Emergency Cardiac Complication Management Algorithms
This comprehensive guide presents a series of algorithms for managing cardiac complications efficiently and systematically. It covers a range of scenarios such as unexpected hemodynamic collapse, no-reflow situations, and dissection cases. These algorithms provide step-by-step instructions for assessing the patient's condition, determining the appropriate interventions, and addressing potential reversible causes. Through a structured approach, healthcare providers can navigate complex cardiac complications effectively to enhance patient outcomes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
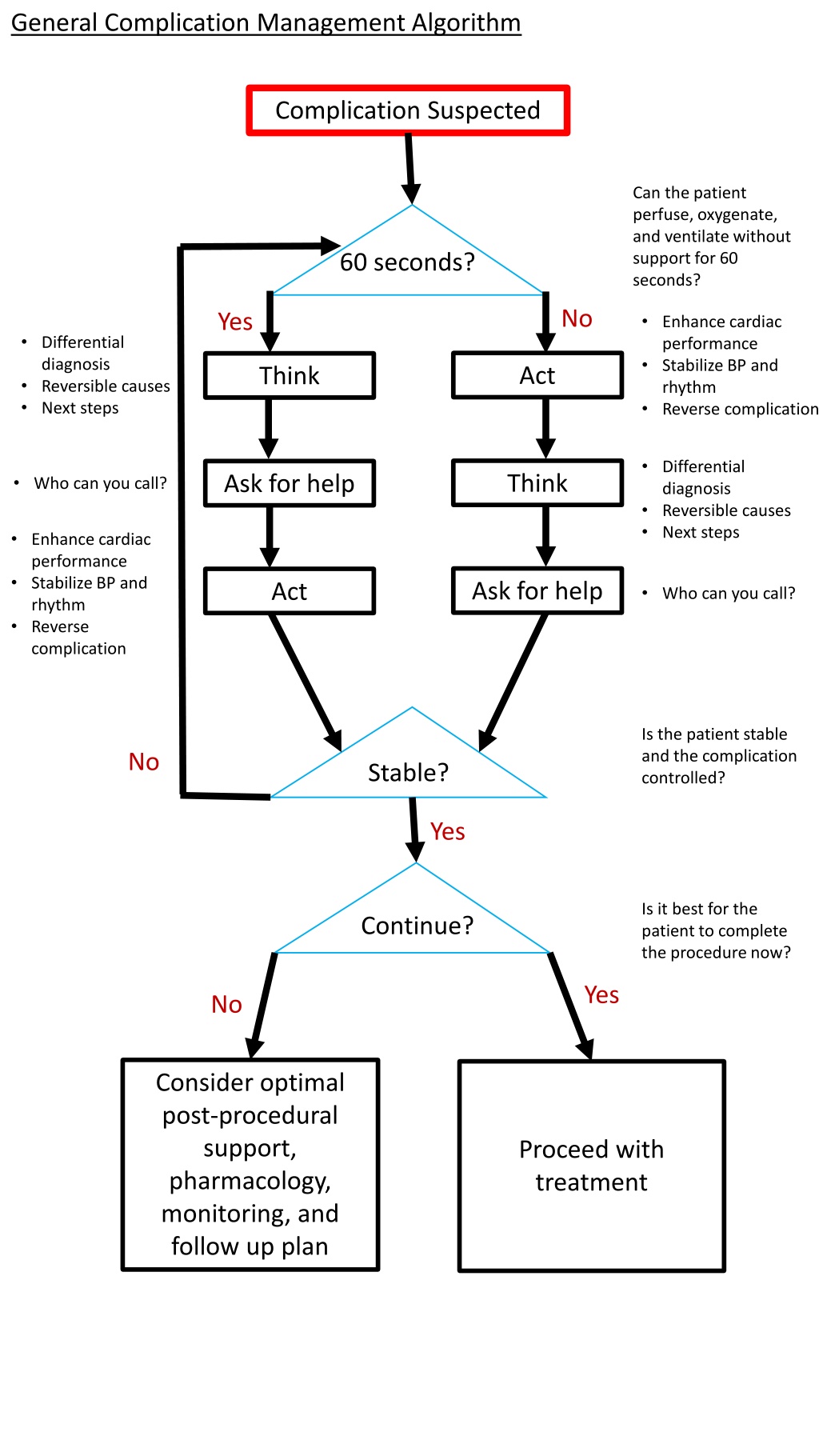
General Complication Management Algorithm Complication Suspected Can the patient perfuse, oxygenate, and ventilate without support for 60 seconds? 60 seconds? No Yes Enhance cardiac performance Stabilize BP and rhythm Reverse complication Differential diagnosis Reversible causes Next steps Act Think Differential diagnosis Reversible causes Next steps Think Ask for help Who can you call? Enhance cardiac performance Stabilize BP and rhythm Reverse complication Ask for help Act Who can you call? Is the patient stable and the complication controlled? No Stable? Yes Is it best for the patient to complete the procedure now? Continue? Yes No Consider optimal post-procedural support, pharmacology, monitoring, and follow up plan Proceed with treatment
Unexpected Hemodynamic Collapse Algorithm Acute Drop in BP Consider spurious causes including guide dampening, iatrogenic AI, and equipment malfunction Is it real? No Yes Proceed with procedure Is there a pulse? Yes No Assess for etiology CPR/ECLS Ischemia/Infarct Guide Dampening Thrombosis Dissection Air Embolism No/Slow Reflow Cardiac Performance Acute AI Acute MR Low output Rhythm Trachyarrhythmias Bradyarrhythmia AV dyssynchrony Vasoplegia Sedation Shock Anaphylaxis Bleeding Perforation Tamponade Access bleeding Quickly reversible? Yes No Consider appropriate hemodynamic support Address underlying etiology
No Reflow Algorithm No Reflow Is there a mechanical obstruction to flow in the epicardial vessel? Epicardial obstruction? No Yes Pharmacologic Treatment Dissection Proximal thrombus or air See Figure 2 Aspiration thrombectomy Balloon angioplasty Agent Optimal delivery location Initial Dose Adenosine Distal vessel 100 ug Verapamil Distal vessel 200 ug Nicardipine Distal vessel 200 ug Epinephrine Distal vessel, Guide 50-200 ug Nitroprusside Distal vessel 100 ug Abciximab Distal vessel, IV 0.25 mg/kg Eptifibitide Distal vessel, IV 180ug/kg Resolution? No Yes Complete case Additional pharmacologic treatment Consider improving perfusion pressure with diuretics, IABP, circulatory support
Dissection Algorithm Dissection Is there a guidewire in the true lumen across the dissection? Wire Across? No Yes Avoid anterograde injections Attempt Is there TIMI 3 flow? Vessel Open? anterograde wiring with spring-coil wire No IVUS useful to confirm luminal position Dilate with Balloon Yes Successful? Yes No Consider: Stent implantation Consider: IVUS (not OCT) to characterize Cutting balloon to release large intramural hematoma Stenting distal edge first, for long dissections Anterograde dissection-reentry (ADR) Retrograde wiring Subintimal tracking and re- entry (STAR) Successful? No Yes Complete PCI Consider: CABG Conservative management Mechanical circulatory and/or pharmacologic support
Perforation Algorithm Distal Vessel/Collateral Perforation Is the patient hemodynamically stable without evidence of tamponade? Stable? No Yes Obtain serial echocardiograms to assess for effusion/tamponade Fluids Pericardiocentesis Transfusion or auto-transfusion Notify CT surgery Wire Across? No Try to wire as close as possible to perforation Consider severity of perforation, size and distribution of perforated vessel, and potential for tamponade. Minor perforations may not require endovascular treatment Yes Successful? No Yes Balloon Injection of thrombin, fat, or microspheres Occlusion of branch with covered stent Coils Tamponade just proximal to perforation Use of contrast echocardiography may identify residual bleeding if contrast is seen in the pericardial space. Is there evidence of continued bleeding despite 30 minutes (or longest tolerated) balloon tamponade? Still bleeding? Yes No Stop procedure Injection of thrombin, fat, or microspheres Suction via microcatheter Coils Anterograde and retrograde occlusion may be required Protamine (after gear removal) Consider protamine (only after all gear is removed from coronaries) Support as needed
Perforation Algorithm Proximal Vessel Perforation Is the patient hemodynamically stable without evidence of tamponade? Stable? No Yes Obtain serial echocardiograms to assess for effusion/tamponade Fluids Pericardiocentesis Transfusion or auto-transfusion Notify CT surgery Wire Across? No Try to wire perforated vessel Consider severity of perforation, size and distribution of perforated vessel, and potential for tamponade. Minor perforations may not require endovascular treatment Yes Successful? No Yes Balloon tamponade proximal to perforation CABG Coils Enter subintimal space to seal with dissection flap Balloon Tamponade Ellis Type III, active extravasation through a large breach, with or without tamponade Severe Perforation? Yes Is there evidence of continued bleeding despite 30 minutes (or longest tolerated) balloon tamponade? No Covered Stent Protamine (after gear removal) Still bleeding? Use of contrast echocardiography may identify residual bleeding if contrast is seen in the pericardial space. Yes No DES or BMS Covered Stent Coils Stop procedure Consider protamine (after gear removal) Support as needed Thrombin, fat, microspheres