Polymers: Classification and Properties
Polymers are large molecules formed by joining many monomers together. The process, known as polymerization, creates long chains with unique structures. This article explores different classifications of polymers based on origin, monomers, thermal response, formation mode, structure, application, ph
2 views • 13 slides
Polymers and Their Properties
Polymers are long chains of repeating monomers, with both natural and synthetic varieties. Natural polymers include silk, cellulose, and DNA, while synthetic ones encompass plastics, fibers, and elastomers. The properties of polymers, such as molar mass and monomer structure, determine their functio
0 views • 15 slides
Polymer Degradation Processes in Chemistry
Polymer degradation involves a reduction in molecular weight due to various factors like heating, mechanical stresses, radiation, oxygen, and moisture. Two main types of degradation include chain end degradation and random degradation, each affecting the polymer structure differently. Chain end degr
2 views • 12 slides
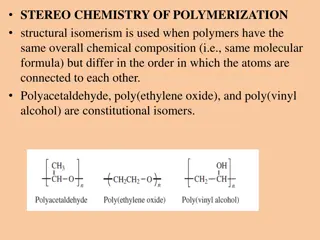
Stereochemistry and Isomerism in Polymerization
Structural isomerism plays a crucial role in polymer chemistry by distinguishing polymers with the same molecular formula but different atom connectivity. Isomeric polymers can stem from different monomers or polymerization routes, resulting in variations in properties. Stereoisomerism, on the other
2 views • 36 slides
Chemical Groups and Macromolecules in Biological Processes
In biological processes, certain chemical groups play crucial roles in molecular functions. These functional groups, including hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, phosphate, and methyl, are essential for the structure and function of biological molecules. Additionally, macromolecules, s
0 views • 9 slides
The Intriguing Structure and Functions of DNA
DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, is a fundamental molecule in living organisms, characterized by its double helical structure consisting of two antiparallel polynucleotide chains. Each strand is composed of nucleotide monomers, comprising deoxyribose sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous bases (puri
0 views • 12 slides
Carbohydrates: Composition, Structure, and Function
Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a specific ratio. Monosaccharides such as glucose, fructose, and galactose are carbohydrate monomers, while polysaccharides like lactose, sucrose, starch, cellulose, and glycogen are carbohydrate polymers. The chemical formula for glucose
0 views • 8 slides
Polymers: Monomers to Polymers
Explore the world of polymers by learning about monomers and polymers, how alkenes are used to create polymers, and the process of polymerisation. Dive into the structure of poly(ethene) and poly(propene) through diagrams and hands-on activities with molymod kits.
0 views • 19 slides
Organic Chemistry and Macromolecules
Organic chemistry focuses on compounds with carbon bonds, while inorganic chemistry deals with other compounds. Carbon is unique due to its ability to form multiple bonds, creating diverse structures like chains and rings. Organic compounds, produced by living organisms, range from simple to complex
0 views • 32 slides
Interactive Polymer Science Experiment for Elementary Students
Engage elementary students in a hands-on polymer science experiment using Gluey Putty. The experiment includes activities like creating polymer chains, skewering a water-filled plastic bag, making Gluey Putty, and exploring its properties. Students learn about solids, liquids, gases, monomers, and p
0 views • 9 slides
Origin and History of Life in AP Biology
Explore the fascinating journey of life from the Big Bang theory to the formation of monomers, polymers, protocells, and self-replicating systems. Delve into the Miller-Urey Experiment, RNA World Hypothesis, LUCA, and the impact of extinctions on the evolution of species.
0 views • 13 slides
Early Earth: Origins of Life and Genetic Evolution
Delve into the mysteries of the early Earth and the origin of life through engaging categories such as the absence of certain gases in the atmosphere, the synthesis of amino acids in lab simulations, the formation of protocells using DNA, and the bombardment of space debris. Discover how reducing at
1 views • 26 slides
DNA Structure and Denaturation Process
DNA is a double helical structure made of 2 antiparallel polynucleotide chains with nucleotide monomers. The structure contains deoxyribose sugar, phosphate groups, and nitrogenous bases (purines and pyrimidines). Hydrogen bonds between base pairs stabilize the structure. Denaturation can occur due
0 views • 16 slides
Development of Self-Crosslinking Acrylics in Interpolymer Company
This presentation explores the development of a family of water-based acrylics based on a unique self-crosslinking mechanism by Mr. Dana Charron in October 2018. It covers the history of interpolymer acrylic development, self-crosslinking theory, monomers used, backbone formation, and the mechanism
0 views • 22 slides
Structural Elements of DNA in Molecular Biology
DNA, the genetic material of living organisms, consists of two antiparallel polynucleotide chains forming a double helical structure. Each chain is composed of nucleotide monomers, consisting of deoxyribose sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous bases (purines and pyrimidines). The backbone of DNA
0 views • 17 slides
Regulatory Compliance for PU Products in Food and Drinking Water Contact
This document outlines the regulatory requirements for polyurethane (PU) products used in food and drinking water contact, including guidelines for monomers, additives, and substances allowed, as well as compliance procedures for both food and drinking water directives. It also details service activ
0 views • 17 slides
Macromolecules and Essential Nutrients for Overall Well-being
Learn about the main types of macromolecules - Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids - and how they contribute to our health. Explore the importance of essential nutrients available in everyday foods for growth and overall well-being, including carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, a
0 views • 31 slides