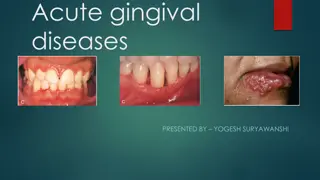
Overview of Acute Gingival Diseases
Acute gingival diseases encompass various conditions such as Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis, Necrotizing Ulcerative Periodontitis, Necrotizing Ulcerative Stomatitis, and others. Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (NUG) is a microbial disease primarily affecting the gingiva, characterized by necros
5 views • 67 slides
Managing Acute Chest Syndrome in Sickle Cell Disease
A case study of a 31-year-old male with sickle cell disease presenting in the emergency department with a pain crisis. The patient has a history of avascular necrosis, priapism, NSTEMI, cholecystectomy, and previous acute chest syndrome. Explore the patient's symptoms, past medical history, and reco
7 views • 19 slides
Rectal Prolapse and Rectal Tears in Animals: Causes and Treatments
Rectal prolapse and rectal tears are common conditions observed in cattle, buffaloes, and small ruminants. Prolonged tenesmus, increased intraabdominal pressure, rectal inflammation, and other factors contribute to the development of these issues. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent
2 views • 34 slides
Understanding Gangrene: Causes, Types, and Symptoms
Gangrene is a severe condition characterized by tissue necrosis, often due to loss of blood supply or bacterial infections. It is classified into dry, moist, and gas gangrene based on various factors like blood supply and fluid loss. Dry gangrene, also known as mummification, typically affects extre
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Inflammation and Its Characteristics
Inflammation is the response of tissues to harmful agents, categorized as acute or chronic. Acute inflammation is rapid and short-lived, while chronic inflammation is insidious and prolonged. Chemical mediators play a crucial role in both forms, leading to tissue necrosis. The five cardinal signs of
3 views • 27 slides
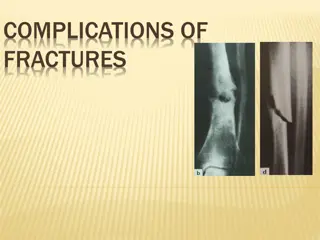
Complications of Fractures: Types and Consequences
Fractures can lead to a variety of complications, both locally and generally. General complications include shock, embolisms, crush syndrome, and more. Local complications can involve visceral, vascular, nerve injuries, compartment syndrome, infections, and more. Late complications may result in del
0 views • 29 slides
Overview of Bacterial and Fungal Corneal Ulcer
Bacterial and fungal corneal ulcers, known as suppurative keratitis, are a significant cause of blindness, included in national blindness control programs. They result from infections by exogenous organisms like S. aureus, S. pneumoniae, Aspergillus, and Candida. Predisposing factors include trauma,
0 views • 28 slides
State-of-the-Art Facilities at Central Instrumental Facility, Bihar Animal Sciences University, Patna
The Central Instrumental Facility at Bihar Animal Sciences University in Patna offers a range of cutting-edge equipment for research purposes, including an electroporator, bench-top flow cytometer, real-time PCR machine, inverted fluorescence microscope, and more. Researchers can utilize these facil
0 views • 27 slides
Overview of Inflammatory Diseases of Bone
Inflammatory diseases of bone encompass conditions like osteitis, osteomyelitis, periostitis, and alveolar osteitis (dry socket). Osteitis is localized and may be associated with infected sockets, while osteomyelitis involves the interior of the bone. Alveolar osteitis commonly follows tooth extract
0 views • 20 slides
Management of Quittor in Equine Medicine
Quittor is a condition in horses characterized by necrosis of lateral cartilage, leading to sinus openings in the coronet region. It can result from infections, pastern region necrosis, or suppuration from neighboring lesions. Symptoms include swollen coronet with sinus openings, potentially leading
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Wound Healing Process by Secondary Intention
Exploring the stages and characteristics of wound healing by secondary intention, including open wounds, infection risks, necrosis, and non-suturing methods. Learn about the initial, inflammatory, granulation tissue formation, wound contraction stages, as well as potential complications like pigment
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Necrosis: Causes, Characteristics, and Differences from Autolysis
Necrosis is the death of cells and tissues in living animals, characterized by various causes such as poisons, toxins, circulatory disturbances, and mechanical injuries. It presents gross appearances like white, gray, or yellow areas with a cooked meat appearance and distinct demarcation from health
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding the Diabetic Foot: Stages, Assessment, and Management
Explore the natural history of the diabetic foot, from initial stages to potential complications like ulcers and infections. Learn about the assessment of ulcerated feet, including identifying signs of infection and necrosis. Discover the role of radiography and microbiological control in managing d
0 views • 51 slides
Understanding Cell Injury and Degeneration in Response to Various Stressors
Cell injury can result from multiple stressors such as hypoxia, physical agents, chemicals, microbes, immunologic factors, nutritional imbalances, and aging. This can lead to reversible changes (degeneration) or irreversible changes (necrosis). Types of degeneration include cloudy swelling, hydropic
0 views • 22 slides
Overview of Corynebacterium diphtheriae Pathogenesis and Virulence Factors
Corynebacterium diphtheriae is a non-spore forming Gram-positive bacillus responsible for causing diphtheria in humans. This bacterium, particularly C. diphtheriae, is known for producing a potent exotoxin called diphtheria toxin, which blocks protein synthesis and leads to serious complications suc
0 views • 25 slides
Overview of Necrotizing Pneumonia in Children
Necrotizing pneumonia in children is characterized by necrosis of pulmonary tissue, leading to the formation of small cavities containing necrotic debris or fluid. Staphylococcus Aureus and Streptococcus Pneumoniae are common pathogens. Treatment involves a prolonged course of IV antibiotics tailore
0 views • 34 slides
Understanding Pressure Sores and Preventive Interventions for Bedridden Patients
Pressure sores, also known as pressure ulcers, are localized areas of tissue necrosis caused by prolonged pressure on skin and soft tissues. This can lead to serious complications, especially in bedridden patients like a 76-year-old man following a stroke. Preventive interventions include relieving
0 views • 26 slides
Comprehensive Overview of Wound Care Strategies
Explore evaluation procedures, treatment techniques, and dressing options for wound care management. Understanding compounding factors, modalities, and proper documentation are essential. Addressing conditions like swelling, necrosis, venous and arterial insufficiencies, and diabetes management play
0 views • 50 slides
Principles and Management of Acute Liver Disorders by Consultant Hepatologist
This presentation discusses the principles, causes, presentations, management, and prognosis of acute liver disorders, with a focus on insult to the normal liver leading to liver injury, inflammation, and necrosis. It covers causes such as drugs, viruses, ischemia, autoimmune conditions, Budd-Chiari
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI)
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) can present as cholestasis, hepatocyte necrosis, steatosis, vascular damage, and hepatic fibrosis. Various drugs like antibiotics, NSAIDs, recreational drugs, and herbal remedies can cause liver damage. Recognizing DILI is crucial in patients with liver dysfunction o
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Tuberculosis and Lung Cancer in Respiratory Pathology at KSU
Explore the detailed pathology of Tuberculosis (TB) and Lung Cancer through images and descriptions prepared by experts at the Pathology Department of King Saud University (KSU). Discover the features of TB such as epithelioid and giant cell granulomas, Ghon's complex, caseous necrosis, miliary TB,
0 views • 52 slides
Understanding Different Types of Cell Death and Tissue Repair
Cell death can be classified into apoptosis and necrotic cell death, with necrosis further categorized into liquefaction, caseous, and coagulative necrosis. Tissue repair occurs through regeneration or connective tissue replacement.
0 views • 11 slides
Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Lung Cancer Images in Respiratory Pathology Dept. KSU
Images showcasing various aspects of pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) and lung cancer in the respiratory pathology department at KSU. The pictures include Ghon's complex, caseous necrosis, miliary TB, tuberculous granulomas, and more, providing visual insights into the conditions and their pathological m
0 views • 39 slides
Understanding Perthes Disease in Pediatric Patients
Perthes disease, also known as Legg-Calve-Perthes disease, is a common pediatric disorder affecting the blood supply to the rounded head of the femur. It typically affects male children aged 3-10 years old and presents with symptoms such as limping, pain, and stiffness in the hip area. The disease p
0 views • 13 slides
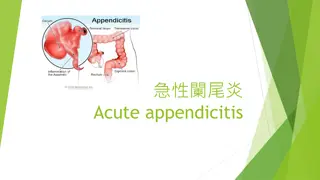
Pathophysiology of Acute Appendicitis
Necrosis, perforation, and arterial compromise in acute appendicitis lead to lumen obstruction, increased luminal pressure, bacterial growth, and venous obstruction. Symptoms typically include periumbilical or epigastric pain due to visceral pain caused by lumen obstruction.
0 views • 7 slides
Hydropericardium Hepatitis Syndrome (HHS) in Poultry: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
HHS is an acute infectious disease in chickens characterized by high morbidity and mortality, excess pericardial fluid, and multifocal hepatic necrosis. It mainly affects broilers and broiler parents, with clinical signs such as sudden mortality, lethargy, and ruffled feathers. Post-mortem lesions i
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Apoptosis: Intrinsic and Extrinsic Pathways
Apoptosis, a programmed cell death process occurring in multicellular organisms, involves characteristic cellular changes leading to cell death. Approximately 50-70 billion cells die daily through apoptosis in humans, serving vital roles like embryo development. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis is a regul
0 views • 18 slides
Caseous Mitral Valve Calcification (C-MAC) and Stroke: Overview and Management
Caseous Mitral Valve Calcification (C-MAC) is a rare condition characterized by spectrum liquefaction necrosis of the mitral annular calcification (MAC), potentially leading to cardiovascular complications like strokes and emboli. This article discusses the features, diagnostic aspects, and treatmen
0 views • 7 slides