Digestive System
Learn about the digestive system's organs and functions in turning food into nutrients for energy and growth. Explore the mouth, throat, esophagus, stomach, and small intestine processes. Discover mechanical and chemical digestion examples.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
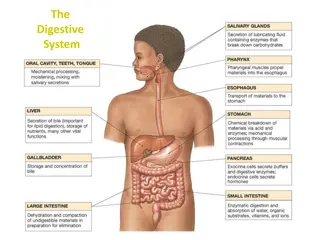
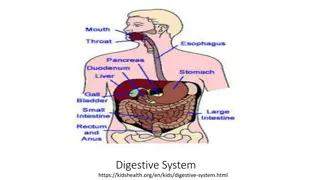
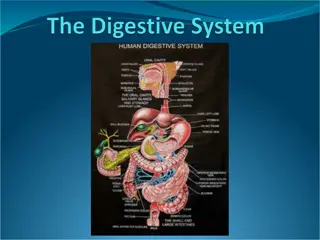
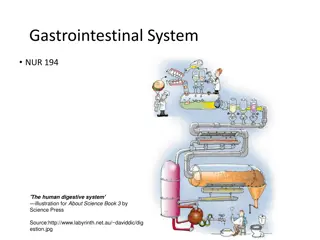
The digestive system is a group of organs working together to turn food into nutrients, which the body uses for energy, growth, and cell repair. Do you recognize any major organs in the diagram above?
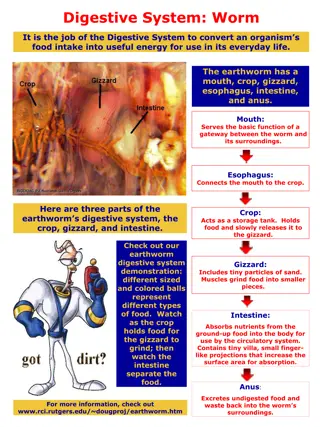
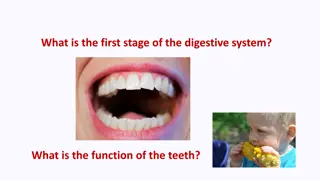
Mouth The beginning of the digestive tract Digestion starts with your first bite. Chewing breaks the food into smaller pieces. (mechanical/physical change) Glands secrete saliva that has enzymes which mixes with food to begin the process of breaking it down. (chemical change) Give one example of mechanical digestion that take place in the mouth. (Hint: mechanical/physical change.) Give one example of chemical digestion that take place in the mouth. (Hint: chemical change.)
Throat or Pharynx The passage that leads from the cavities of the nose and mouth to the larynx and esophagus. Both food and air pass through here, so it s part of the respiratory and digestive systems. Made up of 3 parts The epiglottis acts as a switch to route food to the esophagus and air to the larynx and trachea. What other system does the throat and pharynx work with?
Esophagus Muscular tube connecting the throat to the stomach Approximately 10 long Secretes mucus Moves food from the throat to the stomach using muscle movement (peristalsis). As food moves down the esophagus, it changes shape and size. Would this be classified as mechanical or physical digestion? (Hint: Would this be an example of a physical or chemical change?)
Stomach J-shaped muscular sac-like organ that stores food and grinds and mixes it into a liquid About the size of two fists next to each other Contains hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes that continue the digestion of food Acid in the stomach kills bacteria When food ends up in the stomach, it meets hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes. Would this be an example of mechanical or chemical digestion? (Hint: Would this be an example of a physical or chemical change?)
Small Intestine Long tube about 1 in diameter and 20 long Lining of intestine walls have finger-like projections called villi, to increase surface area for absorption Nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestine walls. Leftover waste continues through to the large intestine. What does the small intestine absorb into the bloodstream?
Large Intestine (Colon) Long, thick tube about 2 1/2 in diameter and about 5 feet long Absorbs water and nutrients the small intestines don t absorb Processes waste so that defecation (excretion of waste) is easy and convenient What does the large intestine absorb?
Rectum The final function of the digestive system Receives stool from the colon Lets the person know stool needs to be evacuated Holds stool until evacuation happens
Accessory Organs Not part of the path of food, but play a critical role in digestion Teeth designed for cutting and grinding food into smaller pieces Tongue helps to push food toward the back part of the mouth for swallowing Salivary Glands moistens food and begins digestion and also lubricates food as it passes through the mouth, throat and esophagus Teet h
Accessory Organs Liver produces bile and secretes it into the small intestine to aid digestion Gallbladder stores and recycles excess bile from the small intestine so that it can be reused for digestion in later meals Pancreas - secretes digestive enzymes into the small intestine to complete the chemical digestion of food.
Diseases of Digestive System Heartburn or acid reflux occurs when stomach acid gets into the esophagus Celiac disease- sensitivity to gluten, which damages your villi Crohn s Disease autoimmune disease that affects the end of the small intestine
Diseases of Digestive System Ulcerative Colitis Inflammatory bowel disease (IBF)affects the large intestines Diverticulitis Small pouches form where there are weak spots in the lining of the colon. Hemorrhoids inflammation of the blood vessels at the end of the digestive tract