BEER cave design and shielding
Explore the cutting-edge advancements in cave design and shielding strategies for radiation protection, including details on the construction materials, structural modifications, and spatial dose rate distributions achieved through simulation and calculations. The designs feature elements like steel doors, concrete walls, boron beamstop shields, and neutron guide shielding. The comprehensive approach ensures safety and efficiency in handling radiation sources.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
BEER cave design and shielding STAP meeting Phase 2
Change in the cave design TG2 design revisited Lift dead high about 50 cm Detectors movable only two, rearrangement Cabinets moved to E02 Personal access stairs position
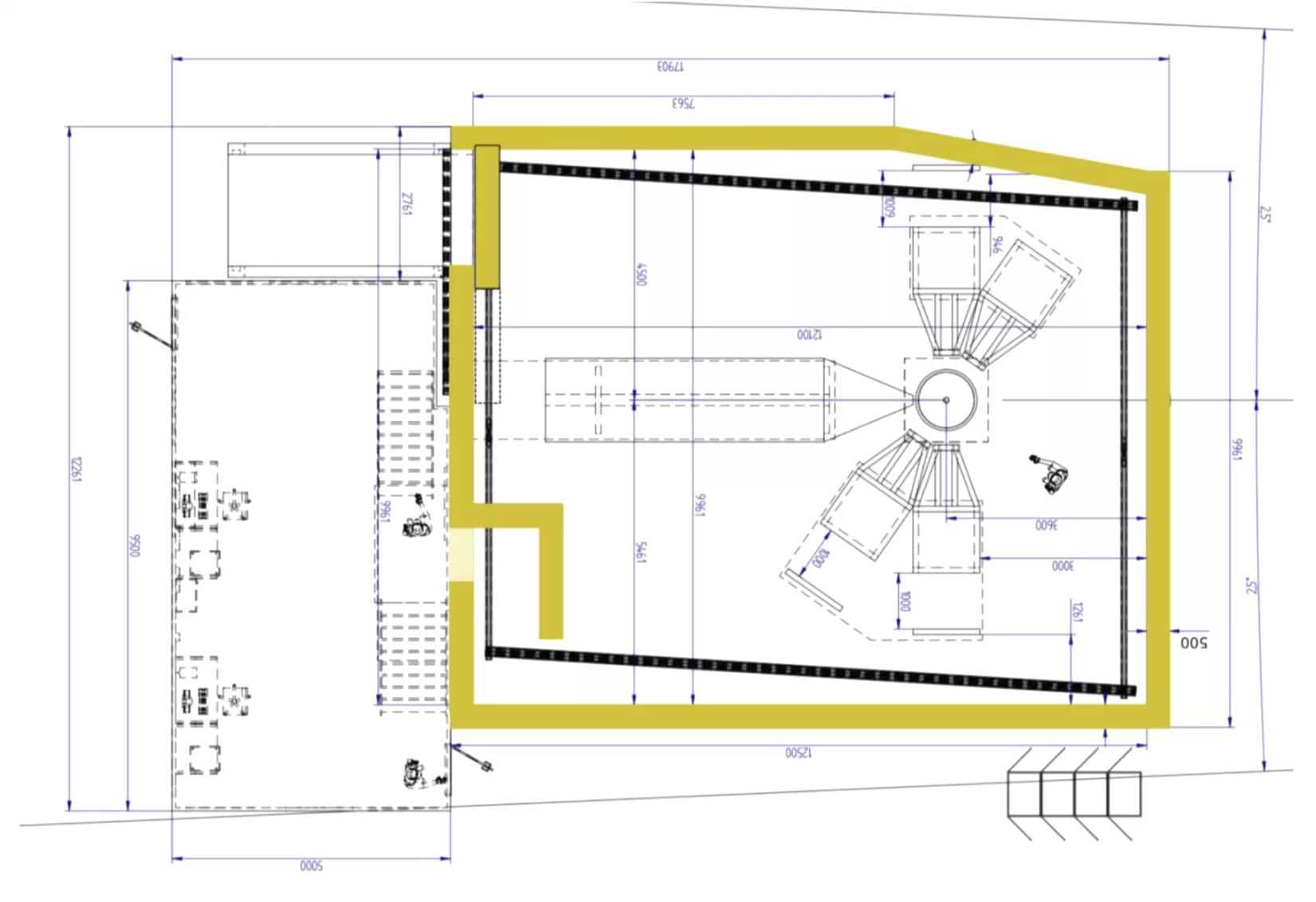
New cave design Cave construction from cast concrete Hutch LYCOS panel system 3.8 m behind hutch asked by ESS SE and big samples access via shaft Short path between prep. lab and cave 4 ton crane in the cave Future installation of the lift possible Personal access 3.8 m SE access
Guide shielding calculation fast thermal Neutron guide shielding Fast neutron after the bunker 10 m 50 m Iron/steel/copper Bunker wall Iron/steel/copper 78 cm Guide Rest of the guide tunnel 10 m after bunker 50 cm concrete (2.35 g/cm3) B4C 1 cm 50 cm concrete (2.35 g/cm3) 5 cm Borated (3%) PE Concrete Shutter design 10 cm concrete (2.35 g/cm3) 15 cm iron/steel
Guide shielding calculation Criteria of 1.5 S/h at the surface is met Spatial neutron dose rate distribution Spatial gamma dose rate distribution Sv/h Sv/h
Cave shielding Simulation made for 55 cm of std. concrete Plan for boron addition in the concrete or paint inside the cave Criteria of 1.5 S/h at the surface is met for H1 scenarios H2 scenario active solution or additional shielding Steel door (17 cm) Personal access door Concrete wall (55 cm) Boron beamstop shielded by lead Sample Concrete wall (60 cm) Beam
Cave shielding Calculation for 0.1 cm3 of Mn in the beam (H1 scenario) Beam size 1x1 cm2, chopper stopped in open position Spatial neutron dose rate distribution Spatial gamma dose rate distribution A A B B Sv/h Sv/h C C
Cave shielding Calculation for 1 cm3 of H2O in the beam (H1 scenario) Beam size 1x1 cm2, chopper stopped in open position Spatial neutron dose rate distribution Spatial gamma dose rate distribution B A B A Sv/h Sv/h C C
Cave shielding Calculation for 1 mm of Cd plate in the beam (H2 scenario) Beam size 10x10 cm2, chopper stopped in open position Spatial neutron dose rate distribution Spatial gamma dose rate distribution A A B B Sv/h Sv/h C C