Signaling Pathway Through TLR4: A Molecular Signal Transduction Process
Signaling through Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4) involves a series of steps starting from receptor activation to transcription factor activation, leading to the synthesis of desired proteins. The pathway can occur through MyD88-dependent or TRIF-dependent pathways, resulting in different downstream effects. Activation of cell membrane-bound TLR4 or endosomal TLR4 leads to distinct signaling cascades that ultimately result in the transcription of innate response genes or Type 1 Interferons. Various adapter proteins and signaling molecules play crucial roles in mediating these processes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
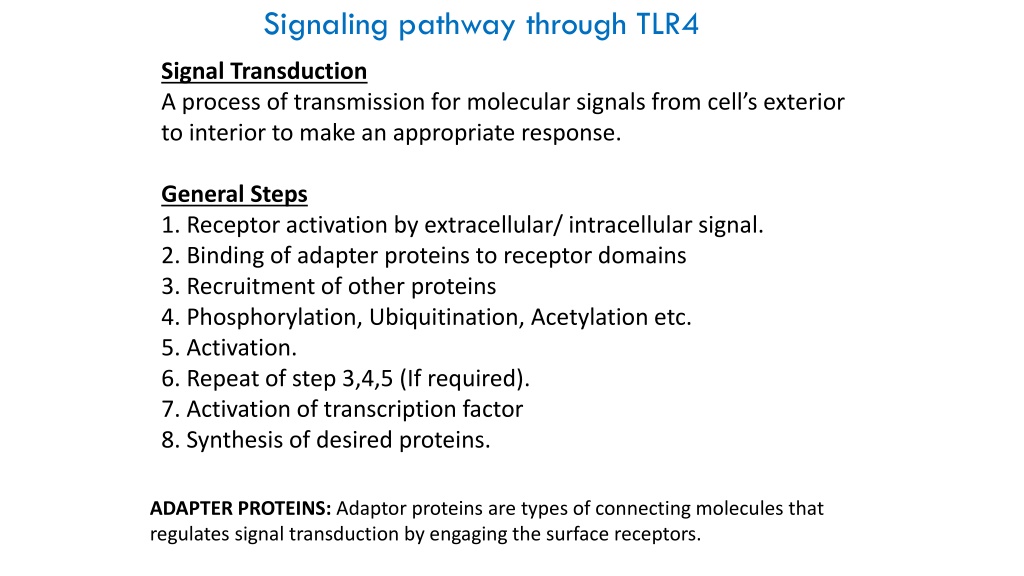
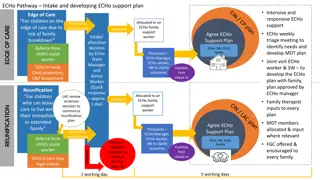
Signaling pathway through TLR4 Signal Transduction A process of transmission for molecular signals from cell s exterior to interior to make an appropriate response. General Steps 1. Receptor activation by extracellular/ intracellular signal. 2. Binding of adapter proteins to receptor domains 3. Recruitment of other proteins 4. Phosphorylation, Ubiquitination, Acetylation etc. 5. Activation. 6. Repeat of step 3,4,5 (If required). 7. Activation of transcription factor 8. Synthesis of desired proteins. ADAPTER PROTEINS: Adaptor proteins are types of connecting molecules that regulates signal transduction by engaging the surface receptors.
Signaling pathway through TLR4 Plasma membrane MyD88 DEPENDENT PATHWAY Activation of cell membrane bound TLR4 occurs through ligands. TRIF DEPENDENT SIGNALING Activation of endosomal TLR4 through ligands. Nuclear membrane MyD88 Myeloid Differentiation TRIF- TIR domain containing adapter inducing interferon-
Signaling pathway through TLR4 Signaling through cell membrane bound TLR4 LPS activation causes binding of MyD88/TRAP. IRAK ubiquitinates and activates TRAF6. TRAF6 ubiquitinates TAB and NEMO. TAK1 activation occurs. Further signaling can be directed in two ways) 1a. TAK1 phosphorylates IKK complex. 1b. IKK complex ubiquitinates and phosphorylates Ikb of NFkB causing entry of NFkB into nucleus that causes transcription of innate response genes. The detached Ikb is degraded.
Signaling pathway through TLR4 2a. TAK1 also activates MAP kinase pathway alternatively. 2b. AP-1 dimer gets activated which causes transcription of IFN and genes (Type 1 Interferons).
Signaling pathway through TLR4 Signaling through endosomal TLR4 Viral protein activation causes binding of TRIF/TRAM. Further signaling can be directed in two ways. 1a. RIP1 ubiqutinates and activates TRAF6. 1b. Steps for signaling through membrane bound TLR4 should be followed. 2a. TRIFF/TRAM binding causes activation of TRAF3/TBK-1/IKK complex 2b. The complex phosphorylates IRF3/7 which enter nucleus to transcribe cytokine genes