Understanding Ecosystems: Definition, Structure, and Function
Ecosystems consist of living and non-living parts forming stable systems. They involve energy flow, nutrient cycling, and interactions between organisms and their environment. Ecosystems vary in abiotic and biotic conditions, with producers, consumers, and decomposers playing key roles. Changes in these conditions can disrupt the balance in ecosystems, impacting their sustainability and evolution.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ECOSYSTEMS V ukov materi l EK 01 - 16 Tv rce: Ing. Marie Jir kov Tv rce anglick verze: Mgr. Milan Smejkal Projekt: S anglick m jazykem do dal ch p edm t Registra n slo: CZ.1.07/1.1.36/03.0005 Tento projekt je spolufinancov n ESF a SR R
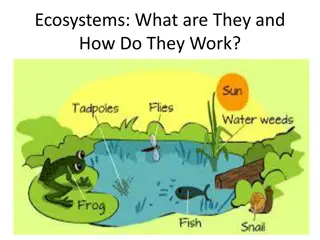
ECOSYSTEM Definition I. Ecosystem is a summary of living and non-living parts to form a stable system that occurs at certain times and in certain space and include the flow of energy via food - chains and food-webs and the cycling of nutrients biogoechemically.
EKOSYSTEM Definition II. Ecosystem is created by the community of organisms together with the abiotic environment.
EKOSYSTEMS ARE DIVIDED water a pond, a rever, the sea etc. land a forest, a meadow, fields etc..
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF ECOSYSTEMS There are different abiotic conditions in various ecosystems. Biotic conditions are created by the organisms and the relationships between them. There is a different function of organisms in an ecosystem : producers, consumers, decomposers
ECOSYSTEM AND LIFE In every ecosystem there is a conversion and transfer of energy and other substances. Ecosystems are restored. Ecosystems evolve.
ECOSYSTEM Each ecosystem reaches a balance under certain conditions. There is a disruption of balance when changing abiotic or biotic components. The balance of the ecosystem is often ruined by human activity.
ECOSYSTEM IS A discrete functional unit of nature.
ECOSYSTEMS ARE DIVIDED INTO : natural constant composition of plant and animal communities at certain abiotic conditions artificial man-made, additional energy
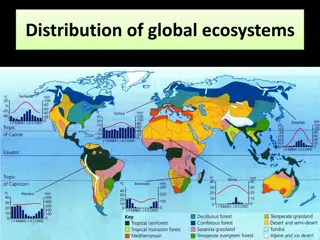
THE MAIN ECOSYSTEMS tundra taiga steppe deciduous forests scrubby forests deserts and semi-deserts tropical deciduous forests and savannas tropical rain forests
CHANGES IN ECOSYSTEMS Large areas of the original natural ecosystems have been altered by human activities.
WORKSHEETS - REVISION What is ecosystem? Give an example of human activities that negatively affects some ecosystems. What are the biotic conditions made up of? Give examples of natural and artificial ecosystems. How the man puts his supplemental energy into the artificial ecosystem of wheat and why.?
SOURCE BRANI , Martin. Z klady ekologie a ochrany ivotn ho prost ed . 2. vyd. Praha: Informatorium, 1999. ISBN 80-86073-52-1. PAP EK, Miroslav a kol. Zoologie. Praha: pedagogick nakladatelstv , 2000, ISBN 80-7183- 203-0. KVASNI KOV , Danu e. Z klady ekologie. Praha: Scientia,spol.s r.o., 1994, ISBN 80-85827- 84-0