Observational Studies in Epidemiology
Delve into the realm of observational studies in epidemiology, exploring concepts such as error, bias, and confounding. Discover the significance of various study designs, from case reports to prospective cohort studies, in elucidating associations and establishing causality in non-communicable dise
2 views • 58 slides
Overview of Ecological Studies in Epidemiology
Ecological studies in epidemiology involve studying groups of individuals at a population level to examine the correlation between exposure and disease occurrence. While cost-effective and useful for generating hypotheses, ecological studies have limitations, such as the inability to control for con
3 views • 21 slides
Research Hypothesis and Variables in Academic Studies
Research hypothesis plays a crucial role in academic research by providing a probable solution to a research problem. It establishes relationships between different variables, which are empirical properties that can vary. Variables can be independent, dependent, confounding, or intervening, influenc
0 views • 15 slides
Design and Analysis of Engineering Experiments in Practice
Explore the fundamentals of engineering experiments, including blocking and confounding systems for two-level factorials. Learn about replicated and unreplicated designs, the importance of blocking in a replicated design, ANOVA for blocked designs, and considerations for confounding in blocks. Dive
1 views • 15 slides
Fixed Effects Regression for Causal Inference in Social Research
Explore the concept of fixed effects regression for obtaining causal estimates with observational data, focusing on the association between social participation and depressive symptoms. Discover how this method controls for time-invariant factors and eliminates confounding variables, providing a clo
1 views • 49 slides
Integration Approaches of Propensity Scores in Epidemiologic Research
Propensity scores play a crucial role in epidemiologic research by helping address confounding variables. They can be integrated into analysis in various ways, such as through regression adjustment, stratification, matching, and inverse probability of treatment weights. Each integration approach has
0 views • 20 slides
Introduction to Econometrics and Machine Learning
Econometrics and machine learning intersect in decision-making scenarios where causal and counterfactual questions arise. This talk explores the relationship between the two fields, highlighting the identification of causal quantities and the flexible estimation techniques employed. Examples demonst
3 views • 53 slides
Bias and Validity in Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis involves considerations of chance, bias, confounding, causation, sample size, and power to ensure valid results. Understanding the impact of these factors is crucial for accurate interpretation of study outcomes and decision-making processes.
0 views • 45 slides
Experiments in Research: Observation vs. Experimentation
Observation and experiments are two crucial methods in research. An observational study involves observing and measuring variables without influencing responses, while an experiment deliberately applies treatments to measure responses. Confounding variables can affect the results, and factors like e
1 views • 13 slides
Random Assignment in Experiments
Explore the importance of random assignment in conducting experiments effectively. Learn how to assign treatments randomly using methods like slips of paper or technology, ensuring equivalent groups and minimizing confounding variables. Discover the significance of random assignment in maintaining r
2 views • 11 slides
Inverse Probability Weights in Epidemiological Analyses
In epidemiological analyses, inverse probability weights play a crucial role in addressing issues such as sampling, confounding, missingness, and censoring. By reshaping the data through up-weighting or down-weighting observations based on probabilities, biases can be mitigated effectively. Differen
1 views • 25 slides
Propensity Score Methods for Reducing Confounding in Studies
This content discusses the use of propensity score methods to address confounding in observational studies, comparing randomized control trials (RCTs) with observational studies, explaining the potential outcome framework, average treatment effects, and common assumptions made in these methods to re
0 views • 12 slides
Naive Bayes Classifier in Data Science
Naive Bayes classifier is a probabilistic framework used in data science for classification problems. It leverages Bayes' Theorem to model probabilistic relationships between attributes and class variables. The classifier is particularly useful in scenarios where the relationship between attributes
1 views • 28 slides
AP Statistics Homework Agenda and Experimental Design Example
In this AP Statistics homework agenda, students work on warm-up questions, checkups, and a controlled experiment design example involving paper airplanes and natural light impact on test scores. The agenda covers various topics such as confounding variables, random vs. blocking, and controlled exper
0 views • 15 slides
Causal Inference and Causal Graphs in Drug Efficacy Studies
This content delves into the concept of causal inference using causal graphs, specifically focusing on the relationship between a drug (D) and its effectiveness in curing a condition (C). It discusses the importance of distinguishing correlation from causation and explores scenarios where confoundin
0 views • 66 slides
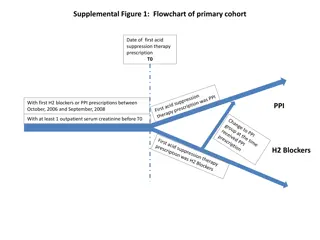
Illustrative Cohort Flowcharts and Analysis in Acid Suppression Therapy Studies
Detailed flowcharts of primary and secondary cohorts in studies related to acid suppression therapy, along with figures estimating the impact of various factors on outcomes like risk of death. The visuals depict the cohort selection process, exposure durations, confounding factors, and external adju
0 views • 6 slides
Fractional Factorials in Experimental Designs
Explore the concept of fractional factorials in experimental designs, including the basics, factors, terms estimation, confounding, and practical considerations for running treatment combinations. Learn how to generate incomplete blocks, use orthogonal contrasts, identify confounded terms, and alloc
0 views • 24 slides
Confounding in Regression Analysis
Confounding in regression analysis refers to the mixing of the effect of an exposure variable on an outcome, leading to potential bias in the results. Addressing confounding is crucial to accurately estimate the impact of variables on outcomes and uncover true relationships in data analysis.
0 views • 16 slides
Basics of Hypothesis Testing in Gene Expression Profiling
The lecture covers the essential aspects of hypothesis testing in gene expression profiling, emphasizing experimental design, confounding factors, normalization of samples, linear modeling, gene-level contrasts, t-tests, ANOVA, and significance assessment techniques. Practical insights are shared on
0 views • 9 slides
Guide to Comparator Selection in Comparative Effectiveness Research
Proper selection of comparators is crucial in comparative effectiveness research to ensure the validity and clinical relevance of study results. This process involves choosing concurrent, active comparators from the same population, addressing potential biases, defining time zero for all comparator
1 views • 15 slides
Experiments and Threats to Validity
Explore the world of experimental research, internal and external validity, threats to validity, and the importance of proper study design in ensuring the credibility of research results. Learn about confounding variables, threats to internal validity such as environmental factors and group comparis
0 views • 15 slides
Methods for Quantifying Efficacy-Effectiveness Gap in Randomized Controlled Trials
This research discusses the quantification of the efficacy-effectiveness gap in randomized controlled trials (RCTs), particularly focusing on examples in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). It explores the challenges of RCTs, ethical considerations, and the use of observational data for caus
0 views • 8 slides
Case-Control Studies in Genetic Research
Case-control studies are a common research design in genetics to investigate the association between genetic variants and diseases. This method involves comparing individuals with a specific phenotype (cases) to those without it (controls). Quality criteria such as study type, power analysis, bias/c
0 views • 23 slides
A QUESTION FROM WEDNESDAY…
A compilation of resources providing information on longitudinal studies worldwide, addressing model selection, correlation in causality analysis, and confounding variables for research clarity.
0 views • 49 slides
Considerations for Statistical Analysis in Observational Research
Careful statistical analysis is crucial in observational comparative effectiveness research to address confounding factors. This involves descriptive statistics, unadjusted analyses, traditional regression models, propensity scores, instrumental variables, and more.
0 views • 15 slides
Sensitivity Analysis in Observational Research
Observational studies rely on various assumptions, and sensitivity analysis helps assess the impact of these assumptions on study results. Explore key aspects such as unmeasured confounding, comparison groups, exposure definitions, and more.
0 views • 16 slides
Most Random Gene Expression Signatures are Significantly Associated with Breast Cancer Outcome
Study explores association of random gene expression signatures with breast cancer outcome, addressing methods, confounding variables, and advancements in research techniques. Results show correlation with various factors and compare published signatures with random ones.
0 views • 12 slides
Statistics Homework Agenda and Classroom Review
In this content, you will find information on a statistics homework agenda covering textbook exercises, AP classroom review topics, warm-up questions related to physical education, and free-response questions for practice. Concepts include observational studies, sampling methods, confounding variabl
0 views • 17 slides
Introduction to Statistics for Future Data Scientists
This content delves into the foundations of statistics for aspiring data scientists. It covers various topics such as statistical thinking, multivariate data analysis, real-world data scenarios, and the application of technology in statistical exploration. Examples include investigating the value of
0 views • 14 slides
Deriving Causal Inference from Nature
Uncover the nuances of causal relationships through experiments focusing on barnacles, substrate types, and potential outcomes. Explore the depth of mechanistic understanding and address confounding factors to refine your experimental design for robust causal inference.
1 views • 52 slides
Understanding Heterogeneity of Treatment Effects in Comparative Research
Explore the concept of heterogeneity of treatment effects in observational comparative effectiveness research, emphasizing the importance of accounting for individual variations in treatment outcomes. Learn how to identify treatment effect modifiers, pre-specify subgroups for evaluation, address con
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Bias in Epidemiological Studies
Explore the types of bias in epidemiological research such as selection bias, information bias, and confounding bias. Learn how these biases can impact study results and discover strategies to minimize bias for more accurate research outcomes.
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Different Types of Experimental Designs
Explore various experimental designs such as basic experiments, posttest-only design, pretest-posttest design, Solomon four-group design, and independent vs. repeated measures designs. Learn about the advantages, disadvantages, and potential confounding variables in independent groups design.
0 views • 19 slides
Efficient Overview of Study Designs for Research Success
Explore various study designs and their strengths and limitations for effective research planning. Understand the process of turning a research question into a proposal, minimizing bias and confounding, and planning study details for optimal outcomes.
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Pathway Survival Analysis: Controls & Logic
Explore the intricacies of pathway survival analysis through controls and logic. Delve into the importance of multiple testing corrections, filtering procedures, and confounding factors in research methodologies. Discover insights on proper normalization and the impact of low-impact mutations in pat
0 views • 11 slides
Blocking and Confounding in Engineering Experiments: Dealing with Nuisance Variables
Explore the concept of blocking to handle controllable nuisance variables in engineered experiments. Learn about replicated and unreplicated designs, with examples and techniques for effective analysis.
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Bias, Confounding Factors, Blocking, and Stratified Sampling in AP Statistics
Explore the concepts of bias, confounding factors, blocking, and stratified sampling in AP Statistics. Understand how bias can skew results, the impact of confounding factors on relationships, and methods to control for confounders. Learn how blocking ensures fair comparisons in experiments and how
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Regression Analysis: Confounding, Mediation, Moderation by Hanno Ulmer at Innsbruck Medical University
Discover the essence of regression analysis in this insightful discussion by Hanno Ulmer at Innsbruck Medical University. Learn about confounding, mediation, and moderation in multivariable statistical techniques for estimating outcomes in research.
0 views • 17 slides
Causal Inference Research Areas and Projects Overview
Explore a comprehensive overview of research areas in causal inference, including unmeasured confounding, network analysis, psychometrics, transfer learning, and more. Delve into notable papers and projects, such as sensitivity analysis in genomic experiments and causal inference with latent variabl
0 views • 18 slides
Strategies for Scalable Causal Discovery of Latent Variable Models
Discover new strategies for causal inference on integrated datasets, comparing their benefits on simulated data and applying a high-performing strategy to real biomedical datasets. Explore Fast Causal Inference (FCI) algorithms for learning causal structures in the presence of confounding factors.
0 views • 40 slides