Understanding VLANs in Networking
Explore the basics of VLANs in networking, including how they work, their benefits, and common configuration commands. Learn about management VLANs, trunk lines, VLAN tagging, and more through a series of informative images and explanations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
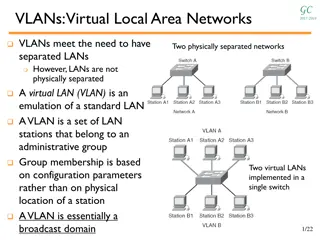
VLANS group hosts _____________________ logically or physically? Logically regardless of physical location Devices in one VLAN do not hear the broadcasts from devices in another VLAN
A Management VLAN is any VLAN that is configured to access management features of the switch. After initial boot of an unconfigured switch, all ports are members of the __________________ Management VLAN
VLAN 1 is always used as the management VLAN and you cannot change management to a different number (T or F) False you can change it to a different number, and in fact you should
Why do you set up trunk lines? The are used between two switches that utilize multiple VLANs to carry the traffic of ALL VLANs
If you have traffic going between two computers that are both on the same VLAN and both attached to the same switch, will the switch add a VLAN tag to the frame? No it is not needed
You have a switch that doesnt have VLANs set up. You enter the following command on interface fa0/18 of the switch Switchport access vlan 20 What effect does this have on the switch in regard to VLANs? VLAN 20 will be created automatically
What command is used to remove a VLAN from a switch? No vlan 20
If a port on a switch has been assigned to the VLAN 30 and then the command is negated by entering no switchport access vlan 30, what will happen to the port? It will return to VLAN1
Which command is used to display the encapsulation type and the access mode of a port Show interface fa0/1 switchport
If a port belongs to VLAN 2 and the network administrator wants to reassign it to the new VLAN 3, what must be done? Enter the command switchport access vlan 3 You do NOT need to remove it from the old vlan first, just reassign it
If you need to clear all VLAN information from the swtich to incorporate a new network design, how should you accomplish this?? Delete the startup configuration file and the vlan.dat file in the flash memory of the switch and reboot the switch
If you have a trunk port and you issue the command switchport trunk allowed vlan 30 on the trunk port interface, what traffic will go to the other switch ?? Only VLAN 30 TRAFFIC
If you have multiple VLANs and do not specify specific vlans allowed on the trunk, which VLANs will be allowed across the trunk?? All VLANs will be allowed
If you have a Cisco switch and a non-Cisco switch, what command should you enter to prevent the transfer of DTP frames? S1(config-if)#switchport nonegotiate
When should you disable DTP while managing a local area network? When connecting a Cisco switch to a non-Cisco switch On links that should not be trunking
What happens to a port that is associated with VLAN 10 when the administrator delete VLAN 10 from the switch? The port becomes inactive
What is a good practice to help prevent VLAN hopping attacks? Change the native VLAN number to one that is distinct from all user VLANs and is not VLAN1 Daisable DTP autonegitiation on end-user ports