Conditional Probability and Bayes Theorem
Conditional probability relates the likelihood of an event to the occurrence of another event. Theorems such as the Multiplication Theorem and Bayes Theorem provide a framework to calculate probabilities based on prior information. Conditional probability is used to analyze scenarios like the relati
5 views • 5 slides
The Coase Theorem: Property Rights and Economic Efficiency
The Coase Theorem, developed by economist Ronald Coase, posits that under certain conditions, bargaining related to property rights will lead to an optimal outcome regardless of the initial distribution. It provides a framework for resolving conflicts by emphasizing negotiation and efficient market
0 views • 10 slides
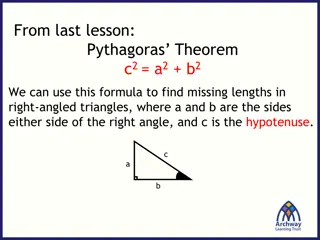
The Pythagorean Theorem and Right-Angled Triangles
Explore the Pythagorean Theorem, which states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (c) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (a and b). Learn how to identify the hypotenuse, use the theorem to find missing lengths, and visually understand th
5 views • 25 slides
Engineering Mechanics: Lami's Theorem and Cylinder Reactions Problem
This course material covers Lami's Theorem in Engineering Mechanics taught by Ranbir Mukhya. It includes an outline of the theorem, problem scenarios involving cylinders with given weights and diameters, and the determination of reactions at various points. Detailed force diagrams and calculations a
4 views • 8 slides
Insights into the Mean Value Theorem and Its Applications
Delve into the Mean Value Theorem (MVT) with a focus on concepts like Lagrange's MVT, Rolle's Theorem, and the physical and geometrical interpretations. Explore the conditions, statements, and special cases of MVT, along with practical applications and geometric insights. Dr. Arnab Gupta, an Assista
3 views • 14 slides
The Residue Theorem in Complex Analysis
The Residue Theorem is a powerful tool in complex analysis that allows us to evaluate line integrals around paths enclosing isolated singularities. By expanding the function in a Laurent series, deforming the contour, and summing residues, we can evaluate these integrals efficiently. This theorem ex
6 views • 31 slides
Superposition Theorem in Electrical Circuits
Superposition theorem in electrical circuits states that the effects of multiple voltage and current sources in a network can be analyzed independently and then combined algebraically. This allows for calculating the voltage and current distribution in a network more efficiently. The theorem involve
5 views • 9 slides
Lami's Theorem in Physics
Lami's Theorem is an equation that explains how the magnitudes of forces acting on a point keep an object in equilibrium. This theorem relates the forces with corresponding angles and is derived by understanding the sum of forces acting on a point. By utilizing complementary angles and the sine rule
4 views • 8 slides
Exploring the Pythagorean Theorem and Its Origins
The Pythagorean Theorem, named after the ancient Greek mathematician Pythagoras, is a fundamental principle in geometry relating to right triangles. While Pythagoras is credited with offering a proof of the theorem, evidence suggests that earlier civilizations like the Babylonians and ancient Chines
2 views • 21 slides
Comparison of Vertical and Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines
Vertical axis wind turbines (VAWT) include Darrieus, H-Rotor, and Savonius designs, while horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWT) have advantages such as better performance at greater heights and stronger winds. VAWT face challenges like self-starting and commercial success. Both turbine types operate
1 views • 9 slides
Parallel Sorting Algorithms and Amdahl's Law
Exploring the concepts of parallel sorting algorithms, analyzing parallel programs, divide and conquer algorithms, parallel speed-up, estimating running time on multiple processors, and understanding Amdahl's Law in parallel computing. The content covers key measures of run-time, divide and conquer
5 views • 40 slides
Bayes Theorem in NLP: Examples and Applications
Introduction to Bayes Theorem in Natural Language Processing (NLP) with detailed examples and applications. Explains how Bayes Theorem is used to calculate probabilities in diagnostic tests and to analyze various scenarios such as disease prediction and feature identification. Covers the concept of
3 views • 13 slides
Problem Solving with Pythagoras Theorem in Geometry
Explore the application of Pythagoras Theorem in solving problems related to right-angled triangles, diagonals of shapes like rectangles and rhombuses, and the height of triangles. Learn how to use Pythagoras Theorem effectively by drawing diagrams, identifying known lengths, and using the theorem t
3 views • 8 slides
The Medial Axis in Geometry
The medial axis in geometry is a fascinating concept related to Voronoi diagrams and maximal empty disks. Explore how the medial axis is constructed, its significance in the study of polygons, and its applications in modeling and algorithms. Learn about associated exercises and different algorithms
5 views • 12 slides
Calculus: From MVT to FTC with Lin McMullin
Join Lin McMullin in exploring the transition from the Mean Value Theorem (MVT) to the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (FTC). Discover the significance of MVT, Fermat's Theorem, Rolle's Theorem, and the Mean Value Theorem, all crucial concepts in calculus. Engage in graphical explorations, proving m
1 views • 45 slides
Rolle's Theorem and The Mean Value Theorem in Calculus
Rolle's Theorem states that for a continuous and differentiable function on a closed interval with equal function values at the endpoints, there exists at least one point where the derivative is zero. The Mean Value Theorem asserts that for a continuous and differentiable function on an interval, th
3 views • 5 slides
Introduction to Analysis: Mean Value Theorem and Related Theorems
This resource delves into key concepts such as the Mean Value Theorem, Fermat's Theorem, Rolle's Theorem, Extreme Value Theorem, local maximums, and more. It presents important results and explores proofs in the context of analysis.
2 views • 71 slides
Parallel Programming Directives and Concepts
Learn about parallel programming directives like Diretiva.parallel and #pragma omp.parallel, which allow code to be executed by multiple threads simultaneously. Explore concepts such as defining parallel regions, setting the number of threads, and utilizing OpenMP directives for parallel for loops.
1 views • 39 slides
Introduction to Applying Pythagorean Theorem in Right Triangles
In this lesson, we will learn how to apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find missing side lengths of right triangles. The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. Through examples and practice problems,
4 views • 13 slides
The Formation and Goals of the Axis Powers in World War II
The Axis Powers, composed of Italy, Japan, and Germany, were established to challenge the existing European order and expand their influence. Through alliances and shared military ambitions, they aimed to dominate different regions of the world during World War II, with Germany targeting Europe, Ita
3 views • 8 slides
Binomial Theorem: Expansion, Examples, and Applications
Binomial theorem is a powerful mathematical concept used to expand expressions involving binomials. This presentation explores the basics of binomial expansion, formulae for positive, negative, and fractional indices, along with examples demonstrating its application. By leveraging the binomial theo
6 views • 10 slides
Moments of Inertia in Structural Mechanics
Moments of inertia of an area play a crucial role in determining the strength and stability of structural members and mechanical elements. This includes concepts such as area moment of inertia, parallel-axis theorem, and radius of gyration. The integration process, positive nature, and units of mome
2 views • 5 slides
Automated Theorem Proving in Lean
Dive into the world of automated theorem proving in Lean with a focus on formal verification, history, and the use of logic and computational methods. Explore how programs can assist in finding and verifying proofs, as well as the significance of interactive theorem provers. Discover the evolution o
5 views • 35 slides
Parallel Approaches for Multiobjective Optimization in CMPE538
This lecture provides a comprehensive overview of parallel approaches for multiobjective optimization in CMPE538. It discusses the design and implementation aspects of algorithms on various parallel and distributed architectures. Multiobjective optimization problems, often NP-hard and time-consuming
5 views • 20 slides
Triangles Inequalities and The Hinge Theorem
Understanding the inequalities in triangles using the Hinge Theorem. The theorem explains how the length of the third side of a triangle relates to the included angles and congruent sides in different triangle configurations. Explore problems that involve applying the Hinge Theorem and its converse
2 views • 8 slides
Parallel Processing Fundamentals
This overview delves into the basics of parallel computing, covering parallel memory architectures, programming models, design issues, and parallelizing serial programs. Parallel computing involves leveraging multiple compute resources simultaneously to enhance computational efficiency and solve pro
4 views • 35 slides
Novel Paradigms of Parallel Programming
Dive into the innovative approaches to parallel programming as elucidated by Professor Smruti R. Sarangi from IIT Delhi. The book outlines new paradigms, strategies, and frameworks for designing and optimizing parallel programs. Readers will gain insights into cutting-edge techniques that improve pe
2 views • 52 slides
Parallel Lines and Their Properties
In this lesson, students will learn about parallel lines and their properties through various examples and explanations. The lesson covers the definition of parallel lines, identifying parallel and non-parallel lines, understanding the concept of transversals, and exploring angles formed by a transv
19 views • 27 slides
Pythagoras’ Theorem
The Pythagoras Theorem explains the relationship between the sides of a right-angled triangle. Discover the history, visualization, and application of this fundamental mathematical concept through a detailed exploration. Uncover how to use Pythagoras Theorem to calculate the length of the hypotenuse
4 views • 14 slides
Bisectors
Explore the concepts of perpendicular and angle bisectors through the Perpendicular Bisector Theorem, Converse of the Perpendicular Bisector Theorem, Angle Bisector Theorem, and Converse of the Angle Bisector Theorem. Learn how these theorems are applied in geometry with illustrative examples. Get i
2 views • 7 slides
Parallel Prefix Algorithms and PRAM Model: A Theoretical Approach
Explore parallel prefix algorithms and the PRAM model of parallel computation in the context of turning serial processes into parallel ones. Understand the concepts of vector operations, broadcast, reduction, and examples of prefix functions. Delve into theoretical insights and practical application
0 views • 33 slides
Advanced Parallel Computing Techniques with OpenMP
Learn to efficiently implement matrix-vector multiplication using OpenMP for parallel computing, utilizing sparse matrix formats and comparing different parallel computing strategies to optimize performance. The content covers C++ code implementations, thread parallelism with OpenMP, and recruiting
3 views • 48 slides
Introduction to Parallel Computing and Parallel Computers
Explore the world of parallel computing, where multiple processing elements collaborate to solve problems simultaneously. Learn about the key elements of parallel computers, contemporary computing systems, parallel programs, and the reasons why parallel computing is essential for large-scale applica
2 views • 36 slides
Boosting Performance Through Parallel Computing Concepts
Explore the realm of parallel computing, where multiple processing elements collaborate to tackle complex problems simultaneously. Discover the significance of parallel computers in modern computing systems, from mobile devices to supercomputers, and the advantages they offer in terms of efficiency
1 views • 15 slides
Properties of Parallel Lines: Theorems and Postulates Explained
Explore the fundamental theorems and postulates related to parallel lines, including Same-Side Interior Angles Postulate, Alternate Interior Angles Theorem, Corresponding Angles Theorem, and Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem. Learn how these geometric principles can help solve angle measurements and
1 views • 12 slides
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Part 2: Evaluation Theorem Explained
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Part 2, also known as the Evaluation Theorem, allows us to evaluate definite integrals by finding antiderivatives. This theorem connects differential calculus and definite integrals, providing a powerful tool in calculus. Learn how to apply this fundamental conce
4 views • 10 slides
Geometry Concepts: Parallel Lines, Triangle Angle-Sum Theorem, Classifying Triangles
Explore key geometry concepts including parallel lines, the triangle angle-sum theorem, triangle classification by angles and sides. Understand the relationships between angles and sides in triangles through practical examples and the exterior angle theorem.
0 views • 10 slides
Introduction to Parallelism in CSE 344: February 23rd Overview
Explore the world of parallel computing in the field of Computer Science and Engineering (CSE) 344 on February 23rd. Discover the importance of computing in parallel, performance metrics, linear vs. non-linear speedup, architectures for parallel databases, and more. Get insights on why sub-linear sp
2 views • 37 slides
Understanding Automated Theorem Proving: Tools and History
Discover the world of automated theorem proving, featuring formal verification, program-assisted proof generation, interactive theorem proving, and a glimpse into historical milestones like JOHNNIAC. Explore the use of logic and computational methods to verify mathematical claims, and the various to
0 views • 35 slides
5 Axis Machining Johor
At Sunyi Precision Engineering, headquartered in Johor, we excel in 5-Axis Machining, delivering unmatched precision and complexity for parts that demand exact tolerances and intricate geometries. Our advanced 5-axis CNC machines enable simultaneous
2 views • 7 slides