Industrial fermentation technology
Industrial fermentation technology involves three key stages - Up-Stream Processing (USP), the fermentation process, and Down-Stream Processing (DSP). USP includes formulating the fermentation medium, sterilization, inoculum preparation, and improving desired microorganisms for increased productivit
1 views • 23 slides
Precision Fermentation in Sustainable Food Production
Precision Fermentation is a specialized bioprocessing technique that utilizes microbes as cell factories to produce specific functional ingredients like proteins, vitamins, enzymes, and more. This innovative technology addresses the challenges of increasing food demands in a sustainable way, offerin
1 views • 12 slides
Our Beautiful Stinky Friends
Delve into the fascinating world of fermentation with chef/scientist David Zilber in this insightful listening guide based on the Science Friday podcast. Explore the science, ingredients, and techniques behind fermentation as Zilber shares his expertise and tips for home fermenters. Enhance your kno
0 views • 9 slides
Overview of Industrial Biochemistry and Biotechnology
This course outline covers key topics in industrial biochemistry, microbiology, and biotechnology, focusing on the use of microorganisms and molecules to achieve specific goals in production processes. It delves into microbial physiology, genetics, metabolic pathways, enzymes, microbial growth, ferm
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding the Rhizosphere: A Historical and Microbial Perspective
The rhizosphere, the region surrounding plant roots, harbors a diverse community of microorganisms influenced by plant roots. Historical background and microbial interactions in the rhizosphere are explored, highlighting the favorable habitat for microbial proliferation and metabolism. Various techn
1 views • 49 slides
Industrial Production of Citric Acid and Microbial Fermentation
Industrial production of citric acid has evolved from extraction processes to microbial fermentation, offering various industrial applications. Citric acid is utilized as an acidulant in food and pharmaceutical industries, a chelating agent in tanning, and a flavor enhancer in carbonated beverages.
1 views • 18 slides
Understanding Different Types of Fermentations
Alcoholic fermentation involves the production of ethanol, commonly carried out by yeasts like Saccharomyces cerevisiae. On the other hand, lactic acid fermentation results in the production of lactic acid through two types: homo-fermentative and heterofermentative pathways. Different substrates and
2 views • 23 slides
Understanding Types and Benefits of Solid State Fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process involving enzymes transforming organic substrates. Solid state fermentation (SSF) is a method without free water, crucial for enzyme production using natural materials like grains and fruit pulps. This process is cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and easy
1 views • 15 slides
Understanding Bioprocess Technology and its Applications
Bioprocess technology involves utilizing living cells or their components like bacteria and enzymes to produce desired products through fermentation. This field covers a range of processes, including microbial bioprocesses, enzyme production, metabolite synthesis, recombinant products, and transform
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Fermentation as a Food Preservation Technique
Fermentation is a natural process where microorganisms alter the sensory and functional properties of food to create a desirable end product. This method not only extends shelf life but also improves nutritional value, aids digestibility, and enhances food safety. Fermentation does not require expen
1 views • 31 slides
Industrial Production of Citric Acid: Fermentation Processes and Applications
Citric acid is industrially produced through microbial fermentation processes. It is widely used in various industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and beverage production. Different methods like surface culture fermentation are employed for citric acid manufacture, with fungi like Aspergillus nig
4 views • 18 slides
Understanding the Industrial Production of Vinegar
Vinegar fermentation, with its rich history and diverse classification based on raw materials, involves two essential fermentations - alcoholic fermentation and acetous fermentation. Various microorganisms, particularly Acetobacter species, play a crucial role in vinegar production. Different method
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Microbial Nutrition and Bacterial Physiology
Microbial nutrition involves essential elements required for microbial growth and energy production. Bacterial physiology delves into the structures and functions that enable bacteria to thrive, from cell wall composition to enzyme activities. Major elements like C, O, H, N, S, and P are crucial for
2 views • 20 slides
Understanding Microbial Nutrition and Growth Factors
Microbes require carbon for metabolic activities, with organisms categorized as heterotrophs or autotrophs based on their carbon source. In addition to carbon, macronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorous, sulfur, potassium, and magnesium are crucial for cell function. Growth factors such as amino acid
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Microbial Genetics and Mutations in Organisms
Explore the world of microbial genetics with Dr. Abhishek Thakur, an Assistant Professor specializing in Microbial Genetics at the College of Fisheries, Kishjanganj, BASU, Patna. Learn about important concepts such as strains, clones, genome, phenotype, genotype, genes, genetic recombination, and mu
0 views • 19 slides
Methods for Determination of Microbial Growth
Quantitative determination of microbial growth is crucial for various purposes, with two commonly used methods being the standard plate count and spectrophotometric measurement. The standard plate count method estimates living microbial cell density, while spectrophotometric measurement relies on tu
2 views • 6 slides
Understanding Fermentation and Bioreactors in Food and Industrial Microbiology
Fermentation is a crucial process where substances break down into simpler forms using organisms, generating energy. Bioreactors are systems supporting biochemically active environments for specific organisms, either aerobic or anaerobic. Learn about the history, importance, and applications of ferm
1 views • 16 slides
Understanding Microbial Ecology: Interactions and Associations in Ecosystems
Interactions of organisms in ecosystems play a crucial role in the functioning of microbial ecology. Dr. Abhishek Thakur explores symbiosis, mutualism, syntrophism, commensalism, predation, and parasitism, shedding light on how different organisms interact with each other and their physical environm
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Fermenter Design and Functionality
The fermenter is essential in the fermentation process, providing a controlled environment for biomass and product yields. It enables aseptic fermentation, optimal mixing, and aeration without excessive power consumption. Key functions include temperature control, pH regulation, and minimizing evapo
1 views • 36 slides
Understanding Fermentation Economics: Key Market Considerations
Studying the fermentation economy involves assessing market potential, competition, cost recovery, and distribution strategies. Market demand, competition, production costs, and potential profits are crucial factors to consider for successful commercial fermentation processes. Foreign sales can offe
0 views • 19 slides
Mechanisms of Nutrient Uptake by Microbial Cells
Nutrient uptake by microbial cells involves various transport mechanisms such as passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, and group translocation. These mechanisms ensure the specific acquisition of required nutrients by the cell through the selectively permeable plasma membrane.
3 views • 15 slides
Industrial Applications of Microbial Biomass Production
Microbial biomass has various industrial applications such as the production of single-cell proteins, antibiotics, ethanol, and organic acids. This biomass can serve as a valuable resource for seed cultures, silage production, biopesticides, animal fodder, and more. Yeasts like Saccharomyces cerevis
2 views • 17 slides
Understanding the Normal Microbial Flora of the Human Body
The normal microbial flora, also known as the indigenous microbiota, inhabit various areas of the human body such as the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, genitourinary tract, and skin. They play a crucial role in maintaining health and can re-establish themselves when disturbed. While resi
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Microbial Nutrition and Essential Elements
Microbial nutrition is crucial for the growth and functioning of microorganisms, requiring various elements in different quantities to construct cellular components and obtain energy. Major elements like carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, and others play vital roles in microbial
0 views • 20 slides
Factors Affecting Microbial Growth in Foods
Moisture content and pH levels are key factors influencing the growth and survival of microorganisms in foods. The water activity (aw) of food substrates affects microbial growth, with bacteria and fungi having varying requirements. Lowering aw below optimum levels can increase the lag phase of grow
2 views • 15 slides
Optimization of Bioethanol Production from Cassava Peels Using Microbial Inoculants
This study focuses on optimizing bioethanol production from cassava peels of different cassava varieties using various microbial inoculants. Cassava, a widely cultivated food crop in tropical regions, provides an attractive source for bioethanol production due to its high yield and ease of cultivati
0 views • 27 slides
Multidimensional Optimality of Microbial Metabolism
Exploring the multidimensional optimality of microbial metabolism through metabolic network analysis, C-based flux analysis, and stoichiometric reaction modeling. The concept of Pareto optimal solutions in multi-objective optimization problems is discussed in the context of microbial metabolic pathw
0 views • 22 slides
The Fascinating World of Food Fermentation
Explore the rich history and benefits of fermentation, from the early nomads' discovery of cheese and yogurt to Louis Pasteur's groundbreaking work. Learn about the different types of respiration, microbial fermentation in food production, and the energy-releasing process of cell respiration. Discov
0 views • 13 slides
Innovative Hygienic Solution for Healthcare Facilities: Introducing Medi-ShowerTM
Multi-Shower GB has developed the award-winning Medi-Shower, a unique anti-microbial showering system designed for healthcare facilities. Featuring color-coded Medi-Flush inserts, quarterly maintenance, and continual protection from bacteria, Medi-Shower provides a comprehensive solution to address
0 views • 11 slides
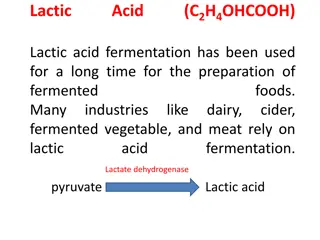
Lactic Acid Fermentation in Food Industry
Lactic acid fermentation is a widely used method for producing fermented foods like dairy, vegetables, and meats. This process involves lactic acid bacteria and filamentous fungi to convert sugars into lactic acid. Various microbial cultures are utilized, and raw materials such as whey, molasses, an
0 views • 23 slides
Effects of Spicy Foods on Pathogenic Microbial Growth: A Study on Rosemary and Clove
Spicy foods like rosemary and clove have shown potential in inhibiting pathogenic microbial growth, which can help enhance food safety by reducing the need for chemical additives. This study explores the antimicrobial effects of these spices using microbial strains like Pseudomonas Fluorescens and S
0 views • 14 slides
Interactions Between Bacteria and Methanogens in the Rumen
The rumen, an anaerobic fermentation chamber in ruminant animals, houses a diverse microbial community including bacteria, fungi, protozoa, methanogenic archaea, and phages. Methanogens play a crucial role in methane production using fermentation end products. Research aims to explore evidence of in
0 views • 21 slides
Applications and Industrial Production of Fermentation in Various Sectors
Fermentation plays a crucial role in the production of organic solvents, food products, condiments, dairy products, processed meats, beverages, vitamins, and pharmaceutical compounds like antibiotics and vaccines. Specific examples include the production of citric acid, lactic acid, monosodium gluta
0 views • 6 slides
Advancing Microbiological Systems Through Genetic Engineering and Microbial Community Engineering
Exploring the intersection of genetic engineering and microbial community engineering to enhance electron bifurcation systems. Addressing trade-offs between synthetic biology and wildtype organisms, incorporating microbial community engineering in Synbio, and investigating CO2 metabolism in the abse
0 views • 8 slides
MicrobeDB Database Analysis for Microbial Diversity
In June 2017, data from MicrobeDB.jp was analyzed, revealing microbial diversity in various phyla and families. The study included Wilcoxon P-values and abundances of different microbial genera. The analysis indicated the presence of various bacterial and archaeal species in different environments,
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Processes
Cellular respiration is the energy-releasing process in which organisms take in glucose and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy. This process is vital for all living organisms. Photosynthesis and respiration are opposite processes, with respiration requiring the products of photosynt
0 views • 10 slides
Anaerobic Fermentation for Biofuel Production: Uses and Applications
Anaerobic fermentation is a key process converting biomass into biogas without oxygen. Biofuels, such as bioethanol and biodiesel, derived from biomass like agricultural and industrial waste, offer renewable and environmentally friendly energy alternatives. The applications of anaerobic fermentation
0 views • 11 slides
Overview of Different Types of Fermentation Processes
Explore the various types of fermentation processes including batch fermentation, fed-batch fermentation, continuous fermentation, solid-state fermentation, anaerobic fermentation, and aerobic fermentation. Each process has its own advantages and disadvantages, influencing factors such as sterilizat
0 views • 18 slides
Raw Materials in Industrial Fermentation Processes
Microorganisms utilized in industrial fermentation require essential raw materials such as water, energy sources, carbon, nitrogen, mineral elements, and sometimes vitamins and oxygen. Various raw materials like cane molasses, beet molasses, cereal grains, starch, glucose, and lactose serve as carbo
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Aquatic Microbial Groups and Their Environments
Explore the diverse world of aquatic microbial groups, their distribution in different water bodies, and their roles in ecosystems. Learn about the factors influencing microbial growth in water, the impact of eutrophication, bioremediation strategies, and the unique microbial communities found in es
0 views • 18 slides