Exploring Pyramid Geometry for Surface Area Calculations
Delve into the concept of surface area calculations for pyramids, ranging from identifying fake pyramids to determining the surface area of iconic structures like the Great Pyramid. Learn about the essential information needed, such as base length and slant height, to derive accurate measurements. Dive into practical exercises to find the surface area of various pyramids by understanding edge lengths and other pertinent details.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Pyramid or not? Why?
What is the film? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YVOPYFU168k 0:57 - end
Think about the fake pyramid What do you think it was made from? How much material do you think was needed to make it? Discuss: What information would you need to know?
What information would you need to know?
186.6 m 229.8 m We want to know the amount of material required. In other words, we want the area of all the outside faces
186.6 m 229.8 m We are trying to find the surface area of the pyramid
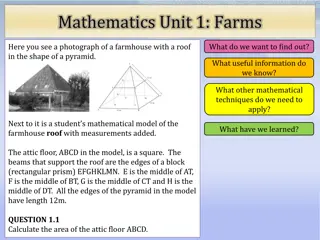
186.6 m 229.8 m This is the Great Pyramid. We know from last lesson that the base length is 229.8 m and its slant height is 186.6 m. How does this help?
Area = 186.6 m It is easier to find the surface area from a net
Area = 186.6 m It is easier to find the surface area from a net
186.6 m Find the surface area of the Great Pyramid
186.6 m Find the surface area of the Great Pyramid SA = 138569m2
Find the surface area of the following pyramids: SA = (25 x 25) + 432 x 25 2 SA = 625 + 4(400) SA = 2225 feet2
Find the surface area of the following pyramids: SA = (40 x 40) + 494 x 40 2 SA = 1600 + 4(1880) SA = 9120 cm2
What is different this time? This time we are given the edge length of the pyramid
What is different this time? Which length do we need to find the surface area?
What is different this time? Slant height How can we use the edge length to help us find the slant height?
What is different this time? Slant height 85cm 12cm What will the dimensions be? How can we find the slant height?
What do the small lines on the base of the pyramid represent?
What is different this time? This time we are given the perpendicular height of pyramid
What is different this time? Which length do we need to find the surface area?
What is different this time? Which length do we need to find the surface area?
What is different this time? Slant height How can we use the perpendicular height to help us find the slant height?
What is different this time? 10cm Slant height 3cm What will the dimensions be? How can we find the slant height?
Find the surface area of the following pyramids: HINT: Find the slant height first 91 x 6 2 SA = (6 x 6) + 4 SA = 36 + 4(3 91) SA = 36 + 12 91 m2 SA = 150.5 m2
Find the surface area of the following pyramids: HINT: Find the slant height first 325 x 20 2 SA = (20 x 20) + 4 SA = 400 + 721.110255 SA = 1121.1 cm2
Challenge: The surface area of this pyramid is 480 cm2 14cm Find the base length