Secure Network Infrastructure Best Practices
Implementing secure network infrastructure practices is crucial to safeguard sensitive data and ensure operational efficiency. This includes utilizing VPNs, VLANs, dedicated circuits, and other technologies to protect against cyber threats. Segregating wireless and wired networks, implementing VoIP
0 views • 9 slides
Basic Switch Configuration Guide for Setting Up VLANs
Configuring switches from basic settings to creating 3 VLANs using subnet 192.168.100.0/24. Follow the commands provided for setting up VLANs, trunk links, and default gateways on switches for efficient network communication.
0 views • 10 slides
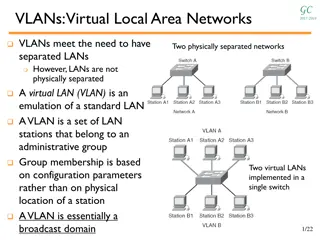
Understanding VLANs in Computer Networking
VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) allow for the logical separation of LANs without physical segregation. They group network stations based on administrative criteria rather than physical location. VLANs enhance security, facilitate group collaboration, and optimize network traffic by segregating d
0 views • 22 slides
Network Switch Configuration Guide
Learn how to configure a network switch with tasks such as setting default gateways, assigning IP addresses, designating ports as trunk or access, adding or removing VLANs from trunk ports, and using various show commands for network management.
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding VLANs and Virtual LANs in Networking
This detailed guide explores VLANs (Virtual LANs) in network configuration, covering concepts like switch hosts, aggregation, subnets, routers, and port configurations. Learn about setting up VLANs, managing broadcast domains, ARP requests, and more to enhance network security and performance.
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding VLANs in Networking
Explore the basics of VLANs in networking, including how they work, their benefits, and common configuration commands. Learn about management VLANs, trunk lines, VLAN tagging, and more through a series of informative images and explanations.
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Layer 3 Switches: Functionality and Configuration
Layer 3 switches combine the features of Ethernet switches and routers, allowing them to process both MAC and IP headers. By configuring VLANs, trunking, and management interfaces, these switches can handle data forwarding across different subnets efficiently. This guide explains the basic principle
0 views • 19 slides