Digestion
Digestion is the process by which the body breaks down food into small nutrient molecules through mechanical and chemical means. The digestive system's major organs include the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, large intestine, rectum, and anus. These organs work together to break down food, absorb nutrients into the bloodstream, and eliminate waste. Types of digestion include mechanical and chemical processes, with each organ playing a specific role in the overall digestive process.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Digestion Chapter 2
What is digestion? Process by which the body breaks down food into small nutrient molecules.
Jobs of the Digestive System Breaks down food into molecules the body can use Absorbs nutrients into the blood to be carried throughout the body Eliminates wastes
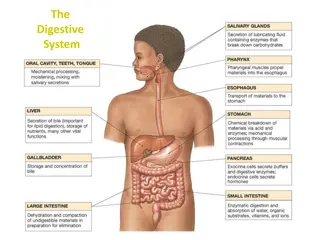
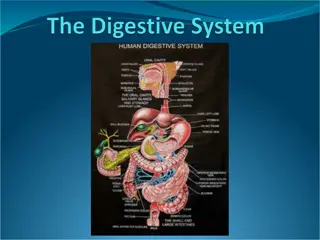
Major Organs Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Liver Gall bladder Pancreas Large intestine Rectum/anus
Types of Digestion Mechanical Mechanical Chemical Chemical Physically breaks down food into smaller pieces Ex: chewing, peristalsis Chemicals in the body such as enzymes and acids break foods into smaller chemical building blocks. Ex: saliva breaks starch into sugar
Mouth Teeth chew food into small pieces Saliva moistens food and mixes it with enzymes
Esophagus Tube that connects mouth to stomach Lined with mucus to help food move to the stomach by peristalsis Epiglottis is a flap that blocks food from going down windpipe.
Stomach J-shaped pouch Mixes food with digestive juices such as enzymes and acids to turn food into liquid form(chyme).
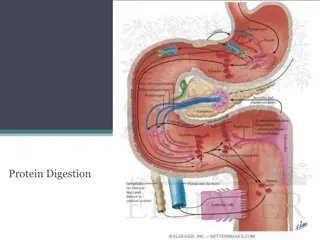
Small intestine Mixes liquid from the stomach with enzymes and secretions from the liver and pancreas. Lined with villi to absorb nutrients into the bloodstream 20-25 ft long!
Liver and Gallbladder Largest organ inside of body Filters chemicals and drugs from blood Produces bile to break up fats Gallbladder stores the bile
Pancreas Triangular organ in between stomach and small intestine Produces insulin and enzymes to break down starches, proteins, and fats
Large intestine Contains helpful bacteria to help feed on digested food Water is removed from waste and absorbed into blood Gets waste ready for elimination from body Only 5 ft long but wider than small intestine
Rectum and Anus Rectum-compresses food into solid form Anus- muscular opening that removes waste from the body