Examples of Food Chains and Webs in Different Ecosystems
In the provided content, food chains and webs are illustrated in various ecosystems including desert, lake, and jungle. Each ecosystem depicts the interdependent relationships between producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers, showcasing the flow of energy throughout the food chain. Arrows indicate the direction of energy transfer, with animals like scorpions, cacti, lions, water lilies, eagles, and more playing different roles in the ecosystems.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
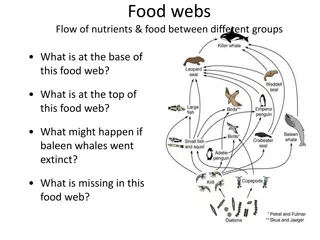
Draw a food chain from the following desert ecosystem that includes a producer, a primary consumer, a secondary consumer and a tertiary consumer Scorpion, cactus, cricket, field mouse, shrub, mountain lion, Snake, Owl, Goat, Lizard, Coyote
Make sure the arrows are going in the right direction!!!!!
Cactus Cricket Lizard Snake Cactus Mouse Snake Owl Shrub Cricket Scorpion Lizard Shrub Goat Coyote Mountain Lion Cactus Cricket Lizard Owl
What do the arrows mean? They show the direction that the energy is passing through the system. It shows which organism is getting its energy by eating.
Draw a food chain from the following lake ecosystem that includes a producer, a primary consumer, a secondary consumer and a tertiary consumer. Water Bird, Frog, Water Lily, Reed (plant), Dragon Fly, Small Fish, Turtle, Algae, Deer, Bear, Eagle, Beetle
Water Bird, Frog, Water Lily, Reed (plant), Dragon Fly, Small Fish, Turtle, Algae, Deer, Bear, Eagle, Beetle Algae Fish Turtle Water Bird Water Lily Beetle Fish Bear Reed Beetle Frog Eagle
Water Bird, Frog, Water Lily, Reed (plant), Dragon Fly, Small Fish, Turtle, Algae, Deer, Bear, Eagle Label the producers Water Lily, Reed, Algae Label the primary consumers: Small Fish, Beetle, Deer Label the higher level consumers: Eagle, Bear, Turtle, Frog
Draw a food web of the following jungle organisms. Lion, wildebeest, impala, shrub, rodent, cheetah, grasses, insect, bird , snake
Lion, wildebeest, impala, shrub, rodent, cheetah, grasses, insect, bird, snake Grass impala Lion Grasses insect snake Lion Shrub wildebeest cheetah
Draw a food web with each of the following: Lion, wildebeest, impala, shrub, rodent, cheetah, grasses, insect
Draw a food web of the following: Water Bird, Frog, Water Lily, Reed (plant), Dragon Fly, Small Fish, Turtle, Algae, Deer, Bear, Eagle, Beetle, small plant
What is a niche? What is an earthworm s niche? It is a decomposer, and is food for some birds and other organisms. What is the niche of a tree? It is a producer, it provides oxygen and provides shade.
When an ecosystem has reached its carrying capacity, it is said to be in equilibrium. What does that mean? The system is in balance. It has the necessary number of each organism living there to keep it going.
Which of the following would be a limiting factor to a population of rabbits A- Decrease in rainfall C- Increase in Predators E- Drought G- Increased Rain I- Decrease in Predators K- Decrease in Habitat M- Climate (weather) Change B- Increase in Birth Rate D- Increase in fish population F- A new disease in the rabbit population H- Less Shade J- More Plants L- Decrease in birth rate Answer: A, C, E, F, K,M
Why do grazing animals stay in herds? For protection against predators
Where is most energy found in any food web, food chain or energy pyramid. What types of organisms produce the most energy for an ecosystem? Producers (plants)
Which organisms are primary consumers? Deer, Beetle, Small Fish
Which are secondary and tertiary consumers? Frog, Large Fish, Turtle, Dragon Fly, Eagle
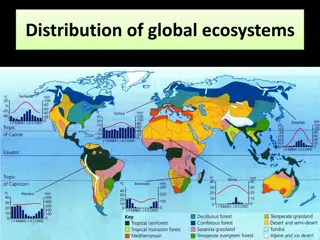
The study of the environment and how living things interact is called Ecology An example of an abiotic factor would be Soil Air Light Temperature water
An ecosystem is made up of Living things and the physical environment In an energy pyramid, the bottom level represents Producers/ Plants In an energy pyramid, the top level represents Higher level consumers In an energy pyramid, the greatest amount of energy is found in Producers
A__________ will eat plants herbivore A__________ will eat meat carnivore A__________will eat both plants and animals omnivore Which direction of arrows in a food chain would be correct? plant insect bird plant insect bird bird insect plant
The arrows in a food chain represent transfer of energy The living parts of the environment only make up a(n) community A group of the same species in an area make up a(n) population Name some limiting factors to plants and animals space, shelter, food, water, light, disease, predators
When a population cannot grow any larger it has reached its carrying capacity Grazing in herds benefits populations of deer because it protects them from predators The purpose or place an organism has in its environment is called its niche The specific place that meets the needs of a living organism is its habitat What are the 5 basic needs of all living organisms food, water, shelter, space, arrangement Which is most complex: Organism, population, community, ecosystem Ecosystem
The purple loosestrife is found in some wetland ecosystems. This invasive species does what to biodiversity? Decreases it An example of a nonrenewable resource is coal, petroleum, gas, oil, anything mined from the Earth (gold, silver ) An example of a renewable resource is air, sunlight, trees, food, water Using the same resources again and again is called recycling An example of an alternative energy source is wind solar Hydroelectric (water) Geothermal (Earth s heat)
A substance that makes air, water or land unfit for life is called a(n) pollutant The many ways that humans can use natural resources without using them up are called sustainable practices A population of an organism is in equilibrium when it has reached its carrying capacity If organisms are considered so similar that if they can produce offspring that can also produce offspring, they are considered a(n) species Primary consumers eat plants An ecosystem differs from a community because a community includes only the living things
What are examples of items that could be conserved: water, air, renewable and nonrenewable resources Things that would increase biodiversity would be higher birth rate more water more food new species not placed there by humans