Dispositional Factors in Obedience Behavior
Dispositional factors, such as the authoritarian personality developed from strict parenting, play a significant role in influencing obedience behavior. Adorno's research on the authoritarian personality highlights traits like blind respect for authority, conventionalism, and cognitive inflexibility. Harsh parenting practices can contribute to the development of an authoritarian personality, leading individuals to exhibit obedience and rigidity in their behavior.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
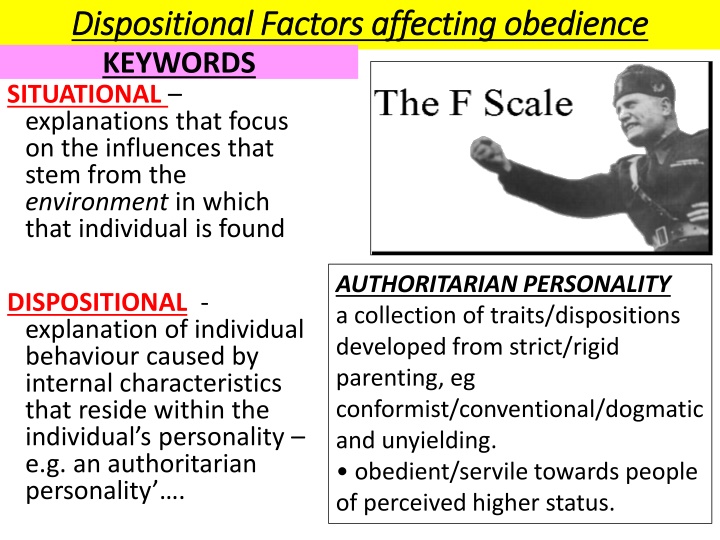
Dispositional Factors affecting obedience Dispositional Factors affecting obedience KEYWORDS SITUATIONAL explanations that focus on the influences that stem from the environment in which that individual is found AUTHORITARIAN PERSONALITY a collection of traits/dispositions developed from strict/rigid parenting, eg conformist/conventional/dogmatic and unyielding. obedient/servile towards people of perceived higher status. DISPOSITIONAL - explanation of individual behaviour caused by internal characteristics that reside within the individual s personality e.g. an authoritarian personality .
Dispositional explanations Dispositional explanations ADORNO et al According to authoritarian personality theory obedient people are the result of a psychological disorder. They obey because, unconsciously, they had harsh parenting (will come to this later). ADORNO et al AUTHORITARIAN PERSONALITY - (ADORNO et al 1950) Procedure: Measured 2000 middle class, white Americans and their unconscious attitudes towards other racial groups. Although Milgram did not believe that there was an obedient personality - there is research which supports the idea of an AUTHORITARIAN PERSONALITY Used the F-SCALE (fascism scale): See examples from the items on this scale (slides).
The Authoritarian Personality The Authoritarian Personality Adorno developed an attitude questionnaire which became known as the F-SCALE (the F stands for fascist submission to authority, usually political, and accepting violence as an acceptable way to achieve this). The scale measures different aspects of personality: Conventionalism Preoccupation with power Findings: People who scored high on the F Scale (authoritarian) identified with strong people and were contemptuous of the weak . They were conscious of their own and others status and showed a blind respect to people with power. Authoritarian people: Cognitive style no fuzziness between categories of people (v. black and white) and were driven by stereotypes and prejudice.
The Authoritarian Personality The Authoritarian Personality Authoritarian Characteristics: Submissive to authority driven by blind respect Obedient to authority Inflexible with their outlook no grey areas Society is going to the dogs need strong and powerful leaders to enforce traditional values Why do people have this personality? Harsh parenting strict discipline, expectations t be completely loyal, high standards, unconditional love for parents even if they do not agree with them. These experiences create hostility and despair in the child who displaces these feelings onto the weak (scapegoating).
TASK: AO3 for Dispositional Explanations TASK: AO3 for Dispositional Explanations CRITICISM: Measurement of authoritarianism relies on self-report (F-scale) data which may be invalid due to social desirability bias. Greenstein (1969) the F-Scale is a comedy of methodological errors e.g. every item is worded in the same direction you could tick the same line of boxes down one side (agree, agree agree) of the page and score as HIGH authoritarian. A decent scale would randomise this, so that agree did not always lead in one direction e.g. OBEDIENT. Acquiescence bias the tendency to simply agree with everything.
AO3: Research Support AO3: Research Support Milgram and Elms (1966) Conducted an interview with a small sample of OBEDIENT participants who scored highly on the F Scale. Results would indicate that the obedience was due to their fascist beliefs but this was a CORRELATION. Impossible to draw causal conclusions based on correlational research therefore cannot conclude that obedience was CAUSED by dispositional factors e.g. an authoritarian personality. THIRD VARIABLE PROBLEM may be due to another variable e.g. level of education (next AO3 point) . (Also difficult to draw conclusions form the range of variables e.g. personality, obedience, parenting style etc).
AO3 for Dispositional Explanations AO3 for Dispositional Explanations CRITICISM: explanation cannot easily account for obedience of entire social groups/societies. Hyman and Sheatsley (1954) found that the Authoritarian Personality is more likely to exist among people who are less well educated and are of low economic social status. This may be the third variable! But these results are inconsistent with the explanation - these people should surely be considered the subordinates and the rebellious, not the strict and oppressive! So perhaps personality is NOT needed to explain obedience. Or
AO3 for Dispositional Explanations AO3 for Dispositional Explanations Finally Comparisons to situational factors. Evidence clearly shows that the situation plays a role in obedience, as demonstrated in Milgram s extensive research. Situational factors, eg proximity (Milgram) and uniform may have greater influence on obedience levels. COMPARE THE METHODOLOGY: Milgram s rigorous and controlled experiments have shown that obedience is affected by the situation. In comparison to Adorno and the use of the F Scale, Milgram s results on the situational variables are more reliable and valid.
Exam Practice Outline two explanations for obedience. [6 marks] NOTE: Authoritarian personality, agency theory, legitimacy AQA will accept situational factors but they need to be linked to the above. A group of protesters is fixing a banner to the top of a tall crane. A plain clothes police officer on the ground uses a loud hailer to order them to stop and to come down, but the protesters refuse. Describe and discuss at least two situational explanations of defiance of authority. Refer to the description above in your answer.
Defiance of Authority Defiance of Authority Why do people disobey? Why do people disobey? A group of protesters is fixing a banner to the top of a tall crane. A plain clothes police officer on the ground uses a loud hailer to order them to stop and to come down, but the protesters refuse. Describe and discuss at least two explanations of defiance of authority. Refer to the description above in your answer. Discuss - how might you link your knowledge of obedience so far to explain the scenario?