbow. 3. ROY G. BIV- colors of the rainbow in order from the longest to the shortest wavelength.
Lesson 3: Nature of Sound Key Vocabulary
3. volume- The amplitude, or loudness, of a sound
4. pitch- How high or low a sound seems to a listener
2. vibration- Very fast back and forth movement of matter
1. sound- A form of energy produced by vibrations
Lesson 14.3 Notes Sound 1. Sound is produced by vibrations of matter. When a material vibrates, it creates sound waves. 2. The energy of the sound wave and the distance the vibration object is from the listener are 2 factors that determine the volume of the sound. 3. Frequency is the number of crests and troughs produced in a given amount of time. Frequency determines pitch.
Lesson 14.3 Notes How You Hear Sound 1. Outer ear- part of the ear you can see; gathers sound waves from the air and funnels them to the eardrum. 2. Eardrum- thin flap of skin that vibrates when sound waves hit it. 3. Middle ear- contains 3 tiny bones that pick up vibrations from the eardrum. 4. Inner ear- has coiled tubes filled with fluid that vibrate causing nerve cells to send signals to the brain.
Lesson 4: Thermal Energy Key Vocabulary
2. convection- The transfer of thermal energy by the movement of fluids
1. conduction- The transfer of thermal energy from particle to particle between two objects that are touching
6. Thermal energy- The kinetic energy of moving particles of matter
3. heat- A measure of how much thermal energy is transferred from a warmer substance to a cooler substance
5. temperature- The average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance
4. radiation- The transfer of thermal energy without matter
Lesson 14.4 Notes Thermal Energy 1. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of tiny moving particles of matter. The hotter a substance is, the faster its particles move. The colder the substance, the slower its particles move. Heat is a measure of how much thermal energy is transferred from one substance to another. Thermal energy is transferred by conduction, convection, or radiation. In conduction, 2 objects need to touch in order to share thermal energy (ex- hot stove touching a pan). In convection, thermal energy is transferred in liquids and gases (warm air rises, cooler air sinks). In radiation, thermal energy is transferred by waves without matter (ex- heat from the sun travels through space to Earth). 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.