Employee Engagement in the 21st Century
Employers are actively seeking to improve employee engagement, viewing it as crucial for success. Engagement is about employees being emotionally and mentally invested in their work and contributing to their employer's success. Studies show a significant percentage of employees in the US are not engaged, costing businesses billions annually. This content explores the importance of creating a culture of engagement and the differences between satisfied and engaged employees.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT For employers, engagement has become the search for the Holy Grail of the 21stcentury. - Mercer, What s Working 2011 research report
OVERVIEW 1. What is engagement and why is causing such a ruckus. 2. The state of engagement today. 3. What drives engagement. 4. How to create a culture of engagement.
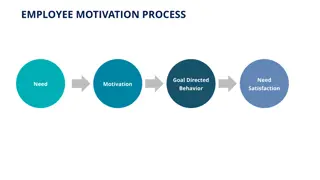
EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT Definition: Engagement is defined as employees who are mentally and emotionally invested in their work and in contributing to their employer s success as well as to their own.
STATE OF EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT According to a recent study on employee engagement, about 54 percent of employees in the United States are not engaged and 17 percent are disengaged. Only 29 percent are engaged Gallop Disengagement has been found to cost between 243 to 270 billion dollars due to low productivity of this group Gallop Highly engaged employees outperform their disengaged colleagues by 20 to 28 percent- Conference Board United States businesses lose $11 billion annually as a result of employee turnover- Bureau of National Affairs
SATISFIED VS. ENGAGED Satisfied employees feel comfortable, and are generally happy that their needs are being met. Engaged employees feel energized, passionate, dedicated, and are highly involved with their work and the company. Characteristics: Characteristics: Minimum requirements met Rarely help others for the better of the organization Generally keep to themselves Committed to the degree that needs are met Stay at the organization because of what they get from it Consistently exceed requirements Highly involved and always help others Recommend improvement opportunities Have a sense of purpose and pride in their work Stay at the organization for what they give to it Average Performance Optimal Performance
EMPLOYEESCANFALLINTOONEOFFOURENGAGEMENT- LEVELCATEGORIES Four Levels of Engagement Sense of ownership, passion, purpose, and pride in the organization. Energized, enthusiastic, and self-motivated. An organization ambassador. Considers the organization s objectives over their own. Generates ideas and exerts discretionary effort to better the company. Volunteers to take on extra tasks. Actively Engaged Feels a sense of satisfaction and commitment to the organization. Frequently motivated to go the extra mile. Considers the organization s objectives and their own objectives equally. Participates in organization and team events. Often volunteers to take on extra tasks. Engaged Does not feel a sense of purpose or pride in their work: it s just a job. Puts in sufficient time to meet minimum requirements. Typically considers their own objectives and interests before the organization s. Indifferent or apathetic to work-related issues or events. Typically does not volunteer to take on extra tasks. Not Engaged Has little care for their job or organization. May not openly show dissatisfaction, but their attitude is negative, affecting their work and peers. Does not meet requirements. Puts in time, but not effort. Disinterested in organizational objectives. Is focused on personal gains. Does not participate in organization or team events. Appears checked out. Complains about their role, the organization, their manager and peers. Disengaged
ONAVERAGE, ONLY 1 IN 3 EMPLOYEESISENGAGED Actively engaged 10 15% 20 25% Engaged 35 40% Not engaged Actively disengaged 20 25% % of employees based at each engagement level Source: McLean & Company 2011-2012
CAUSESOF DISENGAGEMENT Anonymity The feeling of being invisible to management. Not being understood or appreciated as a person. Irrelevance The feeling that what they do is not important or matters. Immeasurement Lack of tangible feedback on level of performance. Attitude Poor attitude regardless of the circumstances.
Drivers of Engagement 1. Treat People Right 2. Pay Slightly Above the Market 3. Recognize and Praise Workers Liberally 4. Create an Engaging and Fun Environment 5. Invest in Training and Career Development 6. Communicate the Hidden Paycheck 7. Promote Financial and Physical Wellness 8. Maximize Employee Involvement
WHAT NOW? Step 1 Form Employee Engagement Committee made up of managers, employees and HR Step 2 Outline strategy for addressing and improving engagement issues and efforts based on employee feedback ( survey, exit survey, focus groups , benchmark) Step 3 Compare objectives and programs against recognized drivers of engagement. Step 4 Evaluate success of efforts and programs
SUMMARY THE FOUR - M APPROACH Measure:Conduct an employee engagement survey. Make change: Effectively implement change initiatives that target priority areas identified from the engagement survey. Manage: Work with your management team to ensure they take responsibility for their employees engagement. Measure Success: Evaluate effectiveness of programs
EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT What is employee engagement if it s not an ongoing sales discussion between your company and your cherished talent? You might think that you re the buyer but actually they are. -Martha I. Finney, Bestselling Author The End