Comprehensive Overview of Thigh Anatomy by Dr. Mohammed Hussein M.B.Ch.B, MSC, PhD
Dr. Mohammed Hussein provides a detailed exploration of the anatomy of the thigh, covering regional anatomy, connections, compartments, and cutaneous nerves. The discussion delves into the front and medial aspects of the thigh, offering valuable insights for medical professionals and enthusiasts alike.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
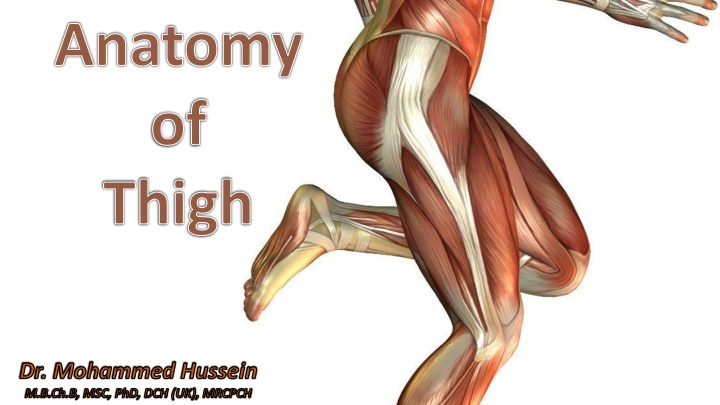
Anatomy of Thigh Dr. Mohammed Hussein M.B.Ch.B, MSC, PhD, DCH (UK), MRCPCH
Overview Overview Introduction Regional anatomy Connections & Gateways of the thigh Compartments of the thigh The Front and Medial Aspects of the Thigh Cutaneous nerves Superficial nerves Inguinal lymph nodes Superficial and deep fasciae Lumbosacral plexus Gray s Anatomy for Students, 4th Edition Snell clinical anatomy by regions - 9th Edition
The Thigh The thigh is the region of the lower limb between the hip and knee joints Gluteal region Gluteal fold Anterior thigh Posterior thigh
Anteriorly It is separated from the abdominal wall by the inguinal ligament. It communicates with the abdominal cavity through the aperture between the inguinal ligament and pelvic bone Abdominal wall Inguinal ligament Thigh
Medially The obturator nerve and associated vessels pass between the thigh and pelvic cavity through the obturator canal. Obturator canal Obturator membrane Obturator foramen
Posteriorly It is separated from the gluteal region by Superficially by the gluteal fold On deeper planes by the inferior margins of the gluteus maximus and quadratus femoris. Quadratus femoris Inferior margin of gluteus maximus Gluteal fold Sciatic nerve
Compartments Compartments
Compartments Compartments The thigh is divided into three compartments by intermuscular septa between the posterior aspect of the femur and the fascia lata.
Intermuscular septa Post. Med. Lat. Ant. Skin Superficial fascia (Subcutaneous tissue) Deep fascia (Fascia lata )
Compartments Compartments 1. The Anterior Compartment of the Thigh contains muscles that mainly Extend the leg at the knee joint Flex the thigh at the hip joint 2. The Posterior Compartment of the Thigh contains muscles that mainly Flex the leg at the knee joint Extend the thigh at the hip joint 3. The Medial Compartment of the Thigh contains muscles that mainly Adduct the thigh at the hip joint
Nerve Supply Post. Med. Lat. Ant. Medial Compartment
The Front and Medial Aspects of the Thigh Skin of the Thigh Superficial Fascia of the Thigh Deep Fascia of the Thigh (Fascia Lata)
Cutaneous Nerves Cutaneous Nerves
Cutaneous Nerves 1. The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh 2. The medial cutaneous nerve of the thigh 3. The intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 4. The femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5. The ilioinguinal nerve 6. The obturator nerve
Posterior Anterior Femoral branch of genitofemoral nerve Ilio-inguinal nerve Lat. cut. N. of thigh Lat. cut. N. of thigh Obturator nerve Post. Cut. N. of thigh Femoral nerve 1. Medial cutaneous nerve of the thigh 2. Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh
Superficial Veins Superficial Veins
The Superficial Veins The Superficial Veins The superficial veins form two major channels 1. The great (long) saphenous vein 2. The small (short) saphenous vein Both veins originate from a dorsal venous arch in the foot
Saphenous opening Femoral vein Popliteal vein Great saphenous vein Small saphenous vein Dorsal venous arch
Saphenous opening Femoral vein Popliteal vein Great saphenous vein Small saphenous vein Dorsal venous arch
Tributaries of the great saphenous vein Tributaries of the great saphenous vein
The Perforating Veins The Perforating Veins The normal flow of blood in the lower limbs is from the skin and subcutaneous tissues superficial veins, which drain via perforating veins to the deep veins, which in turn drain into the iliac veins and inferior vena cava to the
In the clinic In the clinic
Varicose Veins Varicose Veins The normal flow of blood in the venous system depends upon the presence of competent valves, which prevent reflux. Venous return is supplemented with contraction of the muscles in the lower limb, which pump the blood toward the heart.
Typical sites for valvular incompetence Typical sites for valvular incompetence 1. At the saphena varix the saphenofemoral junction where the femoral vein is joined by the great saphenous vein 2. In the mid-thigh perforating vein between the great saphenous vein and the femoral vein 3. At the junction of the small saphenous vein and the popliteal vein 4. In the calf the three sites where perforators occur, 5, 10, and 15 cm above the medial malleolus between the great saphenous vein and the deep veins of the calf
The Great Saphenous Vein in Coronary Bypass Surgery The Great Saphenous Vein in Coronary Bypass Surgery In patients with occlusive coronary disease caused by atherosclerosis, the diseased arterial segment can be bypassed by inserting a graft consisting of a portion of the great saphenous vein. The venous segment is reversed so that its valves do not obstruct the arterial flow.
Lymphatics Lymphatics
Lymphatics Lymphatics Most lymphatic vessels in the lower limb drain into superficial and deep inguinal nodes located in the fascia just inferior to the inguinal ligament
Superficial inguinal L.N Deep inguinal L.N Fascia lata
Superficial Inguinal Nodes Superficial Inguinal Nodes
Superficial inguinal nodes Superficial inguinal nodes The superficial inguinal nodes, approximately 10 in number Lie in the superficial fascia below the inguinal ligament and can be divided into a horizontal and a vertical group
Deep Inguinal Nodes Deep Inguinal Nodes
Deep inguinal nodes Deep inguinal nodes The deep inguinal nodes, up to 3 in number They are medial to the femoral vein.
Deep inguinal L.N Fascia lata
Popliteal Nodes Popliteal Nodes
Popliteal Nodes Popliteal Nodes A small collection of deep nodes posterior to the knee close to the popliteal vessels.
Drainage Areas Superficial inguinal nodes Deep inguinal nodes Receive lymph from 1. Deep lymphatics associated with the femoral vessels 2. The glans penis (or clitoris) in the perineum Receive lymph from 1. Superficial regions of the lower limb 2. Back below iliac crest including the lower half of the anal canal 3. Abdomen below umbilicus 4. The perineum (but not the testes)
The superficial and deep inguinal nodes interconnected and drain into the external iliac nodes via vessels that pass along the medial side of the femoral vein as it passes under the inguinal ligament. The space through which the lymphatic vessels pass under the inguinal ligament is the femoral canal.
External iliac L.N Superficial inguinal L.N Deep inguinal L.N
Fascial compartment for femoral artery Fascial compartment for femoral vein Femoral canal Femoral nerve