Formal Languages and Automata Theory
This course delves into abstract models of computers and computation, offering essential concepts and principles for understanding the fundamental nature of the computer field. Exploring topics such as regular expressions, context-free grammars, and automata theory, students gain insights into the p
4 views • 11 slides
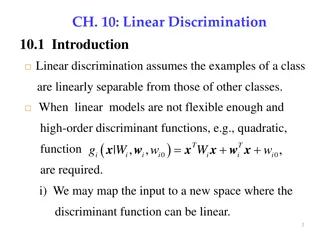
Linear Discrimination for Classification
Linear discrimination is a method for classifying data where examples from one class are separable from others. It involves using linear models or high-order functions like quadratic to map inputs to class separable spaces. This approach can be further categorized as class-based or boundary-based, e
3 views • 37 slides
Decision Analysis and Operations Research in Management
This content delves into Management Decision Analysis and Operations Research techniques such as Linear Programming, Integer Linear Programming, Dynamic Programming, Nonlinear Programming, and Network Programming. It covers the phases of an Operations Research study, mathematical modeling for decisi
0 views • 36 slides
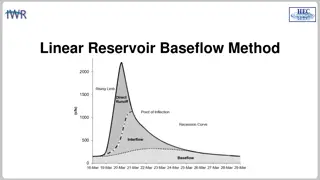
Linear Reservoir Baseflow Method
The linear reservoir baseflow method utilizes linear reservoirs to simulate the movement of water infiltrated into the soil. This method models water movement from the land surface to the stream network by integrating a linear relationship between storage and discharge. Users can select from one, tw
0 views • 11 slides
Linear Transformations and Matrices in Mathematics
Linear transformations play a crucial role in the study of vector spaces and matrices. They involve mapping vectors from one space to another while maintaining certain properties. This summary covers the introduction to linear transformations, the kernel and range of a transformation, matrices for l
1 views • 85 slides
Linear Programming: An Introduction to Optimization
Linear programming, introduced by mathematician George B. Dantzig in 1947, is a mathematical technique for optimizing resource allocation in a systematic manner. It involves formulating linear relationships among variables to achieve desired results like cost minimization or profit maximization. Lin
2 views • 60 slides
Overview of Linear Regression in Machine Learning
Linear regression is a fundamental concept in machine learning where a line or plane is fitted to a set of points to model the input-output relationship. It discusses fitting linear models, transforming inputs for nonlinear relationships, and parameter estimation via calculus. The simplest linear re
0 views • 14 slides
Context-Free Grammars (CFGs) and Pushdown Automata
Exploring Context-Free Grammars (CFGs) and Pushdown Automata, covering definitions, examples, ambiguity, and conversions. Learn about generating strings, CFG formal definitions, ambiguity in grammars, and more. Connect with the basics of context-free languages and their relations to PDAs. Dive into
2 views • 13 slides
Context-Free Grammars: Examples and Construction
Context-free grammars (CFG) are formal grammars used to generate patterns in a given language. This content provides examples of constructing CFGs for different languages, showcasing the process with detailed explanations and visuals.
0 views • 122 slides
Overview of Grammar Types and Chomsky Hierarchy
The four types of grammars are General, Context-Sensitive, Context-Free, and Linear grammars, each recognizing a specific set of languages. Chomsky Hierarchy categorizes these grammars into four levels, indicating subsets of languages they can recognize. Context-free grammars have specific productio
0 views • 17 slides
Comprehensive Overview of Numerical Linear Algebra Methods for Solving Linear Systems
Explore numerical linear algebra techniques for solving linear systems of equations, including direct and iterative methods. Delve into topics like Gaussian elimination, LU factorization, band solvers, sparse solvers, iterative techniques, and more. Gain insights into basic iterative methods, error
6 views • 12 slides
Formulation of Linear Programming Problems in Decision Making
Linear Programming is a mathematical technique used to optimize resource allocation and achieve specific objectives in decision-making. The nature of Linear Programming problems includes product-mix and blending problems, with components like decision variables and constraints. Various terminologies
1 views • 14 slides
Linear Programming: A Tool for Optimizing Business Operations
Explore the application of linear programming in business, as exemplified by the case study of San Miguel Corporation. Learn how linear programming models can help maximize profits, optimize resource allocation, and streamline decision-making processes in various industries. Discover the fundamental
1 views • 19 slides
Basis and Dimension in Linear Algebra
Basis and dimension are fundamental concepts in linear algebra. A basis is a set of vectors that can represent any vector in a given space through linear combinations. The dimension of a vector space is determined by the number of elements in its basis. Linear independence, spanning, finite-dimensio
5 views • 13 slides
Linear Algebra Summary and Solutions
This content delves into the concept of spans in linear algebra, discussing vector sets, generating sets, linear combinations, and solution spaces. It explores the span of vectors, linear independence, and the existence of solutions in a system of equations. The visual aids provided help in understa
0 views • 9 slides
Overview of Sparse Linear Solvers and Gaussian Elimination
Exploring Sparse Linear Solvers and Gaussian Elimination methods in solving systems of linear equations, emphasizing strategies, numerical stability considerations, and the unique approach of Sparse Gaussian Elimination. Topics include iterative and direct methods, factorization, matrix-vector multi
0 views • 35 slides
Linear Dependent and Independent Vectors
In linear algebra, when exploring systems of linear equations and vector sets, it is crucial to distinguish between linear dependent and independent vectors. Linear dependence occurs when one vector can be expressed as a combination of others, leading to various solutions or lack thereof in the give
0 views • 20 slides
Gaussian Elimination and Homogeneous Linear Systems
Gaussian Elimination is a powerful method used to solve systems of linear equations. It involves transforming augmented matrices through row operations to simplify and find solutions. Homogeneous linear systems have consistent solutions, including the trivial solution. This method is essential in li
0 views • 16 slides
Context-Free Languages and Grammars
Context-Free Languages and Grammars (CFLs & CFGs) are essential in theoretical computer science, providing a framework for recognizing non-regular languages. This content explores the distinction between regular and context-free languages, delves into the construction of language recognizers using c
1 views • 40 slides
Examples of Data Analysis Techniques and Linear Regression Models
In these examples, we explore data analysis techniques and linear regression models using scatter plots, linear functions, and residual calculations. We analyze the trends in recorded music sales, antibiotic levels in the body, and predicted values in a linear regression model. The concepts of slope
0 views • 11 slides
A Faster Algorithm for Linear Programming and the Maximum Flow Problem
A comprehensive overview of a new algorithm for linear programming and the maximum flow problem developed by Yin Tat Lee and Aaron Sidford from MIT and Simons. The algorithm aims to improve efficiency by reducing the number of iterations required to reach the optimal solution. It discusses the histo
0 views • 40 slides
The Oldest Applications of Linear Algebra in Ancient Civilizations
Linear algebra has roots in ancient civilizations like Egypt, where mathematical problems related to land measurement, resource distribution, and taxation were solved using techniques like Gaussian elimination and Cramer's Rule. The Rhind Papyrus from 1650 B.C. contains examples of linear systems an
0 views • 30 slides
Linear Function Modeling in Snowy Tree Cricket Chirp Rates
Based on the book "Functions, Data, and Models" by S.P. Gordon and F.S. Gordon, this presentation discusses how to model the chirp rate of snowy tree crickets in relation to temperature using linear functions. It covers finding the linear function, interpreting the slope and intercept, determining d
0 views • 13 slides
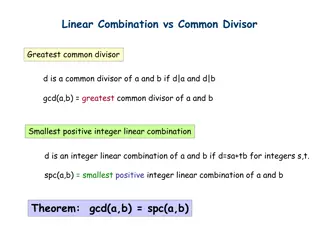
Linear Combinations and Common Divisors Theorem
Exploring the relationship between linear combinations and common divisors through the theorem connecting the greatest common divisor (GCD) and the smallest positive integer linear combination (SPC) of two integers a and b. The theorem states that the GCD is less than or equal to the SPC, with proof
0 views • 45 slides
Breakdown: Linear-time and Field-agnostic SNARKs for R1CS
Breakdown discusses linear-time and field-agnostic SNARKs for R1CS, focusing on achieving fast prover speeds and supporting circuits over arbitrary finite fields. SNARKs offer efficient proof systems with sub-linear proof sizes and verification costs. The work aims to eliminate the need for FFT-frie
0 views • 28 slides
Converting Left Linear Grammar to Right Linear Grammar
Learn about linear grammars, left linear grammars, and right linear grammars. Discover why left linear grammars are considered complex and how right linear grammars offer a simpler solution. Explore the process of converting a left linear grammar to a right linear grammar using a specific algorithm.
0 views • 44 slides
Linear Regression and Gradient Descent
Linear regression is about predicting continuous values, while logistic regression deals with discrete predictions. Gradient descent is a widely used optimization technique in machine learning. To predict commute times for new individuals based on data, we can use linear regression assuming a linear
0 views • 30 slides
Linear Programming for Recreational Site Planning
Learn about linear programming applied to recreational site planning with a specific case study involving Nature Connection and their allocation of forested wilderness and sightseeing park areas. Explore the components of linear programming models, steps in setting up a linear program, and the formu
0 views • 36 slides
Linear Optimization in MS&E 214
Linear optimization involves maximizing or minimizing a linear function subject to constraints. This week's focus in MS&E 214 is on linear programming, basic feasible solutions, duality theory, and extreme point solutions. The concept of linear programs, such as the example of maximizing x + 3y subj
0 views • 36 slides
Introduction to ANTLR: A Brief Overview
ANTLR (Another Tool For Language Recognition) is a parser generator that uses LL(*) for parsing input grammars. It generates source code in Java, C#, JavaScript, Python2, and Python3 to create language recognizers. Learn about LL(k) and LL(*) grammars, the history of ANTLR, and how it works in this
0 views • 32 slides
Adapting Linear Hashing for Flash Memory Constrained Embedded Devices
This research explores the adaptation of linear hashing for improved data handling on flash memory-constrained embedded devices. Motivated by the increasing data collection by IoT devices, the study focuses on implementing database structures like a linear hash table for efficient data processing. T
0 views • 67 slides
Linear Functions in Mathematics
Linear functions play a crucial role in mathematics, focusing on elements like rate of change and initial value. Through examples involving daily car rental costs and profit from selling birdhouses, this content explores the concept of linear functions and how they are applied in real-life scenarios
0 views • 13 slides
Context-Free Grammars in Systems Programming
This insightful content delves into the world of context-free grammars, explaining their significance in parsing computer programming languages. It discusses the hierarchy of language classification, the limitations of regular expressions in expressing certain constructs like palindromes, and the ut
0 views • 31 slides
Theory of Automata: Introduction and Regular Languages Overview
This course delves into the fundamentals of Theory of Automata, exploring topics such as regular languages, finite state models, grammars, Turing machines, and more. Instructor Mr. Muhammad Arif guides students through essential concepts like finite automata, pumping lemma, decidability, and Chomsky
0 views • 95 slides
Automating Grammar Comparison: Insights and Findings
This presentation delves into automating grammar comparison, showcasing the equivalence of CFGs, generating words in CFGs, and uncovering counter-examples. It explores applications such as online grammar tutoring systems and compatibility of programming language grammars. Motivation, contributions,
0 views • 32 slides
LL(1) Grammars and Computing First & Follow Sets
Exploring LL(1) grammars and the computation of First and Follow sets for non-terminals. This involves defining FIRST(.) as the set of tokens that appear as the first token in strings derived from a non-terminal and FOLLOW(A) as the terminals that can appear immediately to the right of A in the sent
0 views • 33 slides
Linear Antenna Arrays: Theory and Applications
Introduction to linear antenna arrays, including the concept of distributing radiating elements, combining array elements for specific beam characteristics, and the theory behind linear antenna arrays. Exploring the benefits of linear arrays in obtaining narrow beams, fan beams, and scanning capabil
0 views • 20 slides
Linear and Nonlinear Functions in Mathematics
Explore the concepts of linear and nonlinear functions in mathematics through identifying linear and nonlinear functions from graphs, understanding the characteristics of linear functions, and identifying linear functions from tables. Learn about the constant rate of change, slope, and how to determ
0 views • 49 slides
Linear Error Control Coding and Syndrome Detection in Binary Linear Codes
Delve into the world of linear error control coding, guided by Prof. Janos Levendovszky, as we explore the development of linear codes, message vectors, error groups, and the process of selecting group leaders with detailed examples. Discover how syndrome detection and decoding tables play a crucial
0 views • 27 slides
Insights on Linear Programming and Pivoting Rules in Optimization
Linear programming involves maximizing a linear objective function within a set of linear constraints to find the optimal point in a polytope. The simplex algorithm, introduced by Dantzig in 1947, navigates through vertices to reach the optimal solution. Deterministic and randomized pivoting rules,
0 views • 30 slides