Understanding Nerves and Muscles Physiology - Lecture Insights
Explore the intricate processes of synaptic transmission, neurotransmitters, spatial summation, temporal summation, chemical substances acting as neurotransmitters, and the effects of various factors and drugs on synapse function. Delve into the clinical significance of sedative-hypnotic drugs and their impact on GABA receptors. Engage with practice questions to enhance comprehension in nerve and muscle physiology.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
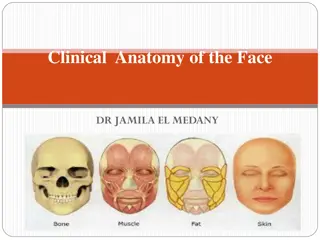
NERVES & MUSCLES PHYSIOLOGY Lecture 4 Dr. Amar AL-Musawi MD, PhD
Objective for this lecture Explain the synaptic transmission and neurotransmitters.
Transmission of signal or impulse across the synapse: [1] May leads to open the neurotransmitter-gated Na+ or Ca2+ channels [2] May lead to open neurotransmitter- gated Cl- or K+-channels [3] May lead to activate enzymes, which in turn activates an internal metabolic system
Spacial Summation Temporal Summation
Chemical substances that function as neurotransmitters: [1]. Small-molecule, rapidly acting transmitters Class 1: Acetylcholine. Class 2: Several different amines. Class 3: several different amino acids. Class 4: nitric oxide (NO). [2]. Large-molecule, slowly acting transmitters (neuropeptides) Removal of the transmitter from the synapse: Diffusion out. Enzymatic destruction. Active transmitter re-uptake . Fatigue of synaptic transmission substance in the synaptic terminal. due to exhaustion of the stores of the transmitter Effect of acidosis and alkalosis on synaptic transmission Effect of drugs on synaptic transmission: O2 and anesthetics excitability Caffeine (coffee), theophylline (tea) and theobromine (cocoa) excitability Strychnine excitability
Clinical significant Sedative-hypnotic drugs (e.g., benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and alcohols) target the GABA receptor, which, through the action of increased Cl influx, results in membrane hyperpolarization. Sedation anxiolysis hypnosis anesthesia medullary depression (respiratory depression) coma. Synergism with other CNS depressants occurs, increasing the risk for potentially lethal overdoses. Effect of strychnine does not reduce the threshold for excitation of the neurons but inhibits the action of some of the inhibitory transmitters on the neurons. In consequence, the effects of the excitatory transmitter become overwhelming.
Some practice questions: 1-An excitatory post-synaptic potential, all the following are false EXCEPT A. It is the depolarization of a post-synaptic nerve cell membrane that occurs when a presynaptic neuron is stimulated B. Involves reversal of polarity across the post-synaptic nerve cell membrane C. Is propagated at the same rate as an action potential D. Is caused by the electrical field induced by activity in the pre-synaptic nerve terminals 2- Regarding the release of neurotransmitter from synaptic vesicles, all the following are true EXCEPT A. Takes place by exocytosis B. Is controlled by neuronal calcium influx C. Is quantal D. Requires neuronal sodium ions influx
3- Each of these is a true statement EXCEPT one. Identify the exception. A. B. C. D. E. EPSPs can make action potentials more likely to occur IPSPs depolarize the membrane EPSPs that reach threshold can initiate an action potential The trigger zone is the integrating part of the neuron All of the above are true statements 4- The release of the neurotransmitter from the synaptic vesicles depends mainly on: A. Ca++ B. K+ C. Na+ D. Mg2+ 5- An inhibitory postsynaptic potential: A. Depolarizes the postsynaptic membrane by opening Na+ channels B. Depolarizes the postsynaptic membrane by opening K+ channels C. Hyperpolarizes the postsynaptic membrane by opening Ca++ channels D. Hyperpolarizes the postsynaptic membrane by opening Cl channels