Coordinate Geometry Concepts
Know the quadrants, distance between points, midpoint calculations, and practical applications through subway journeys. Learn to find distances, endpoints, and midpoints with step-by-step examples and visual aids.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
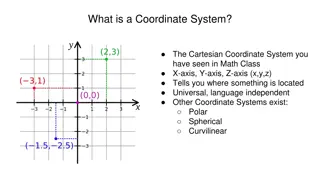
Quadrant I; (+, +) y-axis Quadrant II: (-, +) Quadrant III: (-, -) Quadrant IV: (+, -) Origin (0,0) Coordinate a point Ordered pair (x, y) x-axis
The distance d between two points A(x, y) and B (x , y ) is:
R(-2, 6) and S(6, -2) find the distance to the nearest tenth.
AB has endpoints A (1, -3) and B (-4, 4). Find AB to the nearest tenth.
Each morning Juanita takes the Blue Line subway from Oak Station to Symphony Station. The map shows that Oak Station is one mile west and two miles south of the City Plaza and Symphony Station is one mile east and two miles north. Find the distance.
The coordinates of the midpoint M of AB with endpoints A(x , y ) and B(x , y ) are the following:
AB has endpoints (8,9) and (-6,-3). Find the coordinates of its midpoint M.
Find the coordinates of the midpoint of XY with endpoints X(2, -5) and Y(6, 13)
The midpoint of DG is M(-1,5). One endpoint is D(1,4). Find the coordinates of the other endpoint G.