Alternative Depreciation Method for Modeling PPE Balance
In the context of modeling the balance of existed Property, Plant, and Equipment (PPE) for start-ups and fast-growing IT companies, the challenge lies in determining retirement rates with limited information. The approach involves making assumptions about starting retirement levels and growth rates, setting up a timeline, putting in parameters and assumptions, and using a simple model to calculate retirements and depreciation. The Solver tool can be used to find growth and base levels. This method helps address the puzzle of retirement projections in a dynamic business environment.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Question I'm trying to use alternative depreciation method for modelling existed PPE balance I consider start-up's and fast growing IT companies. Example: Accumulated depr ratio - 56,75% Life - 3.2 years Actual depretiaction for 1 year = 33% Result of function find_growth =-84% Result of function find_base = 84% Is it correct to say that retirement rate in this case is 84%? or i should modify logic of calculation in this case? may be within so short period of depreciation time it is not suitable approach. May be more aplicable approcach = use defined plan of retirement (make assumption). The problem is the lack of reliable information to make assumption. Alexander Komlev
Re-stated Example Example: Gross Plant Accumulated depr Life - 3.2 years Actual Depreciation for 1 year 33 100 56.75
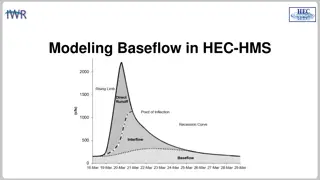
Existing is Like a Puzzel If you can find the retirements you should be ok. You can assume the retirements will start at some level and then grow. You don t know either the starting point or the growth rate. The total amount of gross plant must be retired over the life. The accumulated depreciation over the life must also go to zero.
Set Up Time Line as Usual May have to put in fraction of the year as shown in the example Retirements and depreciation should be smaller in the year with the fraction. Use MOD and CHOOSE in the example below 5
Step 2: Put in Parameters and Make Arbitrary Assumptions for Starting Retirement and Growth Put in the following: Life of Plant Gross Plant Depreciation Rate Starting Retirements Historic Growth to Apply to Retirements
Step 3: Set-up Simple Model with Gross Plant and Accumulated Depreciation Put in Opening and Closing Balances with Arbitrary Data on Retirements. Put in the depreciation and decide about assuming year. Multiply depreciation and retirements by fraction of the year.
Step 4: Use Solver to Find Growth and Base Level Using Sumif First compute the ending balances in the final year. Next use the solver to set the ending gross plant and the ending accumulated depreciation to zero Change both the growth rate and starting balance
Final Simulation In this case, the growth was negative because of the accumulated deprecation relationship
Now, Test the Methods Case 1, Net Plant Method Case 2, Separate Existing and New Error Growth 6.00% Base 36.00 20.00% 15.00% 10.00% 5.00% 0.00% 1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00 6.00 7.00 8.00 9.00 10.00 11.00 12.00 -5.00% -10.00% -15.00%
To Accurately Model Depreciation from Cap Exp, You Should Split New Cap Exp from Existing Plant Model Retirements on New Depreciation Model Retirements on Existing Depreciation Model Existing Depreciation Using Gross Plant 11