Weak Interactions and Hydrogen Bonding in Molecular Forces
Exploring van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonding, and weak interactions in intermolecular forces and surface interactions. Understanding interactions between backbone peptide groups and orientation dependence of hydrogen bonding through dispersion forces and repulsive potentials.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
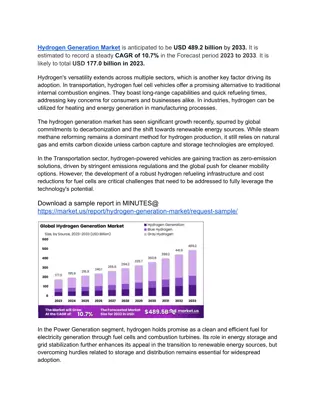
Van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds J. Israelichvili, Intermolecular and Surface Forces , Academic Press, London, 1997
Interactions between backbone peptide groups j C j+1 ij ) 2 ( ij j ( ) ( ) ( ) ij r pj + ; , ; , E E E p p ij i j el ij i j nb i j ( ) ( ( C j T u A u ( ; , ) ) ) E el ij p i j i ij ij j p ( ) i j = T ij 3 r A I r T ( ) ij ij ij ij 3 Dr ij ) 1 ( ij i i cos ( ) = u sin pi C i C i+1 ( ) , , , ) 1 ( ) 2 ( ; , E r ( ) 1 p p ij ij ij ij i j , , , = d d ) 1 ( ) 1 ( ) 2 ( ln exp f r RT i j ( ) ij ij ij ij ij i j 2 2 RT
O C || C C N 1 RT 2 H = + + ) 1 ( ij 2 VDW p p ... f E E E E 2 i j i j i j i j ( ij u 2 ) 1 RT ( 2 ) = + + + 2 2 2 VDW p p E E E E E ij i j insignific insignificant i || i || j || i || j 2 i j j ant 12 6 0 0 r r A ( ) ij ij ij 3 + ) 1 ( 12 ( ) ) 1 ( ) 2 ( 2 3 f ij ij ij ij ij r r r ij ij ij ) 1 ( ij ( ) ijr + B ( ) 2 2 2 ij 6 + 12 ( ) ) 1 ( ) 2 ( ) 1 ( ) 2 ( 4 3 3 ij ij ij ij ij r ij ) 1 ( ij u = = = ) 1 ( ) 2 ( 12 ( ) r r u u u u , , 2 ij i ij ij ij ij i j
2 el e captures the orientation dependence of backbone hydrogen bonding interactions = 0 = ) 1 ( o 90 ij ij ( ij u ) 2 ) 2 ( ij ) 1 ( ij ijr ) 1 ( ij u Approx. ( ij u ) 2 ij ) 2 ( ij ijr ) 1 ( ij u PMF PMF Liwo et al., Prot. Sci., 2, 1697 (1993); J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 9421 (2004)
Dispersion forces = a e 0 2 e = = . 0 53 a A 0 4 ( 2 ) h 0 ( 4 ) 2 2 a e ( ) r = = 0 0 0 w ( ) ( ) 2 2 6 6 4 r r 0 0 3 0 4 a 0 0 2 0 h ( ) r w ( ) 2 6 4 r 0
QM (London, 1930) C 2 0 2 0 3 3 h I ( ) r disp = = = w ( ) ( ) 2 6 6 6 4 4 4 r r 4 r 0 0 Different atoms 1 1 3 3 h h ( ) r = = = 01 02 01 02 2 2 w ( ) ( ) + + 2 2 6 6 2 2 4 4 r r 1 2 1 2 0 I 0 3 I 01 02 1 + 2 I ( ) 2 6 2 I 4 r 1 2 0
Repulsive potentials 0 r ( ) r = w r n r ( ) r = w r ( ) r = exp w c 0
What are hydrogen bonds? + H - Y X X, Y are usualy (99% or so) electronegative atoms is usually close to 180o d(X Y) < rVDW(X)+rVDW(Y); d(H Y)<rVDW(H)+rVDW(Y) d(X-H) is greater than in the free X-H molecule +H and -Y are pronounced wrt non-interacting molecules
rVDW(O)=1.52 A rVDW(H)=1.09 A
Types of hydrogen bonds Weak ( H<1 kcal/mol) usually involve non- polar or weakly polar groups. Moderately strong (1< H<20 kcal/mol) involve polar groups. Strong ( H>20 kcal/mol) involve ions.
Examples weak moderately strong strong
H-bonds in proteins backbone-backbone backbone-sidechain sidechain-sidechain backbone-solvent sidechain-solvent
Hydrogen bonding and proton transfer polarity X-H Y X- H-Y+ X Y H
Symmetric hydrogen bonds Koji -Prodi & Molcanov, Acta Chim. Slov., 2008, 55, 692-708
H-bonding energy surfaces are reflected in structural structures H.B. Burgi, J.D. Dunitz, Acc. Chem. Res., 1983, 16, 153-161
Energy decomposition E=ESX+EPOL+ECT+EDISP E=EES+EXC+EPOL+ECT Singh and Kollman, J. Chem. Phys., 1985, 83, 4033-4040