Understanding IDS/IPS: Enhancing Security with SecurityGen's Advanced Solutions
In the realm of cybersecurity, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) play pivotal roles in safeguarding networks against evolving threats. SecurityGen's IDS IPS solutions are designed to monitor network traffic, detect suspicious activities, and prevent potential i
4 views • 1 slides
Memory Attack Review Overview
This content provides insights on memory attacks, particularly focusing on return-oriented programming and stack canary protection. It explores how stack canaries safeguard against return-oriented programming by detecting buffer overflows and preventing the alteration of return addresses. With a vis
1 views • 32 slides
Python-Based Model for SQL Injection and Web Application Security
The research focuses on combating SQL injection attacks in web applications using a Python-based neural network model. By training the model on a dataset and conducting blind testing, it achieved up to 81% accuracy in detecting malicious network traffic. This innovative approach aims to enhance cybe
2 views • 10 slides
Active Directory Backup and Recovery, cionsystems
Sometimes human error, technology failures and malicious actions can easily corrupt the directory. \/\/rb.gy\/klwubf
1 views • 7 slides
Adversarial Machine Learning in Cybersecurity: Challenges and Defenses
Adversarial Machine Learning (AML) plays a crucial role in cybersecurity as security analysts combat continually evolving attack strategies by malicious adversaries. ML models are increasingly utilized to address the complexity of cyber threats, yet they are susceptible to adversarial attacks. Inves
2 views • 46 slides
Understanding Malicious Attacks, Threats, and Vulnerabilities in IT Security
Malicious attacks, threats, and vulnerabilities in IT systems pose significant risks and damages. This chapter explores the types of attacks, tools used, security breaches, and measures to protect against cyber threats. Learn how security professionals safeguard organizations from malicious attacks
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Typosquatting in Language-Based Package Ecosystems
Typosquatting in language-based package ecosystems refers to the malicious practice of registering domain names that are similar to popular packages or libraries with the intention of tricking developers into downloading malware or compromised software. This threat vector is a serious issue as it ca
0 views • 23 slides
Stuxnet: The Changing Face of Cyberwarfare
A deep dive into the Stuxnet cyberweapon, a malicious computer worm targeting industrial control systems with its sophisticated capabilities, affecting multiple countries and posing significant threats to critical resources. Despite being linked to American and Israeli origins, neither country has a
2 views • 11 slides
Active Directory Backup and Recovery, cionsystems
Sometimes human error, technology failures and malicious actions can easily corrupt the directory. \/\/tinyurl.com\/5xpuutyd
3 views • 7 slides
Top Malware Protection Services in Dallas - Keep Your Business Safe
If you are searching for the best Malware Protection in Dallas, then you are in the right place. For all your Cyber Security needs look no further than Black Swan Cyber Security. As cyber threats continue to evolve, it is important to prevent the introduction of malicious code that can compromise th
2 views • 3 slides
International Approaches to Enhance Nuclear Safety and Security
Understanding the concepts of nuclear safety and security, their differences, and the importance of establishing a robust nuclear security culture are essential for safeguarding nuclear facilities. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) plays a significant role in promoting nuclear safety and
1 views • 10 slides
Understanding Byzantine Fault Tolerance in Distributed Systems
Byzantine fault tolerance is crucial in ensuring the reliability of distributed systems, especially in the presence of malicious nodes. This concept deals with normal faults, crash faults, and the challenging Byzantine faults, where nodes can exhibit deceptive behaviors. The Byzantine Generals Probl
0 views • 29 slides
Essential Steps to Enhance Cyber Security
Implement best practices to counter cyber security attacks, including defense in depth strategies, user account controls, antivirus software installation, OS protection, strong password usage, and avoidance of social engineering and malicious software. Be cautious of hacker tricks and maintain a sec
0 views • 10 slides
Internet Safety Tips: Protect Yourself Online
Internet safety is crucial in safeguarding your online activities from threats like malicious software, hackers, and data leaks. Learn how to protect yourself against these risks, prevent password breaches, save passwords securely, back up your data, and be cautious about what information you share
1 views • 15 slides
Cyber Threat Detection and Network Security Strategies
Threat detection is crucial in analyzing security ecosystems to identify and neutralize malicious activities. Methods like leveraging threat intelligence, behavior analytics, setting intruder traps, and conducting threat hunts are essential for proactive security. Implementing security through obscu
1 views • 51 slides
Efficient Malicious URL Detection with Bloom Filters
Google's Chrome team faces the challenge of detecting malicious URLs without heavy memory usage. Universal hashing and Bloom Filters are discussed as innovative solutions to address this issue efficiently and effectively, illustrating how K-independent hash functions can improve detection accuracy w
0 views • 19 slides
Exploring the Malicious Use of Artificial Intelligence and its Security Risks
Delve into the realm of artificial intelligence and uncover the potential risks associated with its malicious applications, including AI safety concerns and security vulnerabilities. Discover common threat factors and security domains that play a vital role in combating these challenges.
0 views • 30 slides
Fundamentals of Ethical Hacking
Ethical hackers are often called \u201cwhite hats\u201d in contrast to \u201cblack hats,\u201d who are the malicious hackers. White hats use their skills to improve security and protect information, while black hats exploit vulnerabilities for illega
0 views • 1 slides
Understanding Typosquatting in Language-Based Package Ecosystems
Typosquatting in language-based package ecosystems involves malicious actors registering similar-sounding domain names to legitimate ones to deceive users into downloading malware or visiting malicious sites. This practice poses a significant threat as users may unknowingly install compromised packa
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Malicious Software and Its Impact on Computer Systems
Malicious software, commonly known as malware, poses a serious threat to computer systems by exploiting vulnerabilities. This content covers various terminologies, categories, and types of malware, including viruses, worms, rootkits, spyware, and adware. It also delves into how malware can cause dam
0 views • 16 slides
Enhancing Network Security Through Multi-Core Packet Scattering and Deep Packet Inspection
Explore the use of multi-core systems to tackle performance bottlenecks in network intrusion detection systems, specifically focusing on deep packet inspection. Techniques such as load balancing and pattern subset scanning are discussed to optimize DPI processes and improve overall network security
0 views • 43 slides
New Pattern Matching Algorithms for Network Security Applications by Liu Yang
Discusses new pattern matching algorithms for network security applications, focusing on intrusion detection systems (IDS) and the use of signatures and regular expressions to detect malicious patterns in network traffic. Explores the ideal and reality of pattern matching, time-space tradeoffs, and
0 views • 57 slides
Detecting Drive-By Attacks: Analysis of Malicious Javascript in Big Data Environments
Cybersecurity researcher Andrei Bozeanu delves into the complex world of polymorphic viruses, heuristic analysis, and the similarities between polymorphic viruses and malicious Javascript. Discover how these threats operate and evade detection, highlighting the importance of understanding malware be
0 views • 48 slides
Understanding Malware: Types, Symptoms, and Countermeasures
Malware is malicious software that can alter computer settings, behavior, files, services, ports, and speed. Sources of malware include insufficient security, honeypot websites, free downloads, torrents, pop-ups, emails, and infected media. Symptoms of malware include unusual computer behavior, slow
0 views • 9 slides
Advances in Authenticated Garbling for Secure 2PC
The research discusses advancements in authenticated garbling for achieving constant-round malicious secure 2PC using garbled circuits. It emphasizes the utilization of correlated randomness setup and efficient LPN-style assumptions to enhance communication efficiency significantly. Various techniqu
0 views • 30 slides
Stepping Stone Detection at the Server Side: Real-Time Algorithm
An innovative real-time algorithm is introduced to detect the use of a proxy as a stepping stone from the server's perspective. The solution addresses the limitations of existing methods by focusing on TCP connection initiation. Previous research and vulnerabilities related to proxy servers and step
0 views • 37 slides
Importance of Security in Web Development
Our perception of security has evolved to acknowledge the presence of malicious actors and potential vulnerabilities in web applications. To write secure code, developers must assume the worst-case scenario and adopt a security mindset that trusts no one. Attackers have various goals, such as steali
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Malicious Software in Computer Security
In "Computer Security: Principles and Practice," the chapter on Malicious Software covers various types of malware such as viruses, adware, worms, and rootkits. It defines malware, Trojan horses, and other related terms like backdoors, keyloggers, and spyware. The chapter also discusses advanced thr
0 views • 49 slides
Understanding Malicious Software in Data Security
Malicious software, or malware, poses a threat to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data within systems. It can be parasitic or independent, with examples like viruses, worms, Trojan horses, and e-mail viruses. Understanding the different types of malware and their modes of operati
0 views • 5 slides
Buffer Overflow Attack and Vulnerable Programs
Understanding buffer overflow attacks and vulnerable programs, the consequences of such attacks, how to run malicious code, and the setup required for exploiting vulnerabilities in program memory stack layouts. Learn about creating malicious inputs (bad files), finding offsets, and addressing shellc
0 views • 36 slides
New Zealanders' Online Privacy Behaviours and Cyber Security Challenges
New Zealanders exhibit various online privacy behaviors in response to the age of big data, supported by strong privacy values. Different age groups demonstrate diverse strategies for managing online identity. While some benefit from economic prosperity and improved social outcomes, risks such as pr
0 views • 11 slides
Exploring Java Sandbox Flexibility and Usage
The research delves into evaluating the flexibility and practical usage of the Java sandbox in dealing with Java applications. It highlights the importance of investigating how security tools are utilized, aiming to enhance security mechanisms and differentiate between malicious and benign code. The
0 views • 28 slides
Ensuring Secure Internet Connections: Understanding Domain Verification
This content delves into the importance of verifying domain authenticity to safeguard against potential online scams and phishing attempts. It explores how organizations like the Commonwealth Bank of Australia use domain name certification processes, encryption techniques, and trusted third parties
0 views • 54 slides
Transitioning to BGP Security: Incentives and Challenges
Explore the strategies and incentives for transitioning to BGP security in internet routing, including the use of S*BGP to attract traffic and mitigate interception attacks. Learn about RPKI as a key infrastructure and the need for additional security measures beyond RPKI. Discover how S*BGP can hel
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding Malware: Types, Risks, and Prevention
Malware, short for malicious software, is designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems. Malware includes viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, adware, spyware, rootkits, keyloggers, and more. They can be spread through various means like malicious links, untrusted down
0 views • 15 slides
MapReduce Method for Malware Detection in Parallel Systems
This paper presents a system call analysis method using MapReduce for malware detection at the IEEE 17th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems. It discusses detecting malware behavior, evaluation techniques, categories of malware, and approaches like signature-based and behavi
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Malicious Software: Classification and Payload Actions
Malicious software, or malware, can be broadly classified based on how it spreads and the actions it performs once on a target system. This classification includes distinctions between viruses, worms, trojans, botnets, and blended attacks. The payload actions of malware can range from file corruptio
0 views • 44 slides
Understanding Heap Exploitation Techniques in CSE 545 Fall 2020
This collection of images covers various heap exploitation techniques discussed in CSE 545 Fall 2020, such as fastbin use-after-free vulnerabilities, tcache poisoning, double-free exploits, metadata manipulation, and more. The images depict scenarios involving tcache, fast bins, unsorted bins, and f
0 views • 72 slides
Understanding Computer Science and Its Impact on Daily Life
Delve into the world of computer science to grasp its essence in modern society. Explore the significance of computers, variable instructions, programming, and the risks associated with their widespread use. Learn about hacking and malicious activities that can affect our digital ecosystem.
0 views • 18 slides
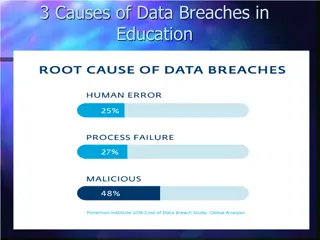
Understanding Data Breach Causes in Education
Data breaches in education are often caused by human errors, process failures, and malicious breaches. Human errors include leaving computers unlocked, sharing passwords, and carelessly discarding sensitive information. Process failures involve not keeping software up-to-date, lack of security polic
0 views • 15 slides