Fat Digestion and Metabolism in Ruminants and Non-Ruminants
This article highlights the digestion and metabolism of fat in both ruminant and non-ruminant species. It explains the differences in lipid digestion in the stomach and small intestine of animals, focusing on the role of lipase, bile, and colipase in the breakdown of triglycerides. The process of micelle formation and absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins is also discussed, along with the unique aspects of fat digestion in ruminants.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DIGESTION & METABOLISM OF FAT IN DIGESTION & METABOLISM OF FAT IN RUMINANTS RUMINANTS AND NON AND NON- -RUMINANTS RUMINANTS Dr. Kaushalendra Kumar Assistant Professor (Animal Nutrition), Bihar Veterinary College, BASU, Patna, India E-mail: drkaushalbvc@gmail.com
Digestion and absorption of fat in non Digestion and absorption of fat in non- -ruminant and ruminant and ruminant species ruminant species Digestion Digestion before before the the small small intestine intestine Substantial Substantial lipolysis lipolysis can can happen happen in in the the stomach stomach of of suckling suckling animals, animals, both both non non- -ruminants ruminants and and ruminants ruminants. . Main Main site site of of secretion secretion of of lipase lipase seems seems to to be be in in the the lingual lingual and and pharyngeal pharyngeal regions regions. . In In adult adult ruminants, ruminants, microbial microbial fermentation fermentation and and lipids lipids undergo undergo hydrolysis, hydrolysis, followed followed by by hydrogenation hydrogenation Major Major difference difference between between ruminant ruminant (form (form of of free free fatty fatty acid) acid) & & non non- - ruminant ruminant (esterified) (esterified) digestion digestion of of lipid lipid appears appears at at the the beginning beginning of of SI SI. .
Cont...... Digestion Digestion in in the the small small intestine intestine of of monogastric monogastric animals animals Dietary Dietary triglycerides triglycerides entering entering the the SI SI from from stomach, stomach, mixed mixed with with discharges discharges of of bile bile & & pancreatic pancreatic juice juice in in the the duodenum duodenum. . Lipase Lipase and and colipase colipase hydrolyse hydrolyse TG TG droplet droplet into into FA FA & & monoglycerides monoglycerides. . In In absence absence of of colipase colipase or or bile bile, , lipase lipase get get absorbed absorbed and and denatured denatured at at the the interface interface. . Bile Bile salt salt but but no no colipase, colipase, lipase lipase remains remains in in the the aqueous aqueous phase phase & & colipase colipase is is required required for for the the attachment attachment of of lipase lipase at at the the substrate substrate- - water water interface interface Micelle Micelle formation formation, , permit permit cholesterol cholesterol & & fat fat- -soluble soluble vitamins vitamins to to be be solubilized solubilized in in the the hydrophobic hydrophobic core, core, and and then then get get absorbed absorbed. .
Cont...... Digestion Digestion in in the the small small intestine intestine of of ruminants ruminants Dietary Dietary lipid lipid reaching reaching the the SI SI of of ruminant ruminant is is the the FFA FFA fractions, fractions, bounded bounded as as an an insoluble insoluble complex complex with with the the feed feed particles particles. . Transfer Transfer of of fatty fatty acid acid from from the the insoluble, insoluble, particulate particulate phase phase to to the the soluble, soluble, micellar micellar phase phase. .
Common enzymes involve in fat digestion Common enzymes involve in fat digestion Cont...... Name of enzymes Name of enzymes Enzymes acting on ester links Enzymes acting on ester links Triacylglycerol lipase (Lipase) Triacylglycerol lipase (Lipase) Systematic name Systematic name Source Source Substrate Substrate Triacylglycerol Triacylglycerol Pancreas Pancreas Triacylglycerols Triacylglycerols acylhydrolase acylhydrolase Sterol Sterol- -ester hydrolase ester hydrolase Cholesterol esterase Cholesterol esterase Pancreas and Pancreas and Cholesterol esters Cholesterol esters small intestine small intestine Pancreas and Pancreas and Phospholipase A2 (Lecithinase A) Phospholipase A2 (Lecithinase A) Phosphatide 2 Phosphatide 2- -acyl acyl- - Lecithin and cephalin Lecithin and cephalin hydrolase hydrolase Lysolecithin acyl Lysolecithin acyl- -hydrolase small intestine small intestine Small intestine Lysolecithin Lysophospholipase Lysophospholipase hydrolase Small intestine Lysolecithin (Lysolecithinase) (Lysolecithinase) Deoxyribonuclease (DNase) Deoxyribonuclease (DNase) Dexoyribonucleate 5 Dexoyribonucleate 5 - - Pancreas and Pancreas and DNA DNA oligonucleotido oligonucleotido- -hydrolase Ribonucleate 3 Ribonucleate 3 - -pyrimidino hydrolase pyrimidino- - small intestine small intestine Pancreas and Pancreas and Ribonuclease 1 (RNase) Ribonuclease 1 (RNase) RNA RNA oligonucleotido oligonucleotido- -hydrolase hydrolase small intestine small intestine Nucleosidase Nucleosidase N N- -Ribosyl Ribosyl- -purine purine Small intestine Small intestine Nucleosides Nucleosides ribohydrolase ribohydrolase Phosphatases Phosphatases Small intestine Small intestine Orthophosphoric acid esters Orthophosphoric acid esters
Cont...... Absorption Absorption of of fat fat in in non non- -ruminant ruminant and and ruminant ruminant species species Absorption of fat occurs in jejunum of SI & micelle formation is crucial Absorption of fat occurs in jejunum of SI & micelle formation is crucial for efficient fatty acid absorption in all species. for efficient fatty acid absorption in all species. In case of non In case of non- -ruminant species, monoacylglycerols are required for ruminant species, monoacylglycerols are required for micelle creation, micelle creation, However, nearly complete hydrolysis of dietary FA in the rumen are However, nearly complete hydrolysis of dietary FA in the rumen are absent from digesta present in the SI of the ruminants. absent from digesta present in the SI of the ruminants. Bile provides, bile salts and lecithin, whereas, pancreatic juice delivers Bile provides, bile salts and lecithin, whereas, pancreatic juice delivers enzymes to convert lecithin to lysolecithins & bicarbonate to elevate enzymes to convert lecithin to lysolecithins & bicarbonate to elevate pH. pH.
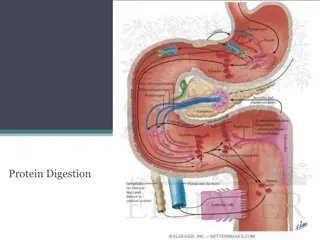
Cont...... Digestion and absorption of lipids in non-ruminant animals
Cont...... Digestion and absorption of lipids in ruminant animals
Cont...... Factors affecting digestion and absorption of fats Factors affecting digestion and absorption of fats Short Short and and medium medium chained chained fatty fatty acid acid are are utilized utilized better better in in comparison comparison with with long long chain chain fatty fatty acid acid. . Unsaturated Unsaturated fatty fatty acids acids are are well well utilized utilized than than saturated saturated fatty fatty acids acids. . Degree Degree of of esterification esterification of of fatty fatty acid acid i i. .e e. . triglyceride triglyceride > > diglyceride diglyceride > > monoglyceride monoglyceride. . Ratio Ratio of of unsaturated unsaturated and and saturated saturated fatty fatty acids acids. .
Metabolism of fat in different species of animals After absorption, either enter oxidative pathways for energy production, After absorption, either enter oxidative pathways for energy production, or transported to the adipose tissues & incorporated into the body fats. or transported to the adipose tissues & incorporated into the body fats. The The complete complete oxidation oxidation of of fat fat yields yields about about 2 2. .25 25 times times more more energy energy than than carbohydrates carbohydrates. .
Cont...... Oxidation of FA to Acetyl CoA & Oxidation of FA to Acetyl CoA & - -Oxidation of palmitic acid Oxidation of palmitic acid
Cont...... Overview of fat metabolism Overview of fat metabolism
Cont...... Net yield of energy on oxidation of tripalmitin and starch Net yield of energy on oxidation of tripalmitin and starch 1. Tripalmitin (806 g/mole) 1. Tripalmitin (806 g/mole) C C51 51H H98 98O O6 6 (+3 H (+3 H2 2O) + 72.5 O O) + 72.5 O2 2 = 51 CO = 51 CO2 2 + 52 H + 52 H2 2O + O + 7657 Kcal 7657 Kcal Glycerol Glycerol 19 ATP 19 ATP Palmitate Palmitate Phosphorylation Phosphorylation - -2 ATP 2 ATP 7 cleavages x 5 ATP 7 cleavages x 5 ATP +35 ATP +35 ATP 8 acetyl CoA x 12 ATP 8 acetyl CoA x 12 ATP +96 ATP +96 ATP Net (129 ATP x 3) Net (129 ATP x 3) 387 ATP 387 ATP Total yield Total yield 406 ATP 406 ATP
Cont...... 2. Starch (162 g/mole, glucose basis) 2. Starch (162 g/mole, glucose basis) C C6 6H H10 10O O5 5 (+H (+H2 2O) + 6O O) + 6O2 2 = 6 CO = 6 CO2 2 + 6 H + 6 H2 2O + O + 680 Kcal 680 Kcal Glycolysis Glycolysis 10 ATP 10 ATP Phosphorylation Phosphorylation - -2 ATP 2 ATP NADH NADH mitochondria mitochondria - -2 ATP 2 ATP Net yield Net yield 6 ATP 6 ATP Oxidation of 2 pyruvate Oxidation of 2 pyruvate 6 ATP 6 ATP 2 acetyl CoA x 12 2 acetyl CoA x 12 24 ATP 24 ATP Total yield Total yield 36 ATP 36 ATP
Cont...... 3. Based on gross energy 3. Based on gross energy a) a) 7657 Kcal 7657 Kcal 806 g = 9.5 Kcal/g of fat 806 g = 9.5 Kcal/g of fat b) b) 680 Kcal 680 Kcal 162 g = 4.20 Kcal/g of 162 g = 4.20 Kcal/g of carbohydrate carbohydrate Net yield Net yield 9.5 Kcal 9.5 Kcal 4.20 Kcal = 2.26 4.20 Kcal = 2.26 4. Based on ATP production 4. Based on ATP production a) a) 406 ATP 406 ATP 806 g = 0.504 ATP/g of fat 806 g = 0.504 ATP/g of fat b) b) 36 ATP 36 ATP 162 g = 0.222 ATP/g of 162 g = 0.222 ATP/g of carbohydrate carbohydrate Net yield Net yield 0.504 ATP 0.504 ATP 0.222 ATP = 2.27 0.222 ATP = 2.27
Cont...... Synthesis of fatty acid Synthesis of fatty acid Synthesis Synthesis of of fat fat (glycerides) (glycerides) occurs occurs in in the the body body from from fatty fatty acyl acyl CoA CoA & & L L- - glycerol glycerol- -3 3- -phosphate, phosphate, take take place place in in most most tissues, tissues, but but is is confined confined mostly mostly to to the the liver liver & & adipose adipose tissue tissue. . Three Three systems systems of of fatty fatty acid acid synthesis synthesis; ; In In the the cell cell cytoplasm, cytoplasm, mainly mainly in in the the production production of of palmitate palmitate from from acetyl acetyl CoA CoA or or butyryl butyryl- -CoA, CoA, Another Another occurs occurs chiefly chiefly in in ER ER & & minor minor extent extent in in mitochondria, mitochondria, elongation elongation of of FA FA chains chains by by 2 2- -C C addition addition with with malonyl malonyl CoA CoA as as donor, donor, Finally Finally they they confined confined to to the the ER ER which which carries carries about about desaturation desaturation of of preformed preformed fatty fatty acids acids. .
Cont...... Cytosolic synthesis of palmitate Cytosolic synthesis of palmitate Desaturation of preformed fatty acids Desaturation of preformed fatty acids Synthesis of triacylglycerols Synthesis of triacylglycerols Elongation of fatty acid chain Elongation of fatty acid chain
Cont...... Fat metabolism in ruminants Fat metabolism in ruminants Hydrolysis Hydrolysis Biohydrogenation Biohydrogenation
Discussion.......... Questions, if any? THANKS