CMOS Comparator
This content discusses the CMOS Comparator designed by Professor Y. Chiu for the EECT 7327 course in Fall 2014. It covers various aspects such as circuit symbol, applications, design considerations, amplification, multi-stage preamp, step response, and more. The content provides insights into voltage/current level comparison, digital communication receivers, sense amplifiers, power electronics, and the characteristics of the CMOS Comparator with practical examples and theoretical explanations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 CMOS Comparator 1
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Comparator Vo 1 Vi Vth Vo ( Digital ) Vi Vth 0 Transfer characteristic (ideal) Circuit symbol Detects the polarity of the analog input signal and produces a digital output (1 or 0) accordingly threshold-crossing detector 2
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Applications Voltage/current level comparison (A/D conversion) Digital communication receivers ( slicer or decision circuit) Sense amplifier in memory readout circuits Power electronics with digital control (dc-dc converter) 3
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Design Considerations Accuracy (offset, noise, resolution) Settling time (tracking BW, regeneration speed) Sensitivity (gain) Metastability (any decision is better than no decision!) Overdrive recovery (memory) CMRR Power consumption 4
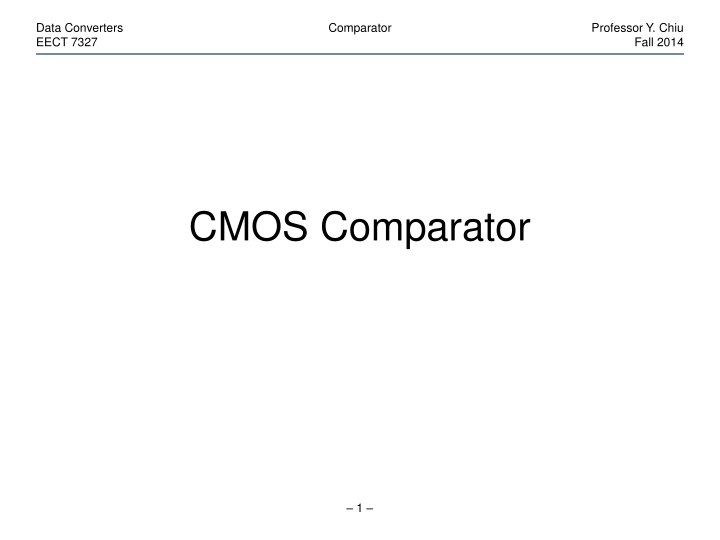
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Comparator Vi Vm Vo Vth Vth Vth Amplification Clipping Precise gain and linearity are often unnecessary simple, low-gain, open- loop, wideband amplifiers + latch (positive feedback) More gain can be derived by cascading multiple gain stages Built-in sampling function with latched comparators 5
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Multi-Stage Preamp Vi Vo A( ) A( ) A( ) A ( ) = A 0 + 1 j / 1/R C Vi Vi+1 0 = 0 L L CL gmVi RL CL gmVi+1 N N A A ( ) = = A 0 0 N + 1 j / ( ) 2 + 1 / 0 N stages: 0 1 N N A ( ) = = = A , 2 1 0 2 N 3dB 3dB 0 6
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Step Response ( ( ) = t/ V V A 1 e V1 V2 1 in 0 ) V A t / for t in 0 Vin gmVin RL CL gmV1 t = V g R in m L R C L L g C = V t m in L Ignore R in all stages, L 2 t t g C g 1 1 1 2 C 0 0 = = = = 2 V g V dt V t, V g Vdt V t m m 1 m in in 2 m 1 in C C L L L L N t N g 1 t N! C 0 = = For small V , V g V dt V m N N m N 1 in C L L 7
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Optimum N 2 10 Vo/Vi=10 Vo/Vi=100 Vo/Vi=1000 For small V , o N N t g = V V m o i N! C L t/(CL/gm) 1 10 1 N V V C g = t N! o L m i 0 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 N Given A0 = Vo/Vi, Nopt can be determined with the above equation For A0 < 100, typical N value ranges between 2 and 4 8
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Comparison 10 8 1 N V V C g = t N! o L 6 m i t/(CL/gm) 4 V V C g = latch: t ln o L N=1 N=3 N=5 Latch 2 m i 0 0 1 2 3 10 10 10 10 Vo/Vi A higher A0 (= Vo/Vi) requires a larger N In comparison, latches regenerate faster than preamps 9
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Multi-Stage PA Offset Vos1 Vos2 Vos3 Individual stage A1 A2 A3 Vos Total input-referred A1 A2 A3 = A A A A T 1 2 3 V V = + + V V os2 A os3 os os1 A A 1 1 2 10
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Input Offset Cancellation 2' C Vos 1 Vi Vo A 2 AC coupling at input with input-referred offset stored in C Two-phase operation, one phase ( 2) is used to store offset 11
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Offset Storage 2 2' ( ) = V A V V Vc Vos c c os A + Vo = V os 1 A A 2 V os Closed-loop stability (amplifier in unity-gain feedback) Ref: J. L. McCreary and P. R. Gray, All-MOS charge redistribution analog-to-digital conversion techniques. I, JSSC, vol. 10, pp. 371-379, issue 6, 1975. 12
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Amplifying Phase 1 Vc Vos 1 ( ) = + V A V V V o in c os Vi Vo V = A V os A in + 1 A Input-referred offset: V = V os os,in + 1 A Offset cancellation is incomplete if A is finite Input AC coupling attenuates signal gain 13
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 CF and CI of Switches 2' Vc Vos 1 Vo A 2 2' 2 What s the optimum phase relationship between 2 and 2'? Bottom-plate sampling 2' switches off slightly before 2 (note the operation in this phase is signal independent anyway) 14
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Output Offset Cancellation Vos 1 C 1 Vi Vo A 2 2' AC coupling at output with offset stored in C A must be small and well controlled (independent of Vo) Does not work for high-gain op-amps 15
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Offset Storage 2 Vos Vc A ( ) 2 = = V A V AV 2' c os os Closed-loop stability is not required CF and CI of 2' gets divided by A when referred to input Ref: R. Poujois and J. Borel, A low drift fully integrated MOSFET operational amplifier, JSSC, vol. 13, pp. 499-503, issue 4, 1978. 16
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Amplifying Phase 1 Vos 1 Vc 1 Vi Vo A ( ) = + Input-referred offset: V = 0 V A V V AV o i os os = AV os,in in Cancellation is complete if A is constant (independent of Vo) AC coupling at output attenuates signal gain 17
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Offset Cancellation w/ Auxiliary Input + Vo C1 S3 RL Vos1 Vos2 S1 S5 + Vi Vi - S2 Gm2 S6 RL S4 Gm1 C2 - Vo Gm1 and Gm2 are the preamp and latch, respectively A form of output offset cancellation technique Ref: B. Razavi and B. A. Wooley, Design techniques for high-speed, high-resolution comparators, JSSC, vol. 27, pp. 1916-1926, issue 12, 1992. 18
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Offset Sampling + Vo C1 S3 RL Vos1 Vos2 S1 S5 S3-S6 closed S1-S2 open + Vi Vi - S2 Gm2 S6 RL S4 Gm1 C2 - Vo Gm1 and Gm2 are grounded and the PFB of Gm2 is disabled Vos1 and Vos2 are amplified by Gm1 and Gm2 to appear at Vo When S5 & S6 open (slightly before S3 & S4), offset voltage is sampled and stored in C1 and C2 CF/CI of S5 & S6 gets divided by (Gm1/Gm2) when referred to input 19
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Comparison + Vo C1 S3 RL Vos1 Vos2 S1 S5 S3-S6 open S1-S2 closed + Vi Vi - S2 Gm2 S6 RL S4 Gm1 C2 - Vo Differential input is amplified by Gm1 to establish an imbalance at the output and AC coupled to the input of Gm2 Gm2 starts regeneration with this imbalance 20
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Potential Problems + Vo C1 S3 RL Vos1 Vos2 S1 S5 + Vi Vi - S2 Gm2 S6 RL S4 Gm1 C2 - Vo Very complicated slow conversion speed C1 and C2 and their parasitics add loading to the output Finite on-resistance of S5 & S6 cannot completely break PFB CF/CI imbalance of S5 & S6 can trigger regeneration 21
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Razavi s Comparator + Vo C1 S7 S3 RL S9 S1 S5 + Vi Vi - S2 Gm2 S6 RL S10 S4 Gm1 S8 C2 - Vo Even more complicated! 22
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Overdrive Recovery 23
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Overdrive Recovery Test Vi Vi Vi = VFS Vi = VFS Vi = LSB/2 Vi = -LSB/2 + + Vo Vo Vo Vo 0 1 - - Vo Vo Case I Case II A small input ( 0.5 LSB) is applied to the comparator input in a cycle right after a full-scale input is applied; the comparator should be able to resolve to the right output in either case memoryless 24
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Passive Clamp M3 M4 Limit the output swing with diode clamps signal-dependent Ro Clamps add parasitics to the PA output + - Vo Vo M5 M6 + - Vi Vi M1 M2 25
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Active Reset M3 M4 Kill PA gain with a crowbar switch time-dependent Ro Switch adds parasitics to the PA output + - Vo Vo M5 + - Vi Vi M1 M2 26
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 PA Autozeroing M3 M4 2' + - Vo Vo 2' C Vos 1 M5 M6 Vi Vo + - Vi Vi M1 M2 A 2 Two-phase operation, 2 phase is used for offset storage Autozeroing switch 2' also resets and removes the PA memory 27
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 CMOS Preamplifier 28
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Pull-Up NMOS diode pull up : ( ( ) )L W L g = = A m1 1 Pull-up V g W L mL + - Vo Vo PMOS diode pull up : + - ( ( ) )L Vi Vi M1 M2 W L g = = A m1 n 1 V g W L mL p Resistor = pull up : A g R V m1 L NMOS pull-up suffers from body effect, affecting gain accuracy PMOS pull-up is free from body effect, but subject to P/N mismatch Gain accuracy is the worst for resistive pull-up as resistors (poly, diffusion, well, etc.) don t track transistors; but it is fast! 29
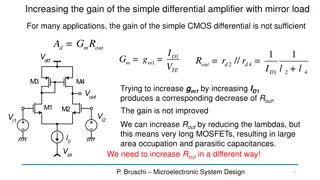
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 To Obtain More Gain Ip diverts current away from PMOS diodes (M3 & M4), reducing (W/L)3 Higher gain w/o CMFB Ip Ip M3 M4 + - Vo Vo Needs biasing for Ip M3 & M4 may cut off for large Vin, resulting in a slow recovery + - Vi Vi M1 M2 I ( ( ) )3 W L g I 2 = A m1 n 1 V g I 2 I W L m3 p p 30
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Bult s Preamp NMOS diff. pair loaded with PMOS diodes and PMOS latch (PFB) M3 M5 M6 M4 + - Vo Vo High DM gain, low CM gain, good CMRR + - Vi Vi M1 M2 Simple, no CMFB (W/L)34 > (W/L)56 needs to be ensured for stability M7 Ref: K. Bult and A. Buchwald, An embedded 240-mW 10-b 50-MS/s CMOS ADC in 1-mm2, JSSC, vol. 32, pp. 1887-1895, issue 12, 1997. 31
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 DM M3 M5 M6 M4 + - Vo Vo 1 -1 gm5 ro3 ro5 gm3 + - Vi Vi M1 M2 Vid gm1Vid ro1 Vod M7 g r 1 1 dm = DM gain A : g // //r //r //r m1 o1 V m1 o1 o3 o5 g g 3 m3 m5 32
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 CM 1 1 M3 M5 M6 M4 gm3 gm5 + - Vo Vo Vgs1 gm1Vgs1 + - Vi Vi M1 M2 Vic Voc 2ro7 M7 g 1 1 1 = cm CM gain: A / / m1 ( ) V + + 1 2g r g g 2 g g o7 r m1 o7 m3 m5 m3 m5 33
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Song s Preamp M3 M4 NMOS diff. pair loaded with PMOS diodes and resistors RL RL + - Vo Vo X High DM gain, low CM gain, good CMRR + - Vi Vi M1 M2 Simple, no CMFB Gain not well-defined M5 Ref: B.-S. Song et al., A 1 V 6 b 50 MHz current-interpolating CMOS ADC, in Symp.VLSI Circuits, 1999, pp. 79-80. 34
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Song s Preamp 1 gm3 ro3 RL Vgs1 gm1Vgs1 Vic Voc Vid gm1Vid ro1 Vod 2ro5 DM CM ( ) g 1 dm = A g o1 r //r //R cm A m1 V m1 o3 L V + 1 2g r 1 2g r g g R m1 o5 m3 m1 L m3 o5 35
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 CMOS Latch 36
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Static Latch Active pull-up and pull- down full CMOS logic levels M3 M4 + - Vi Vi Very fast! M1 M2 Q+ and Q- are not well defined in reset mode ( = 1) Q+ Q- Large short-circuit current in reset mode M7 M5 M6 Zero DC current after full regeneration Very noisy 37
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Semi-Dynamic Latch Diode divider disabled in reset mode less short-circuit current M8 M3 M4 + - Vi Vi Pull-up not as fast M1 M2 Q+ and Q- are still not well defined in reset mode ( = 1) Q+ Q- M7 Zero DC current after full regeneration M5 M6 Still very noisy 38
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Current-Steering Latch Constant current very quite RL RL Q+ Q- M7 Higher gain in tracking mode + - Vi Vi Cannot produce full logic levels M1 M2 M3 M4 M5 M6 Fast Trip point of the inverters M8 39
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Dynamic Latch Zero DC current in reset mode M7 M5 M6 M8 Q+ and Q- are both reset to 0 Q+ Q- Full logic level after regeneration M9 M10 Slow + - Vi Vi M1 M3 M4 M2 No seed voltage Ref: A. Yukawa, A CMOS 8-Bit High-Speed A/D Converter IC, JSSC, vol. 20, pp. 775-779, issue 3, 1985. 40
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Modified Dynamic Latch Zero DC current in reset mode M7 M5 M6 M8 Q+ and Q- are both reset to 0 Q+ Q- Full logic level after regeneration M9 M10 M3 M4 Slow No seed voltage + - Vi Vi M1 M2 Ref: T. B. Cho and P. R. Gray, A 10 b, 20 Msample/s, 35 mW pipeline A/D converter, JSSC, vol. 30, pp. 166-172, issue 3, 1995. 41
Data Converters EECT 7327 Comparator Professor Y. Chiu Fall 2014 Cho s Comparator W L W L W L W L ( ) ( ) M7 M5 M6 M8 + = + G k V V V V i R 1 i t R t ( ) ( ) Q+ Q- + = + G k V V V V i R 2 i t R t M9 M10 M3 M4 W W ( ) + V = V V R th R R + - Vi Vi M1 M1R M2R M2 i - + VR VR M1R and M2R added to set the comparator threshold 42