Importance of a Healthy Breakfast and Planning Guidelines
Breakfast is essential as it provides energy, stabilizes blood sugar levels, enhances concentration, and prevents tiredness and accidents. Planning a healthy breakfast involves including food from main groups, fruit for hydration and vitamin C, high-fiber cereals, wholemeal bread, spreads in moderation, protein-rich dishes, and calcium-rich milk or yogurt.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Breakfast Chapter 11: Breakfast and Packed Meals
What I Will Learn To explain why a healthy breakfast is important To compile a set of breakfast planning guidelines To identify foods suitable for breakfast from the main food groups To create a nourishing breakfast To learn how to set a breakfast tray
Breakfast Breakfast is one of the most important meals of the day. The word breakfast comes from the 15th century expression breaking the fast , because it s the first meal you have after fasting (not eating) overnight. As we sleep at night, our blood sugar levels drop. This can make a person tired and irritable in the morning. See Activity 11.1 in the TRB
You Should Never Skip Breakfast Because It gives you energy and raises blood sugar levels It may prevent you from snacking on high-calorie foods later in the day It will aid your concentration at school or work, and help you work more efficiently It prevents headaches and tiredness It helps prevent accidents caused by fatigue
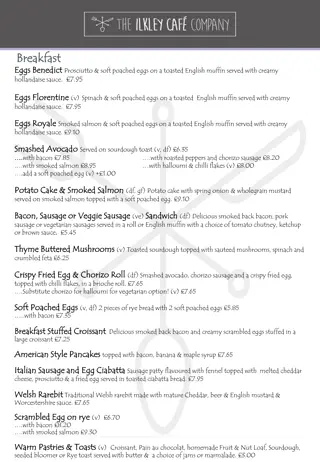
How to Plan a Healthy Breakfast Get up early and leave time to sit down and enjoy your breakfast. Include at least three of the four main food groups. Include fruit or fruit juices to rehydrate and include vitamin C. Use high-fibre cereals to provide fibre, vitamin B and iron and avoid those high in sugar. Wholemeal bread can also be included to increase fibre, e.g. wholemeal toast, brown breakfast scones or oatmeal blueberry muffins.
How to Plan a Healthy Breakfast (continued) Spreads like butter, Flora, Low-Low, honey or marmalade can be used in small amounts. Milk or yoghurt provides calcium, vitamin A and D. Main course dishes should have a protein food, e.g. eggs, beans, grilled bacon or kippers. Drinks like fruit juice, milk, tea, coffee or hot chocolate can also be included.
Foods Suitable for Breakfast Food group Vegetables, salad and fruit Foods Fruit: Juices, smoothies, segments of grapefruit or mandarins, mixed fresh fruit, stewed fruits like apple and prunes, in cereals or whole, e.g. bananas Vegetables: Juices, grilled tomatoes, grilled mushrooms
Foods Suitable for Breakfast (continued) Food group Wholemeal cereals and breads, potatoes, pasta and rice Foods Breakfast cereals: Porridge, muesli, granola, All-bran, Bran flakes, Weetabix, Shredded Wheat Breads: Brown or white bread, soda bread, scones, muffins, bagels, croissants, baguettes, French toast, pancakes, waffles and crackers Potatoes: Potato farls, potato cakes Rice: Kedgeree
Foods Suitable for Breakfast (continued) Food group Foods Milk, yoghurt and cheese Milk: On cereals (hot or cold), milkshakes, in tea, coffee (latte) or hot chocolate Yoghurt: In smoothies, on cereals and in muffins Cheese: In slices, chunks or cream cheese
Foods Suitable for Breakfast (continued) Food group Meat, poultry, fish, eggs, beans and nuts Foods Meat: Grilled rashers, sausages, black and white pudding, ham, salami and chorizo Fish: Kippers and kedgeree and smoked salmon or mackerel Eggs: Boiled, poached, scrambled, fried or in an omelette Beans: Baked beans and hummus Nuts and seeds: Can be sprinkled into cereals, smoothies or muffins, peanut butter
Foods Suitable for Breakfast (continued) Food Group Fats, spreads and oils Foods Flora, low-fat butters and spreads, e.g. Benecol and LowLow Use honey, syrups, jam or marmalade sparingly Foods and drinks high in fat, sugar and salt
Discovery Learning Design a healthy breakfast for each of the following people: i. An active school-going teenager ii. A woman in her thirties working in an office (sedentary) iii. A man in his fifties recovering from a heart attack Don t forget to use the guidelines for planning a healthy breakfast
How to Set a Breakfast Tray Collect everything you need tray, cutlery, delph and glassware. Make sure everything is clean. The tray should look attractive and be colour-coordinated with a small flower to finish off. Use a tray cloth to decorate a plain tray. Choose small dishes, jugs and teapots to suit the tray. Place items in a logical order, e.g. teapot, milk and sugar near each other (see tray on next slide). Make sure to include cutlery for each dish, condiments and a napkin. The hot main course should be covered.
Discovery Learning 1. Find out the differences between a Continental breakfast and a full Irish breakfast in a hotel. 2. Suggest a menu for each type of breakfast.
Quick Revision Explain why a healthy breakfast is important. List the guidelines that should be followed when planning a breakfast menu. Design a breakfast menu suitable for an active school- going child and give reasons for your choices. Plan a breakfast to be served on a tray. Draw the tray setting.