Infinite Impulse Response Filters
This lecture discusses the design and implementation of Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) filters using biquad structures. It covers topics such as stability, bounded-input bounded-output equalization, filter design, and filter implementation. The lecture also includes demos on filter design and concl
11 views • 29 slides
Understanding Case Studies in Research Methodology
A case study is a detailed inquiry method in research that focuses on specific cases to gain insights, understand complex phenomena, and develop theories or frameworks. It involves studying activities and meanings within a bounded system to provide rich descriptions and learning opportunities withou
5 views • 26 slides
COORDINATION PATTERNS
Coordination patterns play a crucial role in designing concurrent code, ensuring smooth operation and efficient performance. They help in managing interactions between threads or processes, preventing malfunctions and performance drops. Examples like producer-consumer pattern and bounded buffers ill
1 views • 69 slides
Understanding Complexity in Polynomial Time: MAJORITY-3SAT and Related Problems
Dive into the world of MAJORITY-3SAT and its related problems, exploring the complexity of CNF formulas and the satisfiability of assignments. Discover the intricacies of solving canonical NP-complete problems and the significance of variables in determining computational complexity.
3 views • 35 slides
Understanding Real Analysis: Intervals, Bounds, and Problem-solving
Explore the concepts of intervals and bounds in real analysis, including open and closed intervals, semi-closed intervals, least upper bound, and greatest lower bound. Learn how to solve problems based on intervals and bounded sets through detailed explanations and examples.
0 views • 11 slides
Polygon Clipping Techniques and Algorithms
Polygon clipping involves modifying line-clipping procedures to achieve bounded areas after clipping. The Sutherland-Hodgman algorithm is commonly used, where polygon boundaries are processed against window edges to generate closed areas for appropriate area fill. This process involves testing for v
1 views • 17 slides
Understanding Real Analysis: Intervals, Bounds, and Problem Solving
Explore the world of real analysis through intervals, bounds, and problem-solving techniques. Learn about open intervals, closed intervals, semi-closed intervals, infinite intervals, least upper bound, greatest lower bound, and solve problems based on intervals and bounded sets. Enhance your underst
0 views • 11 slides
Exploring Time-Sensitive Networking Horizons and Possibilities for Low Latency Solutions
Delve into the world of time-sensitive networking (TSN) as it offers bounded low-latency solutions for various applications. Discover TSN components, tools, and protocols such as frame replication, path control, per-stream filtering, time synchronization, and more. Gain insights from Jnos Farkas's p
2 views • 23 slides
Generalization of Empirical Risk Minimization in Stochastic Convex Optimization by Vitaly Feldman
This study delves into the generalization of Empirical Risk Minimization (ERM) in stochastic convex optimization, focusing on minimizing true objective functions while considering generalization errors. It explores the application of ERM in machine learning and statistics, particularly in supervised
0 views • 11 slides
RESOLUTION METHOD IN AI
Resolution method in AI is an inference rule used in propositional and first-order predicate logic to prove sentence satisfiability. It employs a proof by refutation technique to achieve contradiction, ultimately concluding the original goal's truth. The process involves converting statements to cla
0 views • 12 slides
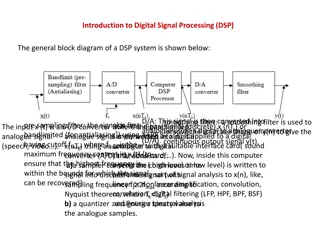
Understanding Digital Signal Processing (DSP) Systems: Linearity, Causality, and Stability
Digital Signal Processing (DSP) involves converting signals between digital and analog forms for processing. The general block diagram of a DSP system includes components like D/A converters, smoothing filters, analog-to-digital converters, and quantizers. DSP systems can be classified based on line
1 views • 12 slides
Scalable Task Pool with Adjustable Fairness
Explore CAF, a scalable task pool with adjustable fairness and contention, offering a solution to the inherent scalability problems of FIFO queues. The system allows for control over the level of relaxation, providing more fairness or less contention as needed. With a focus on bounded non-FIFO pools
5 views • 26 slides
Formal Verification and Automata Abstraction in Esterel
This content delves into the applications of formal verification and automata abstraction in Esterel, focusing on techniques such as verification by abstraction of automata, boolean verification using BDDs, bounded model checking in SAT/SMT, and more. The work of Gérard Berry at the Collège de Fra
0 views • 38 slides
Theoretical Studies on Recognizing Languages
Various models such as Deterministic Turing Machines, Probabilistic Models, and Quantum Classes are explored for recognizing languages, with discussions on regular, nonregular, and uncountable languages. Theoretical concepts like bounded-error recognition, computational complexities, and enumeration
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding GPolygon Class in Graphical Structures
The GPolygon class in graphical structures is utilized to represent graphical objects bounded by line segments, such as polygons. This class allows for the creation of polygons with vertices connected by edges, utilizing methods like addVertex and addEdge to construct the shape. The reference point
0 views • 26 slides
Satisfiability Modulo Abstraction for Separation Logic with Linked Lists
This study explores the application of satisfiability modulo abstraction in separation logic with linked lists. It presents a technique using abstract interpretation concepts to handle separation logic formulas beyond previous methods, specifically focusing on over-approximating heaps that satisfy t
0 views • 41 slides
Understanding Satisfiability Modulo Theories: Lecture Insights
Variables, terms, signatures, and formulas explained in first-order logic. Explore models, interpretations, and satisfiability modulo theories (SMT). Discover common theories like EUF, LIA, LRA, and decision procedures for EUF.
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Regular Polyhedra and Polygons
Regular polygons and polyhedra are fundamental shapes in geometry. A regular polygon has sides and angles that are congruent, such as equilateral triangles and squares. Polygons are simple closed figures made with line segments. Polyhedra are solids bounded by polygons as faces. Regular polyhedra ar
0 views • 18 slides
Constant-Time Algorithms for Sparsity Matroids
This paper discusses constant-time algorithms for sparsity matroids, focusing on (k, l)-sparse and (k, l)-full matroids in graphic representations. It explores properties, testing methods, and graph models like the bounded-degree model. The objective is to efficiently determine if a graph satisfies
0 views • 21 slides
Solving for Area Between Parabolas
Determine the bounded area between two parabolas by finding their intersection points and calculating the area enclosed. Follow a systematic approach independent of constants, consider translations to avoid negative areas, and evaluate the area accurately by tracking the curve shift. The mathematica
0 views • 32 slides
Accelerating Lemma Learning Using Joins in Satisfiability Modulo Theories
Explore the use of joins in accelerating lemma learning within the context of Satisfiability Modulo Theories (SMT). The study covers various SMT applications at Microsoft and delves into the development of the Z3 solver. Key topics include theories, arithmetic operations, array theory, uninterpreted
0 views • 25 slides
Introduction to PDDL Planning Domain Language
PDDL (Planning Domain Description Language) is a language based on STRIPS with various extensions, widely used in the International Planning Competition. It allows for specifying tasks via domain and problem files, representing predicates, operators, objects, initial states, and goal states. Blackbo
0 views • 11 slides
Cryptography in the Bounded Storage Model: Revisited - Eurocrypt 2023
Cryptography researchers revisit the Bounded Storage Model (BSM) to enhance security in transmitting messages while considering limited storage capacities. The BSM restricts adversaries to limited storage, enabling unconditional security. The model aims to address challenges in message transmission
0 views • 16 slides
Bounded Satisfiability Checking for Early Legal Compliance Verification
Early verification of legal compliance is crucial to avoid consequences such as violating regulations like GDPR. Through bounded satisfiability checking using Metric First-order Temporal Logic (MFOTL), this research focuses on system design verification for regulatory compliance. The study addresses
0 views • 29 slides
Understanding SAT Problems and Solution Techniques
Exploring SAT problems and solution techniques such as truth table enumeration, theorem proving, and specialized algorithms for definite clauses. Dive into forward chaining algorithms and their role in solving satisfiability problems efficiently.
0 views • 45 slides
Achieving Bounded Latency in Data Centers: A Comprehensive Study
Data centers face challenges in providing consistent low latencies due to in-network interference and varying workloads. This study explores solutions to guarantee strong latency performance, mitigate latency variance, and minimize performance degradation for latency-sensitive applications. By analy
0 views • 18 slides
Bounded Degree Polyhedronization of Point Sets in R3
The problem of finding a polyhedron in R3 with no four points coplanar, having the set of points as vertices, being simple in structure, with each vertex connected to O(1) edges, and featuring both a tetrahedralization and chain dual. This task has historical importance with Euler's formula setting
0 views • 24 slides
Lower Bounds on Sampling Good Codes in Bounded-Depth Circuits
Bounded-depth circuits are proven unable to sample or approximate good codes effectively. This work delves into lower bounds, showcasing that bounded families of circuits face limitations in computing specific functions or sampling distributions. The example of Parity in AC0 circuits illustrates the
0 views • 21 slides
Regret-Bounded Vehicle Routing Approximation Algorithms
Regret-bounded vehicle routing problems aim to minimize client delays by considering client-centric views and bounded client regret measures. This involves measuring waiting times relative to shortest-path distances from the starting depot. Additive and multiplicative regret measures are used to add
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Definite Integrals in Mathematics
Explore the concept of definite integrals in mathematics, covering properties, solving methods, and applications in finding areas bounded by curves. Prior knowledge of functions, limits, derivatives, and indefinite integrals is essential to grasp this topic effectively. Dive into the unique value of
0 views • 32 slides
Cryptography in Bounded Storage Model: Ensuring Secure Communication
Cryptography in the Bounded Storage Model provides insights into securing communication with secrecy and authenticity. The model limits adversaries' memory without runtime restrictions, ensuring unconditional security for various primitives. Explore how this model safeguards messages from eavesdropp
0 views • 42 slides
Approximation Algorithms for Regret-Bounded Vehicle Routing
This research explores regret-bounded vehicle routing problems (VRPs) where the focus is on minimizing client delays based on their distances from the starting depot. The study introduces a client-centric view to measure regret and devises algorithms for both additive and multiplicative regret-based
0 views • 23 slides
Graph Property Testing and Algorithms Overview
Explore testable bounded degree graph properties, sparse graphs, d-bounded degree graphs, hyperfinite graphs, arboricity, maximum matching algorithms, and sublinear time approximation algorithms in graph data streams. Learn about various graph models and properties with examples, showcasing the impo
0 views • 53 slides
Understanding Bounded Arithmetic and Definable Functions in Complexity Theory
Bounded arithmetic, as explored in complexity theory, focuses on theories like PA but with restrictions on formulas. The comprehension axiom determines sets that can exist, and TC is a first-order arithmetic theory defining functions within a specific complexity class. The witnessing theorem in TC e
0 views • 16 slides
Object-Oriented Design by Contract with Declarative Bounded Testing
Comprehensive overview of Object-Oriented Design by Contract (DbC) with Declarative Bounded Testing, exploring its background, principles, implementation in programming languages, and application through bounded exhaustive testing. Learn how DbC enhances software reliability and development practice
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding Z3: An Efficient SMT Solver
Z3 is an efficient Satisfiability Modulo Theories (SMT) solver that integrates various decision procedures for program analysis, verification, and test case generation. It supports linear arithmetic, bit-vectors, uninterpreted functions, quantifiers, and offers an extensive API for different program
0 views • 16 slides
SMT-LIB: The Satisfiability Modulo Theories Library Overview
The Satisfiability Modulo Theories Library (SMT-LIB) is a comprehensive tool for formal reasoning in various supported theories such as arrays, bit vectors, and integer and real arithmetic. It provides a wide range of supported sublogics for precise specifications and verifications. Moonzoo Kim, fro
0 views • 14 slides
Theorems on Convergent Sequences with Proofs and Examples
The lecture covers theorems on convergent sequences, including the convergence of monotonic increasing and decreasing sequences when bounded. Detailed proofs for these theorems are provided, along with examples to determine if a sequence is bounded. The presentation includes step-by-step explanation
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding NP-Completeness: Cook-Levin Theorem and Clique Problem
Today's lecture delved into NP-completeness, focusing on the Cook-Levin Theorem and the Clique Problem. NP-completeness is defined as a language that is in NP and all other languages in NP are polynomial-time reducible to it. The Cook-Levin Theorem states that SAT, a Boolean satisfiability problem,
0 views • 10 slides
Quantum Space-Bounded Complexity in Logarithmic Space: A Comprehensive Overview
Quantum space-bounded complexity explores the memory requirements for solving problems in log space. Examples include matrix multiplication, undirected graph connectivity, and problems like inverting matrices and determining connectivity. The significance of deterministic log space (NL) and nondeter
0 views • 49 slides