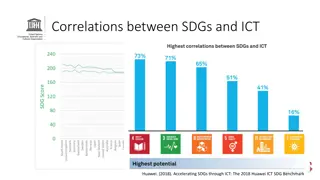
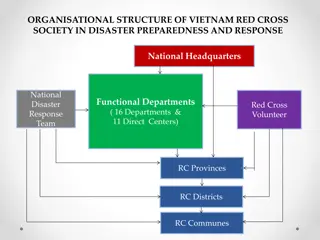
Role of Department of ICT in Disaster Risk Reduction in Bangladesh
The Department of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in Bangladesh plays a crucial role in promoting the use of ICT for disaster risk reduction. Bangladesh faces numerous catastrophic hazards, making it essential to utilize ICT for warning systems, relief management, and post-disaster activities. The National ICT Policies of 2009 and 2015 focus on leveraging modern technology, including GIS-based systems and remote sensing technologies, to protect citizens from natural disasters and ensure efficient disaster management.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Presentation on Role of Department of ICT in Promoting ICT Uses in Disaster Risk Reduction Jashim Uddin Ahmed (Additional Secretary) Director General, DoICT Department of Information and Communication Technology Information and Communication Technology Division Ministry of Posts, Telecommunications and IT BANGLADESH
ICT in Bangladesh Foreword Progress Election Pledge; Vision 2021: Digital Bangladesh ICT Division and Department of ICT are formed Government committed for inclusive uses of ICT ICT rollout is happened all over the country ICT for unlocking tremendous social and economic benefit Development of National ICT infra- network promotes cross sectoral synergy Middle income country by 2021
DRR Why Important in Bangladesh ? Bangladesh is one of the worst disaster prone country of the world. Catastrophic Hazards ---Floods (1988,1998 and 2004), Cyclones and Storm Surges (1970,1991,2007 SIDR and 2009 AILA), Tornado (1974, 1977, 2005 etc), River Bank Erosion, Earthquake, Drought, Arsenic Contamination, Salinity Intrusion, Fire, Infrastructure Collapse (RANA Plaza), Tsunami and Landslide.
National ICT Policy 2009 Addressing Disaster Risk Reduction Strategic Objectives Protect citizens from natural disasters through ICT-based disaster warning and management technologies Promote efficient relief management and post-disaster activities monitoring Activities Utilize remote sensing technologies for disaster management and mitigations Promote cell phone/SMS-based disaster warning systems targeted to the population likely to be affected Utilize Geographic Information System (GIS)-based systems to monitor flood and cyclone shelters (including equitable distribution in vulnerable areas) Utilize Geographic Information System (GIS)-based systems to ensure equitable distribution of relief goods with special focus on the hard-to-reach area
National ICT Policy 2015 Addressing Disaster Risk Reduction Strategic Objectives Protect citizens from natural disasters through ICT-based disaster warning and management technologies Promote efficient relief management and monitoring to ensure post- disaster activities Activities Utilize Modern Technology in Disaster Management & Risk Reduction Introduce Community Radio, Television and Mobile Technology based Disaster Warning System for Disaster Prevention Introduce ICT uses for Post Disaster Measure, Estimate losses and also for equitable distribution of relief goods.
Disaster Management Institutions in Bangladesh National Disaster Management Council Ministry of Food and Disaster Management (MoFDM) Inter Ministerial Disaster Management Coordination Committee (IMDMCC) National Disaster Management Advisory Committee (NDMAC) National Platform for Disaster Risk Reduction (NPDRR) Disaster Management and Relief Division (DM&RD) Earthquake Preparedness and Awareness Food Division CPP Implementation Board (CPPIB) Disaster Management Bureau (DMB) Directorate of Relief and Rehabilitation (DRR) Director General of Food (DGFood) District Disaster Management Committee (DDMC) Municipal Disaster Management Committee (MDMC) City Corporation Disaster Management Committee (CCDMC) Upazila Disaster Management Committee (UzDMC) CSDDWS Zone/ Upazila FPOCG NGOCC Union Disaster Management Committee (UDMC) Union DMTATF Figure: Disaster Management Institutions in Bangladesh
ICT uses Impact on Disaster Management- An example from cyclone death trend Time Max. Wind Speed (km/hr) Death Toll Death toll comparison between 1970 and 2007 cyclones significantly highlighted the ICT uses impact on disaster. 11 May, 1965 161 19,279 15 December, 1965 217 873 01 October, 1966 139 850 12 November, 1970 3,000,00 224 25 May, 1985 154 11,069 In case of SIDR Early warning (72 hrs before the event) from RSMC, New Delhi, India through their geo-stationary satellite, INSAT substantially reduces the death toll. 29 April, 1991 225 138882 19 May, 1997 232 155 15 Nov, 2007 (SIDR) 3,363 223 25 May, 2009 (AILA) 92 190
Our Linkage DOICTs functions Ensure the proper utilization of ICT & coordination of ICT activities among all the Government offices for smooth functioning. Support to create appropriate ICT infrastructure and maintenance support of all government offices up to grass root level.
SDG and DRR framework Bangladesh have signed United Nations Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 2030. Signatory of DRR Sendai framework, 2015-2030 UN-ESCAP is working for promoting use of ICT as a key tool for mainstreaming DRR into development planning.
Achievements Department of Disaster Management Program namely Comprehensive Disaster Management Program (CDMP) took an initiative for earthquake hazard and risk assessment of three major cities (Dhaka, Chittagong and Sylhet) in Bangladesh. Early Landslide warning saves life due to earlier evacuation in Chittagong. CDMP makes available cyclone shelter database information online
Achievements Disaster Management Information Centre (DMIC) introduce Early warning through Cell Broadcast in two districts- Sirajgonj for flood and Cox s Bazaar for cyclones Interactive Voice Response 10941dial updated message is available for weather, disaster info and early warning. >1 lakh responses were made in 2013 through IVR (Interactive Voice Response) SMS- Mobile no. database is formed for the key actors at the root level. They are instructed through SMS
Policy Achievements Bangladesh is signed a contract with SAARC Disaster Management Centre (SDMC) to develop Bangladesh Disaster Knowledge Network under South Asian Disaster Knowledge Network project. National Disaster Management Council amended Standing order on Disaster through including orders on Earthquake, Tsunami and fire hazards in SOD in 2010. Government initiative in DRR decrease casualties in the Business sector. Climate Change Trust Fund and Climate Change Resilient Fund is key to infrastructure development in DRR
Sensitization/ Educative Program Disaster Reduction Chapter include in Class III to Class X curriculum. Disaster Management and Climate Change Related Subject is included in Class XI and XII Disaster Management is sensitize through UDC (Union Digital Center). 10000 booklets are distributed in 4500 UDC. Solution Exchange a email based communication system was formed for the actors of Disaster Management and Climate Change Adaptation.
Way Forward Almost 98% of Bangladesh is under the coverage of Mobile network. DoICT along with Bangladesh Meteorological Department can establish information repository. Real time data on weather parameters like Rainfall, Humidity, Air Pressure, Wind Velocity, Temperature etc. can be stored for information generation. Data Collection can be done through mobile network. huge weather
Challenges Earthquake forecasting system is not well developed. Due to rapid urbanization/ huge unsafe buildings, buildings developed mostly violating Bangladesh national building codes subject to make Bangladesh an earthquake vulnerable. To develop good governance in this sector through e-governance is a key challenging area for us.