Advanced Functionality of Open Workbench Training Course
Enhance your project management skills with the PPM Educational Community's half-day course on mastering Open Workbench (OWB). Dive into advanced features such as building, scheduling, and controlling projects, manipulating views and structures, assigning resources, and more. Learn how to access OWB, navigate effectively, and optimize your project management workflow for efficient results.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
www.regouniversity.com PPM Educational Community Building Solutions with Open Workbench (half day)
Course Goals and Objectives Goal: To learn the advanced functionality of Open Workbench (OWB) to build, schedule and control a project. Objectives: At the end of this course you will have the knowledge to: Access and Navigate in Open Workbench Use and Manipulate Views Manipulate the Work Breakdown Structure Build Task Dependencies 2 PPM Educational Community
Goals & Objectives Continued. Assign Resources to Tasks Use Autoschedule Baseline your Project Transfer Assignments Understand the role of timesheets in the tracking and control cycle. Manage Pending Actuals and ETCs Accept or Reject Pending ETCs Update Task and Project Status 3 PPM Educational Community
Module One: Getting Started Learn about Open Workbench options. Learn about Open Workbench defaults. Learn how to navigate in Open Workbench. 4 PPM Educational Community
Accessing OWB From PPM Logon to PPM Open a project From Project Properties Main - General, select either Read/Write or Read Only and click Go to open the project in OWB. This is the preferred method of opening plans in OWB. 5 PPM Educational Community
Couple of Things to Remember: Project will Lock in PPM when it s checked out so no one can update the plan when it s open in Workbench. The lock is retained until the project is checked back in to PPM and you close out of OWB. There is no Autosave in OWB so remember to click on Save periodically to save the plan back to PPM. 6 PPM Educational Community
Things to Remember Actuals will not post to the project while the project is in locked status . Resources are controlled by PPM do not manipulate resource data (Resource ID) or the plan will not be accepted back into PPM. You can work offline File, Save As *rmp file type. (still locked) 7 PPM Educational Community
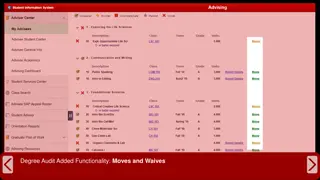
Open Workbench Navigation Have a project open in memory File pull-down menus and icons Resource and WBS filters Time Scale and Gantt Chart View Shortcut Bar, Views and View Groups Header/Task/Resource Sections Project and View Tabs (multiple projects and/or multiple views) 8 PPM Educational Community
Navigation Current Application Name Project Name Column Titles Time scaled Data Project and/or View Tabs Header Buttons aka Row Selectors Task Detail Views View Groups Resource Detail Pane Separators 9 PPM Educational Community
Module Two: Using Views Discuss Corporate and User view libraries Amend the layout of an existing view Use Open Workbench standard Views Format elements in a view Use level of analysis and filters on views Customizing the Timescale Formatting Quantity Fields Multiple Timescales Creating Permanent Filters 10 PPM Educational Community
Using Views Corporate View Library Corporate View Libraries reside on the network. Your access to the library is read-only. User View Library User View Libraries reside on your workstation (note that location may differ due to security rights) You create and customize your own views. 11 PPM Educational Community
Using Views Modifying the Gantt Chart How to customize a View F3 on the keyboard Or View, Edit View Or the Edit View Icon Deleting and Adding Columns Formatting Data Elements Time Scales Filters and Sorts Saving a View into a View Group 12 12 PPM Educational Community
Highlights Modifying the existing highlights How to create highlights Add line at location for hierarchy Set look and feel for results Establish conditions for new highlight Double click condition field Fill in filter elements Save with new file name Switch highlight files 13 13 PPM Educational Community
Entering Task Dependencies Terminology: Predecessor is the task that comes before and the Successor task is the one that comes after. Using the Dependencies View How to Break Dependencies Dialog box only! Note: OWB and PPM only support dependencies at the lowest level of the Work Breakdown Structure (Task) OWB supports the following dependency types: Finish to Start (most commonly used) Finish to Finish Start to Start Start to Finish 14 PPM Educational Community
Module Three: Resource Planning Look at resource properties. Use a resource s calendar to view availability. Assign roles and estimates to tasks. 15 PPM Educational Community
Resource Assignment to Task Accessing Resource Information: Right click on a resource name and select Modify to review properties and the resource calendar. Assigning Resources to Tasks Spreadsheet View: Resource Assignment Spreadsheet View: Drag and Drop Task Dialog Box Task Dialog Box: Releasing a Resource 16 PPM Educational Community
Resource Calendars When actual resources are added to a plan, the PM needs to addressed planned time off for the project team. Resource Calendars can be accessed via Open Workbench as well as CA PPM. 17 PPM Educational Community
Task Duration Fixed duration tasks are time constrained Variable duration tasks are resource constrained 18 PPM Educational Community
Loading Patterns Front Contour Back Fixed Uniform 19 PPM Educational Community
Availability 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Unused Availability 0 0 7 3 0 7 7 7 7 7 Where s the first availability of 15 hours? 20 PPM Educational Community
Availability 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Unused Availability 0 0 7 3 0 7 7 7 7 7 Days 3 through 6 contain at least 15 hours of availability 21 PPM Educational Community
Variable Duration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Unused Availability 0 0 7 3 0 7 7 7 7 7 Front 7 7 1 Contour 5 5 5 Back 1 7 7 Uniform 5 5 5 Fixed 5 0 5 0 5 22 PPM Educational Community
Variable Duration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Unused Availability 7 7 1 0 0 7 3 0 7 7 7 7 7 Front 7 3 0 5 Contour 5 5 5 Back 1 7 7 Uniform 5 5 5 Fixed 5 0 5 0 5 23 PPM Educational Community
Variable Duration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Unused Availability Front 7 7 1 0 0 7 3 0 7 7 7 7 7 7 3 0 5 Contour 5 5 5 6 3 0 6 Back 1 7 7 Uniform 5 5 5 Fixed 5 0 5 0 5 24 PPM Educational Community
Variable Duration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Unused Availability Front 7 7 1 0 0 7 3 0 7 7 7 7 7 7 3 0 5 Contour 5 5 5 6 3 0 6 Back 1 7 7 5 3 0 7 Uniform 5 5 5 Fixed 5 0 5 0 5 25 PPM Educational Community
Variable Duration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Unused Availability Front 7 7 1 0 0 7 3 0 7 7 7 7 7 7 3 0 5 Contour 5 5 5 6 3 0 6 Back 1 7 7 5 3 0 7 Uniform 5 5 5 5 5 5 Fixed 5 0 5 0 5 26 PPM Educational Community
Variable Duration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Unused Availability 0 0 7 3 0 7 7 7 7 7 Front 5 5 5 7 3 0 5 Contour 7 7 1 6 3 0 6 Back 1 7 7 5 3 0 7 Uniform 5 5 5 5 5 5 Fixed 5 0 5 0 5 5 0 5 0 5 27 PPM Educational Community
Fixed Duration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Unused Availability Front 7 7 1 0 0 7 3 0 7 7 7 7 7 0 0 Contour 3 3 3 3 3 Back 0 0 1 7 7 Uniform 3 3 3 3 3 Fixed 5 0 5 0 5 28 PPM Educational Community
Fixed Duration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Unused Availability Front 7 7 1 0 0 7 3 0 7 7 7 7 7 0 0 7 3 0 5 0 Contour 3 3 3 3 3 Back 0 0 1 7 7 Uniform 3 3 3 3 3 Fixed 5 0 5 0 5 29 PPM Educational Community
Fixed Duration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Unused Availability Front 7 7 1 0 0 7 3 0 7 7 7 7 7 0 0 7 3 0 5 0 Contour 3 3 3 3 3 4 3 0 4 4 Back 0 0 1 7 7 Uniform 3 3 3 3 3 Fixed 5 0 5 0 5 30 PPM Educational Community
Fixed Duration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Unused Availability 0 0 7 3 0 7 7 7 7 7 Front 7 7 1 0 0 7 3 0 5 0 Contour 3 3 3 3 3 4 3 0 4 4 Back 0 0 1 7 7 0 5 3 0 7 Uniform 3 3 3 3 3 Fixed 5 0 5 0 5 31 PPM Educational Community
Fixed Duration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Unused Availability Front 7 7 1 0 0 7 3 0 7 7 7 7 7 0 0 7 3 0 5 0 Contour 3 3 3 3 3 4 3 0 4 4 Back 0 0 1 7 7 0 5 3 0 7 Uniform 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Fixed 5 0 5 0 5 32 PPM Educational Community
Fixed Duration 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Unused Availability Front 7 7 1 0 0 7 3 0 7 7 7 7 7 0 0 7 3 0 5 0 Contour 3 3 3 3 3 4 3 0 4 4 Back 0 0 1 7 7 0 5 3 0 7 Uniform 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Fixed 5 0 5 0 5 5 0 5 0 5 33 PPM Educational Community
Module Four: Schedule Development Calculate task durations Calculate the critical path Create a basic schedule using automated methods 34 PPM Educational Community
Calculating Critical Path C A B D How many paths are there through this network? 35 PPM Educational Community
Calculating Critical Path C 6 A 2 B 8 D 4 Which path is the longest? 36 PPM Educational Community
Calculating Critical Path C 6 6 A 2 B 8 D 4 Critical Path: The longest path through the network based on task duration and dependencies. 37 37 PPM Educational Community
Module Five: Autoschedule To effectively create a schedule, a manager must take into account: The tasks to be performed The relationships between those tasks, and The availability of the resources to do the work Autoschedule is a automated way to create project schedules. Tasks are scheduled sequentially as they appear in the WBS, or in order of priority. 38 PPM Educational Community
Autoschedule Each task is scheduled to start at the earliest or latest possible time, subject to constraints. Before scheduling, Autoschedule automatically calculates the project s critical path. Autoschedule uses an internal set of rules to create a schedule that takes task constraints, dependencies, priority, and optionally, resource constraints into account. 39 PPM Educational Community
Autoschedule Continued By default, Autoschedule operates on the entire project, but does not change tasks that meet the following conditions: Tasks starting earlier than the date in the Ignore Before text box Tasks starting later than the date in the Ignore After text box Tasks marked as Locked or Completed Tasks that have actuals, except for the time period between the last actuals thru date and the finish date. Autoschedule performs three passes of the project to create a schedule that satisfies all dependencies and does not over- allocate selected resources. Each includes a forward pass and a backward pass. 40 PPM Educational Community
Autoschedule Continued To develop a schedule, the following three passes are performed whether you schedule from the project start or finish date: During the first pass, Autoschedule creates a baseline schedule and performs a priority sort to resolve potential scheduling conflicts. During the second pass, the schedule is created. (Availability, Allocation, Calendars, ETCs, Loading Patterns, Resource Constraints, Task Constraints, etc.) During the third pass, Autoschedule recalculates the critical path based on the schedule developed in the second pass. 41 PPM Educational Community
Autoschedule Rules Autoschedule does not reschedule tasks that are locked, have a fixed loading pattern or are completed. The start date of started tasks is not changed. Started tasks are given a higher scheduling priority than non-started tasks. The duration of a fixed-duration task is not changed. The date constraints Must Start On and Must Finish On for forward and backward scheduling respectively will override dependencies. 42 PPM Educational Community
Autoschedule Rules Tasks are scheduled at a daily level (e.g. resource conflicts are resolved on a day by day basis). Loading patterns for each resource on each task into account. Note: It is possible to set dependencies, constraints, and resource availability so that it is impossible for Autoschedule to produce a schedule free of dependency violations or resource over allocations 43 PPM Educational Community
Establishing a Baseline Applies when the plan or portions of the plan have been approved. Allows a snapshot of the project to be taken. Enables revisions to be compared against the original plan. The only way to track planned vs. actual 44 PPM Educational Community
What Is Baselined Baseline duration Baseline start Baseline finish Baseline total usage Baseline resource usage 45 PPM Educational Community
Module Six: Execution Review the tracking cycle Review pending actuals Review pending estimates Review posted actuals Update task status Complete the tracking cycle in OWB 46 PPM Educational Community
Pending Actuals 47 47 PPM Educational Community
Pending Actuals Build a Filter to see only those tasks with Pending Actuals 48 PPM Educational Community
Pending Estimates 49 PPM Educational Community
Pending Estimates 50 PPM Educational Community