Neonatal Vomiting: Causes, Diagnosis, and Differential Diagnosis
Neonatal vomiting can be a concern when presenting with bile-stained or blood-stained vomit, projectile vomiting, or associated with weight loss and failure to grow. Various non-surgical and surgical conditions like Pyloric Stenosis can lead to vomiting in neonates. Common causes include Mid-gut vol
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Anorectal Malformations in Pediatric Surgery
Anorectal malformations are congenital abnormalities involving the development of the anal canal and sphincter muscles. They may present with imperforate anus, fistulous connections, or rectal atresia. Classification in males and females helps in determining the types of surgical treatments required
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Achalasia: Therapeutic Approaches, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Manifestations
Achalasia is characterized by a failure of the lower esophageal sphincter to relax, leading to difficulty in swallowing and regurgitation. The exact cause is unknown, but autoimmune factors and chronic infections may play a role. Symptoms include dysphagia, chest pain, regurgitation, and weight loss
0 views • 59 slides
Understanding Gastrointestinal Motility: Key Concepts and Mechanisms
Gastrointestinal motility involves various processes like peristalsis, segmentation, basic electrical activity, and the migrating motor complex. Peristalsis is the reflex response to gut wall stretching, while segmentation helps mix intestinal contents and digestive juices. Basic Electrical Rhythm (
0 views • 19 slides
Physiotherapy Support for Mothers with OASI - Expert Guidance and Rehabilitation
Providing specialized physiotherapy support for mothers experiencing Obstetric Anal Sphincter Injuries (OASI) is crucial for addressing immediate problems like pain, urinary or fecal incontinence, and more. With a focus on pelvic health, this approach involves reassurance, tailored pelvic floor musc
0 views • 12 slides
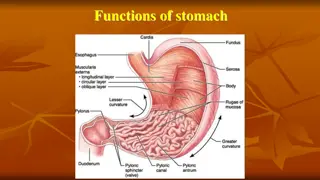
Understanding the Anatomy and Function of the Stomach
The stomach is a vital organ in the digestive system with functions like food storage, mixing with gastric secretions, and controlling chyme delivery to the small intestine. It has a J-shaped structure with various parts like the fundus, body, antrum, and pylorus. The lesser and greater curvatures,
0 views • 21 slides
Anatomy and Blood Supply of the Equine Stomach
The equine stomach is relatively small compared to the horse's body size, with distinct regions such as the cardia, fundus, body, and pyloric region. It is located on the left side of the abdomen, under the ribs. The stomach's blood supply includes branches from the aorta, splenic artery, and hepati
0 views • 23 slides
Functions and Secretions of the Stomach
The stomach plays crucial roles in digestion through its secretions such as stomach juice, hydrochloric acid, and mucus. These secretions aid in breaking down food components, promoting optimal enzymatic activity, and providing a protective barrier against bacteria. The stomach juice is composed of
0 views • 8 slides
Radiology Imaging of Esophagus and Stomach by Dr. A. Alhawas
View detailed radiology imaging of the esophagus and stomach conducted by Dr. A. Alhawas, showcasing various anatomical structures such as the splenic artery, abdominal aorta, common hepatic artery, and more. Explore pathologically changed layers in pyloric stenosis, arterial blood supply to the pyl
0 views • 8 slides
Overview of Stomach Surgery and Treatment Options
The stomach plays a crucial role in digestion and is divided into four regions - cardia, fundus, body, and pyloric part. Understanding the anatomy of the stomach is essential for surgical interventions, including treatment for benign and malignant gastric diseases like peptic ulcer disease. Surgical
0 views • 30 slides
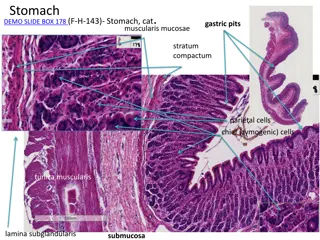
Various Stomach Anatomy Slides of Different Animal Species
Explore a series of detailed histological slides showcasing the stomach anatomy of different animal species including cats, rabbits, dogs, pigs, sheep, and goats. The images highlight key features such as gastric pits, mucosal layers, chief and parietal cells, proper gastric glands, cardiac and pylo
0 views • 29 slides
Pediatric Intestinal Obstruction: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Pediatric intestinal obstruction in newborns and older children can result from various conditions such as foregut obstruction, midgut obstruction, and hindgut obstruction. Common causes include esophageal atresia, pyloric stenosis, and Hirschsprung disease. Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, i
0 views • 81 slides
Teat Canal Disorders in Dairy Cows: Causes and Procedures
Teat canal disorders such as contract sphincter, enlarged teat orifice, calculus, polyps, and teat orifice occlusion can affect milk flow in dairy cows. Procedures for addressing these issues include local anesthesia, orifice cleaning, enlargement, and removal of obstructions. Images provided depict
0 views • 5 slides