Chemical equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium is a state where reactants and products reach a balance in a reaction. Learn about reversible and irreversible reactions, equilibrium constants, and how they affect chemical analysis. Discover the accuracy and applications of volumetric analysis, including titration methods like
3 views • 13 slides
Understanding Environmental Stress and Plant Management
Environmental stress, whether biotic or abiotic, can adversely affect plant growth and yield. Factors such as temperature extremes, waterlogging, radiation, chemicals, and pollution can lead to plant strains that may be reversible or permanent. Effective management of stress due to excessive moistur
9 views • 35 slides
Understanding the Fate of Herbicides in Soil
The fate of herbicides in soil is influenced by factors such as micro-organism decomposition, chemical decomposition, photodecomposition, adsorption by soil, surface runoff, leaching, plant uptake, and volatilization. Micro-organisms like algae, fungi, actinomyces, and bacteria play a crucial role i
6 views • 7 slides
Understanding Surfaces and Interfacial Energy in Chemistry
Surfaces play a crucial role in free energy and dissolution processes, impacting surface tension and interfacial energy. Learn about the adsorption of molecules, surface excess properties, and the contributions of surface area and curvature to surface energy. Dive into concepts such as Laplace's equ
6 views • 71 slides
Cryogenic Sub-systems
Explore the relationship between liquefaction, refrigeration, and isothermal processes in accelerator systems. Understand the equivalent exergy in Watts for different gases at 1 bar and 300K. Calculate the reversible input power required for latent cooling and the total cooling in different scenario
1 views • 9 slides
Understanding Thermodynamic and Kinetic Characteristics in Adsorption Systems
Explore the thermodynamics and kinetics of adsorption through discussions on equilibrium thermodynamics, adsorption isotherms, kinetic measurements, technical applications, and interaction forces. Learn about the distinctions between physisorption and chemisorption, as well as the terminology associ
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Reversible and Irreversible Changes in Chemistry
Exploring the concepts of reversible and irreversible changes in chemistry through examples such as heating, mixing, and burning. Reversible changes allow original materials to be recovered, while irreversible changes result in the formation of new materials. Various chemical reactions are highlight
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Reversible and Irreversible Changes in Science
Explore the differences between reversible and irreversible changes through a crystal experiment and vocabulary development. Discover examples of reversible changes like dissolving and test various materials for solubility. Engage in designing a presentation to illustrate the contrast between revers
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Fluorescence Analysis in Pharmaceutical Sciences
Fluorescence analysis is a crucial technique in pharmaceutical analysis, involving the emission of radiation by molecules when excited at specific wavelengths. Factors influencing fluorescence, such as concentration, light intensity, adsorption, oxygen presence, pH, temperature, viscosity, and photo
2 views • 26 slides
Understanding Surface Chemistry and Adsorption Processes
Surface chemistry is the study of processes at the interface of two bulk phases, such as liquid-liquid interactions. Adsorption and absorption are key phenomena where atoms, ions, or molecules adhere to surfaces or enter bulk phases. The accumulation of molecular species at the surface, known as ads
1 views • 28 slides
Understanding Column Chromatography: Methodology, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications
Column chromatography, a type of adsorption chromatography, involves separating components based on their affinity to an adsorbent. The methodology includes passing a solvent through a column to improve separation, obtaining a chromatogram, and eluting components for analysis. The principle relies o
2 views • 24 slides
Understanding Chemical Equilibrium in Reversible Reactions and Laws
Chemical equilibrium in reversible reactions involves the balance between forward and backward reactions, as governed by laws like the law of mass action and the law of chemical equilibrium. These laws help in understanding the rates of reactions, equilibrium constants, and the relationship between
1 views • 12 slides
Understanding Dynamic Equilibrium in Chemical Reactions
Explanation of reversible reactions, dynamic equilibrium, and the characteristics of equilibrium in chemical systems. Covers the concept of reversible reactions, dynamic equilibrium, rules for dynamic equilibrium, and examples to illustrate these concepts visually.
0 views • 54 slides
Understanding Precipitation Titration in Analytical Chemistry
Precipitation titration is a method where a precipitate is formed by converting one reacting species. An example is the estimation of chloride using AgNO3, where AgCl is precipitated. The titration is based on the formation of precipitates, and suitable conditions, indicators, and methods are vital
0 views • 30 slides
Electric Properties of Colloids in Liquid Media: Charging Mechanisms and Electrokinetic Phenomena
Colloidal particles dispersed in liquid media can acquire a charge through selective adsorption of ionic species or ionization of surface groups. This leads to electrokinetic phenomena like electrophoresis, electro-osmosis, sedimentation potential, and streaming potential. The stability of colloids
2 views • 16 slides
Understanding HPLC: A Powerful Liquid Chromatography Technique
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a powerful tool in analysis, offering high performance and speed compared to traditional chromatography methods. It involves separating components through a stationary phase and mobile phase, utilizing adsorption principles for separation. HPLC is wid
6 views • 58 slides
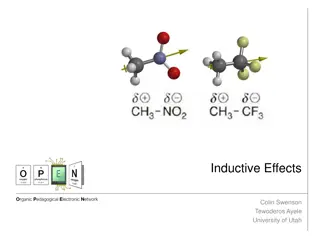
Understanding Inductive Effects in Organic Chemistry
Inductive effects play a crucial role in the reactivity and properties of organic molecules. This phenomenon involves the withdrawal or donation of electron density due to differences in electronegativity, impacting acidity, stability, and interactions with other molecules. Explore how inductive eff
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Ion-Pair Chromatography (IPC): Theory and Applications
Ion-Pair Chromatography (IPC) involves adding ionic surfactants to a reversed-phase Chromatography system to affect retention and selectivity of ionic compounds. Developed by Dr. Gordon Schill, IPC is crucial for resolving hydrophilic samples and controlling selectivity in separations. The theory in
7 views • 18 slides
Understanding Interfacial Phenomena in Surfactant Solutions
Micelle formation is a key process in surfactant solutions, where the critical micelle concentration (CMC) is reached leading to the formation of micelles. The CMC decreases with longer hydrophobic chains and is influenced by the addition of electrolytes. Adsorption at solid interfaces and wetting p
1 views • 21 slides
Understanding Column Chromatography Methods
Column Chromatography (CC) involves separating solutes based on different mechanisms within a packed column with a mobile phase. The five major types of CC are adsorption, partition, ion exchange, molecular exclusion, and affinity chromatography. Each type utilizes specific stationary and mobile pha
0 views • 11 slides
Immobilization of Enzymes in Biochemistry
Enzyme immobilization involves confining enzyme molecules to a distinct phase from substrates and products, attaching them to solid matrices for enhanced specificity and reduced inhibition. Inert polymers or inorganic materials are used as carrier matrices with methods like physical adsorption onto
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Filtration: Process, Applications, and Mechanisms
Filtration is a process of separating solid particles or suspended matter from liquid or gas by passing it through a porous medium. This article discusses the definition of filtration, factors affecting its rate, applications in various industries, mechanisms involved, and different types of filtrat
1 views • 6 slides
Understanding Small-State Noncryptographic Pseudorandom Number Generators
Explore the design and testing of small-state noncryptographic pseudorandom number generators, including definitions, rules of thumb, chisquare tests, existing and new generators, and more. Learn about block cipher encryption, hash functions, pseudorandom number generation, reversible mixing, and re
0 views • 46 slides
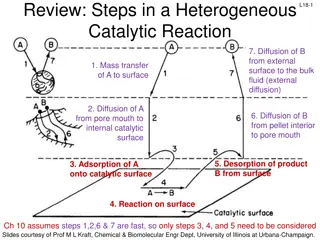
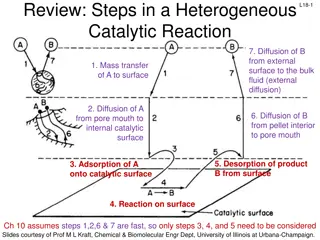
Understanding Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions: Key Steps Explained
In a heterogeneous catalytic reaction, various important steps occur, including diffusion of reactants, adsorption onto the catalyst surface, surface reactions, and desorption of products. Different mechanisms like single-site, dual-site, and Eley-Rideal mechanisms are involved in the surface reacti
0 views • 17 slides
Study on the Influence of Movable Oil on Pore Structure of Fengcheng Formation Shale Using Fractal Theory
This study by Hong Zhang at Peking University delves into the impact of movable oil on pore structure in different shale types, focusing on the Fengcheng Formation Shale in Well MY1 of the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, China. Utilizing fractal theory, the research explores the geological setting, methods
4 views • 13 slides
Sawdust as a Low-Cost Adsorbent for Water Treatment
Sawdust, a renewable natural resource, has been studied for its effectiveness as an adsorbent for removing contaminants from water. It contains cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, and other components that aid in adsorption. Research indicates its suitability for removing dyes, toxic salts, and heavy
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Interfacial Phenomena and Micelle Formation
Interfacial phenomena play a crucial role in the formation of micelles in surfactant solutions, leading to a decrease in surface tension. The critical micelle concentration (CMC) marks the point where micelles first form in the solution. Factors like chain length and electrolytes impact CMC and mice
0 views • 20 slides
Arsenic Removal by Activated Carbon: Study & Findings
The research delves into the efficient removal of arsenic from water using various types of activated carbon. Findings indicate the impact of modification, pH, temperature, and co-ions on adsorption capacity and efficiency, showcasing superior results with iron-modified activated carbon and biomass-
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Chemical Equilibrium in Reversible Reactions
Chemical equilibrium occurs when the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant over time in a reversible reaction. Reaction rate is proportional to concentration, and equilibrium is reached when the rate of formation equals the rate of consumption in both directions. Reversible reacti
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Cyclic Voltammetry in Electrochemical Methods
Electrochemical methods, such as cyclic voltammetry, are crucial for studying electron transfer processes, redox reactions, and adsorption on surfaces. Cyclic voltammetry involves varying the applied potential at a working electrode to monitor electron flow and chemical reactions. Peaks in the curre
0 views • 11 slides
Thin Layer Chromatography: Introduction, Principle, Methodology, and Applications
Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) is a technique for separating and identifying compounds in a mixture based on adsorption. The principle involves the relative affinity of components to the stationary and mobile phases. The methodology is similar to paper chromatography, using coatings like silica gel
0 views • 21 slides
Comparing Indigenous Laterite and Bauxite with Imported Activated Alumina for Fluoride Adsorption in Rural Northern Ghana
This study compares the effectiveness of indigenous laterite and bauxite with imported activated alumina for use in small-scale fluoride adsorption filters in rural Northern Ghana. It discusses the study area, the issue of fluorosis, and potential solutions using different sorbents. Physical and che
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Adsorption Process in Physical Pharmacy Lab
Adsorption is a significant process in physical pharmacy involving the attachment of solutes or gaseous molecules onto the surface of a solid. This process can be strong or weak depending on the forces between the solid surface and the gas/solute. Types include physical (reversible) and chemical (ir
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Surface Chemistry and Adsorption Phenomena
Surface chemistry is a crucial branch of chemistry that focuses on the chemical processes occurring at interfaces between different surfaces like solid-liquid, solid-gas, and liquid-gas. This field plays a significant role in various industries, including electronics. Adsorption, absorption, and sor
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Surface Chemistry and Adsorption Phenomenon
Surface chemistry explores the interactions that occur at surfaces and interfaces, with adsorption being a key phenomenon. Adsorption involves the concentration of molecules on a surface, with adsorbents and adsorbates playing crucial roles. Desorption, the opposite process, removes adsorbed substan
1 views • 21 slides
Innovative Solutions for Pollution Control Using Natural Adsorbents
Workshop explores new trends in biotechnology for pollutant removal. Focus on adsorption of dyes onto low-cost adsorbents, with analysis of equilibrium state. Various techniques discussed include bioaccumulation, biosorption, and use of non-living biomasses. Emphasis on eco-friendly filtering techni
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions: Steps and Mechanisms
The content discusses the key steps involved in a heterogeneous catalytic reaction, focusing on diffusion, mass transfer, adsorption, desorption, and surface reactions. It highlights the importance of considering external diffusion effects and provides guidelines for deducing reaction mechanisms in
0 views • 40 slides
Gas Processing: Dew Point Control and Refrigeration Systems
Gas processing involves gathering raw gas from wells, passing it through various units like feed gas receiving, condensate stabilization, gas treating, dew point control, and refrigeration units to control liquid condensation and recover natural gas liquids. Dew point control helps prevent condensat
0 views • 26 slides
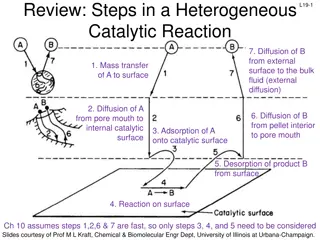
Understanding Steps in Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions and Adsorption Mechanisms
This review discusses the steps involved in a heterogeneous catalytic reaction, focusing on diffusion, mass transfer, adsorption, and desorption processes. It details the site balance, surface reaction mechanisms, and desorption steps, providing insights into the complexities of catalytic processes.
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Reversible Strain Behavior in Bi-2212 Magnet Design Literature
Literature review on the strain sensitivity of Bi-2212 wires, focusing on reversible transverse pressure strain and its impact on magnet design. Discussions on the correlation between axial and transverse strain behavior, the effects of heat treatments, and variations in strain sensitivity among man
0 views • 5 slides