Deep Eutectic Solvents: Classification, Synthesis, and Applications
Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) are versatile solvents formed by mixing specific acids and bases. These solvents exhibit unique hydrogen bonding properties, resulting in a lower melting point compared to individual components. DES can be classified into hydrophobic and hydrophilic types, each with distinct advantages. The synthesis of DES involves intricate hydrogen bonding networks, leading to significant freezing point depression. DES finds applications in various fields such as extraction, bio-catalysis, gas absorption, biomass pretreatment, electrochemical detection, and pharmaceuticals.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Deep Eutectic Solvents: Classification, Synthesis and Application Dr. Pratap Chhotaray
Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) Systems formed by mixing Lewis or Bronsted acids and bases One component is known as hydrogen bond acceptor (HBA) and other hydrogen bond donor (HBD) DES is composed of neutral as well as ionic species 2
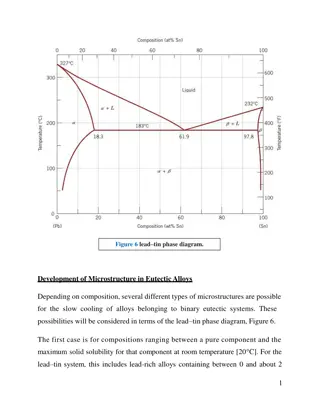
Synthesis of DES Generally, M.P of DES is lower than individual components The parent components of DES engage in a complex hydrogen bonding network which results in significant freezing point depression as compared to the parent compounds 1:2 molar ratio @ 50 + Choline Urea Reline DES MP: 302 133 12 Professor Andrew P Abbott University of Leicester, UK 3
Classification of DES DES are of four types 1. Hydrophobic DES 2. Hydrophilic DES 5
Applications of DES Extraction Bio-catalysis Gas Absorption Biomass Pretreatment Electrochemical Detection Nano- materials Pharma- ceuticals 6