Understanding Virus-Cell Interactions: Mechanisms and Consequences
Viruses interact with host cells in various ways, encoding genes that manipulate cell functions for their benefit. These interactions can range from benign to lethal outcomes. Factors influencing these interactions include viral factors, cellular responses, and the presence of virulence factors. Dif
0 views • 37 slides
Exploring Particles and Fundamental Interactions in the Universe
Delve into the intricate world of particles and fundamental interactions in the Universe as explained by Professor Emeritus George Lazarides from Aristotle University of Thessaloniki. Discover the structure of matter, classification of particles based on interactions, constituents of hadrons, conser
1 views • 36 slides
Understanding Species Interactions and Predator-Prey Dynamics
Species interactions refer to the associations between different organisms that can be positive or negative, influencing the growth and evolution of populations. Predation is a key interaction where one organism hunts and feeds on another. In predator-prey dynamics, populations fluctuate in a cyclic
3 views • 36 slides
Understanding Hyperfine Interactions in Atomic Physics
Hyperfine interactions play a crucial role in atomic physics, leading to small energy shifts and splitting of degenerate levels in atoms and molecules. These interactions involve the electromagnetic multipole interactions between the nucleus and electron clouds, resulting in the splitting of energy
13 views • 154 slides
5 Medical Cannabis Interactions Every Physician Must Understand
As medical cannabis becomes increasingly integrated into healthcare practices, itu2019s imperative for physicians to be well-versed in potential interactions with other medications. While cannabis offers promising therapeutic benefits, its interactions with certain drugs can pose risks to patients.
1 views • 2 slides
Understanding Three-Way Interactions in Regression Models
Three-way interactions in regression models add complexity to interpreting the effects of predictors. This article explains how to decompose three-way interactions in Stata, model them effectively, and assess their significance using contrast tests. Practical examples and Stata commands are provided
0 views • 17 slides
Interactions Between Ancient Greece and Ethiopia: A Historical Overview
Ancient Greece and Ethiopia had significant interactions throughout history. The relationship started with trade and the employment of Greek mercenaries by the Egyptian rulers. Greeks were intrigued by rumors about Ethiopians, leading to explorations and interactions. This period ended with Alexande
0 views • 9 slides
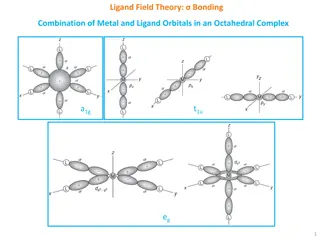
Understanding Ligand Field Theory in Octahedral Complexes
Ligand Field Theory explains the bonding interactions between metal and ligand orbitals in octahedral complexes. This theory involves the combination of metal and ligand orbitals to form molecular orbitals, leading to specific electronic configurations. The overlap of metal and ligand group orbitals
1 views • 10 slides
Exploring Influences on Consciousness Through Neocortical Interactions
Delve into the intriguing realm of consciousness with Lester Ingber's research on the influences stemming from multiple scales of neocortical interactions. The investigations cover various aspects such as mind over matter, recursive interactions, neuronal scales in the neocortex, and statistical mec
1 views • 41 slides
Understanding Virus-Cell Interactions and Infections
Viral infections exhibit diverse cellular tropism based on receptor interactions, impacting cell function through modulation and potential host defense responses. Infections can lead to various outcomes, from cell death to persistent or latent states, with nuanced effects on cellular behavior. Diffe
0 views • 8 slides
Principles of Ecology: Understanding Organism-Environment Interactions
Ecology is the scientific study of how living organisms interact with each other and their environment. It involves understanding organisms at their native habitats, from individuals to ecosystems. The discipline encompasses various branches and focuses on the relationships shaping the distribution
1 views • 14 slides
Exploring Drosophila Melanogaster: A Model Organism for Genetics Research
Discover the stages of development in Drosophila Melanogaster, a prominent genetic model organism. Learn about its different life stages, egg-laying behavior, and how to identify males versus females based on various characteristics. Explore the intricate world of fruit fly genetics and research thr
0 views • 16 slides
Adding Interactions to Students: A Comprehensive Guide
Enhance your students' learning journey by adding interactions to record their careers education and provide necessary guidance. This guide covers adding interactions directly for groups and individuals, utilizing matching, maximizing interaction benefits, and troubleshooting tips. Start by selectin
5 views • 26 slides
Understanding Antibiotics: Nursing Implications and Therapeutic Considerations
Antibiotics are essential medications used to treat bacterial infections. Before initiating antibiotic therapy, it is crucial to culture the suspected infection sites to identify the causative organism and select appropriate antibiotics. Nursing implications include assessing for drug allergies, mon
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Lichens: A Symbiotic Organism in Nature
Lichens, a unique symbiotic organism combining a fungus and alga or cyanobacterium, are widely distributed and diverse in nature. Comprising of 186 plant species from 148 genera and 63 families, lichens are versatile in their adaptation to different habitats and substrates. This article delves into
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Paramoecium Caudatum: A Microscopic Organism with Unique Characteristics
Paramoecium caudatum is a typical ciliate protozoan characterized by the presence of cilia as a locomotor organelle, nuclear dimorphism, and a unique form of sexual reproduction called conjugation. Commonly found in freshwater habitats, this microscopic organism has a distinct structure with a pelli
3 views • 10 slides
Exploring Trust and Distrust in Social Interactions
Understanding the dynamics of trust and distrust within social interactions is vital for successful service delivery and relationship-building, especially in youth work settings. This case study highlights the complexities of gaining trust, the significance of trusting relationships, and the cultura
1 views • 50 slides
Biology Revision with AQA Trilogy: Cell Biology and Organism Organization
In this biology revision session for AQA Trilogy, we delve into topics like cell biology, organism organization, diffusion, osmosis, active transport, enzymes, and more. Explore the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, understand cell specialization, and learn about key processes like mit
0 views • 8 slides
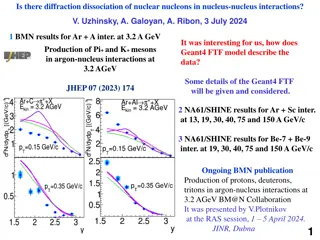
Understanding Diffraction Processes and Meson Production in Nuclear Interactions
Exploration of diffraction dissociation of nuclear nucleons in nucleus-nucleus interactions using Geant4 FTF model and NA61/SHINE results for various nucleus combinations. Insights into meson production in argon-nucleus interactions at different energies and the impact of models like DCM/AGT, UrQMD,
0 views • 17 slides
Interactions Among Living Things and Adaptations in Nature
Understanding the interactions among living things, such as competition, predation, and symbiosis, sheds light on how organisms adapt to their environments through natural selection. Each organism occupies a unique niche, defining its role in the ecosystem. Predation plays a crucial role in populati
0 views • 14 slides
PuReMD Design - Initialization, Interactions, and Experimental Results
PuReMD Design involves the initialization of neighbor lists, bond lists, hydrogen bond lists, and coefficients of QEq matrix for bonded interactions. It also implements non-bonded interactions such as charge equilibration, Coulomb's forces, and Van der Waals forces. The process includes the generati
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Epistasis: Genetic Interactions and Their Implications
Epistasis is a phenomenon where the phenotypic expression of one gene is influenced by interactions with another gene. This concept, first introduced in 1909, plays a crucial role in genetics, affecting various traits and evolutionary processes. The difference between dominance and epistasis lies in
0 views • 41 slides
Understanding UML Sequence Diagrams
UML Sequence Diagrams illustrate high-level interactions between class instances in software programs. They represent method calls and interactions among objects during program execution. The diagrams show interactions for specific circumstances like startup or button clicks. Each class/object is re
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Matter Transfer in Food Chains
Explore the journey of matter in a food chain, from organism to organism, and learn how it is utilized and transformed. Discover the role of molecules in the process and delve into the functions of living things in the ecosystem. Engage in hands-on activities and discussions to deepen understanding
0 views • 32 slides
Exploring Paramecium: A Detailed Study of a Protozoan Organism
Paramecium, a widely studied protozoan organism, is found in various freshwater habitats. It exhibits unique characteristics such as locomotion through cilia, holozoic nutrition, and intracellular digestion. This microscopic organism reproduces both asexually and sexually, displaying a complex nucle
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Genotype and Phenotype: The Genetic Basis of Organism Variation
Genotype determines the genetic makeup of an organism, while phenotype encompasses its observable traits. Johannsen's theory states that phenotype is a result of genotype, which remains constant throughout life. The concept of phenocopy refers to mimicking another phenotype without altering the geno
0 views • 15 slides
Comparison of Models of Nucleus-Nucleus Interactions in CORSIKA
Introduction to the study on models of hadronic interactions at high energies implemented in CORSIKA, a simulation tool used to analyze cosmic ray interactions with Earth's atmosphere. The study compares four widely used models, detailing their features and variants in simulation parameters. Results
0 views • 10 slides
Population Interactions in Nature: Competitive and Cooperative Interactions
Every population, whether animal or plant, engages in competitive and cooperative interactions to fulfill their needs for food, shelter, and resources. Intraspecific competition is common among individuals of the same species, leading to a struggle for survival. Interspecific interactions also play
0 views • 17 slides
Weak Interactions and Hydrogen Bonding in Molecular Forces
Exploring van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonding, and weak interactions in intermolecular forces and surface interactions. Understanding interactions between backbone peptide groups and orientation dependence of hydrogen bonding through dispersion forces and repulsive potentials.
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Intermolecular Forces in Chemistry
Interactions between static charge distributions in chemistry are governed by Coulomb's Law, playing a crucial role in understanding intermolecular forces. From ion-ion interactions to charge-dipole and charge-quadrupole interactions, the strength of forces varies based on factors like distance and
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Use Cases and Actors in System Design
Explore the concept of use cases in system design, including user goals versus interactions, system boundaries, actors, and how they all come together in use case diagrams. Learn how use cases capture user-visible functions, achieve discrete goals, and represent the interactions between actors and t
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Targeted Clinical Investigation in Pharmacovigilance
Targeted clinical investigation plays a crucial role in pharmacovigilance by further evaluating significant risks identified in pre-approval clinical trials. This involves conducting pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies, genetic testing, interaction studies, and large simplified trials to ass
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Population Interactions in Communities
Communities are made up of populations of organisms that interact in various ways, shaping the structure of the community. Population interactions include predator-prey relationships, symbiotic interactions like mutualism and commensalism, parasitism, and competitive exclusion. These interactions in
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Symbiotic Relationships in Nature
Symbiosis is the act of organisms living together, benefiting each other or having one organism harmed while the other benefits or remains unaffected. It includes mutualism, parasitism, and commensalism, each showcasing different types of interactions in nature. Examples such as flowers and insects
0 views • 12 slides
Quantum Interactions: Electrons, Phonons, and Hubbard Interaction
Exploring the complexities of electron-electron and electron-phonon interactions, nonequilibrium Green's functions, Hartree-Fock method, Coulomb's law, quantum operator forms, Hubbard interaction, and electron-phonon interactions from first principles. The interactions delve into the behavior of cha
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Non-Covalent Pi-System Interactions in Molecular Structures
Non-covalent interactions play a crucial role in chemical selectivity and molecular recognition. This article discusses the significance of Pi-system interactions, including Pi-Pi and Cation-Pi interactions, in stabilizing molecular structures like DNA helices and G-quadruplexes. Insights into molec
0 views • 6 slides
Creating a Model Organism Database: The Importance and Process
In the realm of bioinformatics, the creation of Model Organism Databases (MODs) plays a crucial role in advancing genomic research and understanding the complexities of various organisms. MODs facilitate pathway analyses, omics data analysis, and the development of metabolic models, serving as valua
0 views • 17 slides
The Role of DNA in Cellular Information Storage
Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA play critical roles in storing cellular information in the form of codes, enabling the formation of an organism's enzymes and structural proteins. Nucleotides, the building blocks of nucleic acids, consist of a simple sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. B
0 views • 21 slides
Genetic Interactions in Chicken Combs: Epistatic and Non-Epistatic Examples
In chicken genetics, epistatic and non-epistatic interactions play a crucial role in determining comb size and shape. Bateson and Punnett's studies on fowls revealed how different gene pairs interact to produce distinctive phenotypes. Epistatic interactions, such as dominant epistasis, influence the
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Genotype and Phenotype in Genetics
Genotype refers to the genetic code responsible for specific traits, while phenotype is the outward appearance and characteristics of an organism. Traits can be dominant or recessive, with alleles representing the possible choices for a characteristic. Genotypes consist of two letters, one from each
0 views • 7 slides