Critique of Causal Metaphysics and Empiricism
In this content, the author critiques the metaphysics of causation from an empiricist perspective, exploring the limitations of empiricism in understanding the contingent truths of the world. It discusses causal antifundamentalism, various forms of skepticism, including Humean skepticism, and challe
4 views • 55 slides
Optimizing Homework Effect on Student Achievement Through Causal Machine Learning
Using TIMSS 2019 data from Ireland, a study conducted at Maynooth University explores the impact of homework frequency, duration, and question types on student achievement in math and science. By leveraging causal machine learning techniques, researchers aim to provide insights for educators on effe
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding Association and Causation in Epidemiological Studies
Exploring the concepts of association and causation in epidemiological studies, this content delves into the complexities of determining if exposure leads to disease risk. It discusses different types of associations, such as spurious, indirect, and direct causal associations, illustrating the chall
5 views • 43 slides
Understanding the Five Parts of a Classical Argument
The classical argument is composed of five main parts: Introduction, Narration, Confirmation, Refutation and Concession, and Summation. Each part plays a crucial role in presenting a well-structured and persuasive argument, with devices and strategies such as diction, syntax, and figurative language
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Disease Causation and Frequency Measures
The concept of disease causation delves into the factors that play a role in the development of diseases, emphasizing the importance of studying causation for prevention, control, and treatment. To infer causation, certain conditions must be met, and a causal relationship is characterized by associa
0 views • 47 slides
Understanding Fixed Effects Regression for Causal Inference in Social Research
Explore the concept of fixed effects regression for obtaining causal estimates with observational data, focusing on the association between social participation and depressive symptoms. Discover how this method controls for time-invariant factors and eliminates confounding variables, providing a clo
0 views • 49 slides
Introduction to Econometrics and Machine Learning
Econometrics and machine learning intersect in decision-making scenarios where causal and counterfactual questions arise. This talk explores the relationship between the two fields, highlighting the identification of causal quantities and the flexible estimation techniques employed. Examples demonst
1 views • 53 slides
Targeted Learning Framework for Causal Effect Estimation Using Real World Data
Hana Lee, Ph.D., presents a webinar on the Targeted Learning Framework for Causal Effect Estimation using Real World Data (TMLE). The project aims to help the FDA develop a structured approach to incorporating real-world data into regulatory decision-making. TMLE offers a systematic roadmap aligned
0 views • 27 slides
Understanding the Process and Types of Research Design
The process of research design involves interactive stages occurring simultaneously, leading to the creation of a structured study. There are three main types of research design: exploratory, descriptive, and experimental (or causal). Each type has its own objectives and methods. Exploratory researc
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding the Key Elements of an Argument
An argument is an intellectual process that involves a series of connected statements to establish the validity of a proposition. This process typically includes elements such as a hook, claim, support with reasons and evidence, and counterclaims with concessions and refutations. Each element plays
0 views • 13 slides
Preparing for Oral Argument in the Eleventh Circuit: Essential Tips
Understand the process of oral arguments in the Eleventh Circuit, including when to request oral argument, FRAP 34 guidelines, and how to handle the notice of oral argument. Get insights on making the most of oral argument opportunities and potentially shaping circuit law.
0 views • 32 slides
Understanding Indirect Proofs: Contradiction and Contraposition Examples
Indirect proofs offer a roundabout approach to proving statements, with argument by contradiction and argument by contraposition being the main techniques. Argument by contradiction involves supposing the statement is false and deriving a contradiction, while argument by contraposition relies on the
1 views • 18 slides
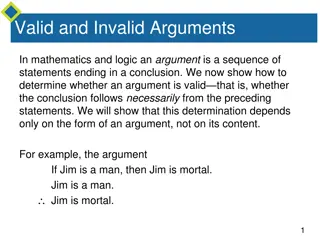
Understanding Valid and Invalid Arguments in Mathematics and Logic
In mathematics and logic, determining the validity of an argument depends on its form rather than its content. An argument is considered valid if the conclusion necessarily follows from the premises. This determination involves analyzing the abstract form of the argument, constructing truth tables t
0 views • 32 slides
Understanding Research Methods: Quantitative, Qualitative, and Mixed Approaches
This introduction provides an overview of qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods research, highlighting key differences and various types of research approaches. It delves into exploratory, descriptive, and causal research methodologies, offering insights into problem discovery, data collectio
0 views • 50 slides
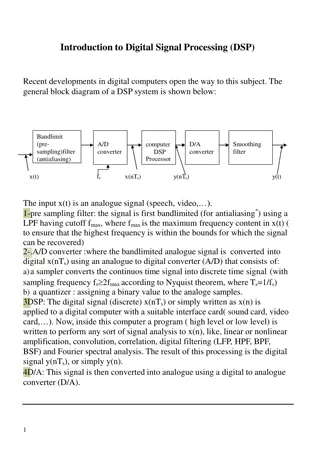
Overview of Digital Signal Processing (DSP) Systems and Implementations
Recent advancements in digital computers have paved the way for Digital Signal Processing (DSP). The DSP system involves bandlimiting, A/D conversion, DSP processing, D/A conversion, and smoothing filtering. This system enables the conversion of analog signals to digital, processing using digital co
1 views • 24 slides
Understanding Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) for Causal Inference
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) play a crucial role in documenting causal assumptions and guiding variable selection in epidemiological models. They inform us about causal relationships between variables and help answer complex questions related to causality. DAGs must meet specific requirements like
1 views • 63 slides
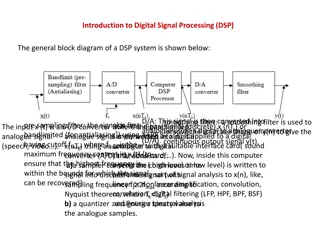
Understanding Digital Signal Processing (DSP) Systems: Linearity, Causality, and Stability
Digital Signal Processing (DSP) involves converting signals between digital and analog forms for processing. The general block diagram of a DSP system includes components like D/A converters, smoothing filters, analog-to-digital converters, and quantizers. DSP systems can be classified based on line
1 views • 12 slides
Understanding Causal Consistency in Distributed Systems
This content covers the concept of causal consistency in computing systems, exploring consistency models such as Causal Linearizability and Eventual Sequential. It explains the importance of logical clocks like Lamport and vector clocks, and how they ensure order in distributed systems. The concept
0 views • 35 slides
Scalable Causal Consistency for Wide-Area Storage with COPS
This paper delves into the importance of scalable causal consistency for wide-area storage with the COPS system. It explores desired properties such as availability, low latency, partition tolerance, and scalability within data centers. The document discusses the challenges of achieving consistency
0 views • 41 slides
Subject-Object Asymmetries in Zazaki Argument Ellipsis
Many languages allow argument ellipsis (AE), where an argument can be omitted for sloppy or quantificational interpretations. Subject-object asymmetries arise in languages due to subject-verb agreement. This study presents evidence from Zazaki, a Northwestern Iranian language, challenging the anti-a
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Causal Inference and Scientific Goals
Explore the significance of causal inference in science, the goals of scientific research, and the importance of developing an understanding of causal associations. Delve into topics like causal pattern recognition, mechanistic understanding, and potential outcomes frameworks to enhance your underst
0 views • 76 slides
Understanding the Scientific Method: Observations, Questions, and Hypotheses
Explore the scientific method concept of making observations, asking questions, and forming hypotheses. Learn the difference between causal and descriptive questions and practice applying them. Understand how to approach a situation like a non-starting washing machine through causal and descriptive
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding the Kalam Argument in the Cosmological Debate
The Kalam Argument, a form of the Cosmological Argument, asserts that everything with existence has a cause, including the universe. Developed by thinkers like al-Kindi, al-Ghazali, and William Lane Craig, it aims to prove that God was the initial cause of the universe. This argument suggests that t
0 views • 17 slides
Exploring Argument Structure and Diagramming in Critical Reasoning
Understanding the two types of argument structures - atomic and complex, with examples and diagrams. Learn how argument diagrams visually represent the structure of an argument, identify significant units like premises and conclusions, and distinguish main conclusions from sub-conclusions. Dive into
1 views • 10 slides
Estimation of Causal Effects using Propensity Score Weighting
Understanding causal effects through methods like propensity score weighting is crucial in institutional research. This approach helps in estimating the impact of various interventions, such as a writing program, by distinguishing causation from correlation. The use of propensity score matching aids
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Causal Inference and Causal Graphs in Drug Efficacy Studies
This content delves into the concept of causal inference using causal graphs, specifically focusing on the relationship between a drug (D) and its effectiveness in curing a condition (C). It discusses the importance of distinguishing correlation from causation and explores scenarios where confoundin
0 views • 66 slides
Understanding Anselm's Ontological Argument for the Existence of God
Anselm's Ontological Argument posits that the greatest possible being, referred to as God, must exist in reality because existing in reality is greater than existing only in thought. This argument centers on the concept of necessary vs. contingent beings and the idea that the greatest being cannot e
0 views • 32 slides
Enhancements in Causal Forecasting: SPM 11.0.1/11.1 Overview
Key enhancements in SPM 11.0.1/11.1 focus on improving forecast accuracy through variable history slices, causal forecasting for multiple streams, multi-threading capabilities, easy access to product rollout and causal value pages, and more. The Next Gen Causal Forecasting introduces additional feat
0 views • 6 slides
Mastering the Art of Argument in Essay Writing
Embrace the challenges of essay writing by understanding the essence of crafting a strong argument. Learn how to structure your thoughts logically, present evidence convincingly, and engage your readers effectively. Discover the importance of argument in various fields of life and the vital role it
0 views • 20 slides
Analyzing Hume's Critique of the Design Argument by Michael Lacewing
The design argument contends that the intricate order in the universe suggests a designer. Michael Lacewing delves into Hume's objections to this argument, highlighting how the analogy between human-made objects and the universe falls short in establishing a similar cause. Hume questions the logic o
0 views • 10 slides
Making a Convincing Causal Argument on Teen Smoking Effects
In collaboration with classmates, brainstorm about addressing various audiences regarding the detrimental health effects of teen smoking. Explore potential causes, gather supporting evidence, and consider audience engagement to craft a persuasive argument. Analyze existing causal arguments presented
0 views • 52 slides
Understanding Causal Consistency in Computing Systems
Explore the concept of Causal Consistency in Computing Systems, covering topics such as consistency hierarchy, Causal+ Consistency, relationships in causal consistency, practical examples, and its implementation within replication systems. Learn how it ensures partial ordering of operations and conv
0 views • 31 slides
Scalable Causal Consistency for Wide-Area Storage with COPS
This paper discusses the implementation of scalable causal consistency in wide-area storage systems using COPS. It delves into the key-value abstraction, wide-area storage capabilities, desired properties such as ALPS, scalability improvements, and the importance of consistency in operations. Variou
0 views • 42 slides
Understanding SDSU's Writing Placement Assessment (WPA)
SDSU's GWAR, an argument-based Writing Placement Assessment, requires students to write an essay analyzing a given argument. Scores range from 2-10, with different score bands dictating course requirements. Achieving a perfect score is subjective, emphasizing clear and concise argument analysis. Som
0 views • 35 slides
Understanding Experimental and Quasi-Experimental Designs
Explore the foundations of experimental and quasi-experimental designs, delving into causal relationships, counterfactual reasoning, and the importance of validating statistical and internal conclusions. Learn about causes, effects, and the complexity of determining causation in research. Discover R
0 views • 46 slides
Ontological Argument for God's Existence and Challenges
The ontological argument posits that a being than which nothing greater can be conceived must exist in reality, not just in the mind. Critics challenge this argument, citing issues with defining God and debating whether existence can be a characteristic. Gaunilo and Kant present criticisms focusing
0 views • 30 slides
Exploring Different Versions of the Ontological Argument
This content delves into various versions of the ontological argument, including Descartes' and Kant's perspectives. Descartes sought to prove God's existence through reason alone, emphasizing the innate conception of a supremely perfect being. The challenges posed by Kant and Malcolm to this argume
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Experimental Design and Validity Trade-offs in Research
Explore the concepts of experimental design, trade-offs in research validity, causal relationships, evidence, and controls in experiments. Delve into lab and field experiments, manipulation of variables, controls, and the importance of causal evidence in research. Consider the impact of extraneous f
0 views • 42 slides
Overview of DAGs in Causal Inference
Understanding Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) in causal inference is crucial for guiding research questions and analyzing causal relationships. This overview covers the basics of DAGs, their requirements, and applications in analyzing causal assumptions. Dive into the world of DAGs to enhance your re
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Latent Variable Modeling in Statistical Analysis
Latent Variable Modeling, including Factor Analysis and Path Analysis, plays a crucial role in statistical analysis to uncover hidden relationships and causal effects among observed variables. This method involves exploring covariances, partitioning variances, and estimating causal versus non-causal
0 views • 59 slides