Understanding Chemical Bonding and Stability in Atoms
Explore the significance of chemical bonds in providing stability to atoms through ionic and covalent bonding mechanisms. Learn about valence electrons, types of bonds, and why atoms form bonds for enhanced stability.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Why bond? Most atoms are not stable by themselves. A chemical bond provides stability for both atoms involved by lowering the potential energy of both atoms. chemical bond = a mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei (positive) and valence electrons (negative) of different atoms that binds the atoms together. valence electrons = electrons located in the outermost (last) energy levels of an atom (max of 8e-). all atoms want 8 valence electrons for maximum stability (like a noble gas), so they either lose, gain, or share e-from their outermost energy levels to get 8. three types of bonds: ionic bond = bond that results from the electrical attraction of large numbers of cations (pos. ions) and anions (neg. ions). Electrons transfer from one atom to another in an ionic bond. He 1 2 Valence e-# 3 4 5 6 7 8 +1+2 Ion Charge +3 4 -3 -2 -1 0
three types of bonds: ionic bond = bond that results from the electrical attraction of large numbers of cations (pos. ions) and anions (neg. ions). Electrons transfer from one atom to another in an ionic bond. polar covalent bond = results from unequal sharing of electrons btwn atoms. non-polar covalent bond = results from equal sharing of electrons btwn atoms.
polar covalent bond = results from unequal sharing of electrons btwn atoms. non-polar covalent bond = results from equal sharing of electrons btwn atoms.
Self-Check Question! Why do atoms form chemical bonds? to become more stable
Self-Check Question! True or False? Valence electrons are the only electrons involved in the bonding process.
Self-Check Question! 8 All atoms want ___ valence electrons for maximum stability.
Self-Check Question! (Ionic, Covalent) bonds can be described as a transferring of electrons.
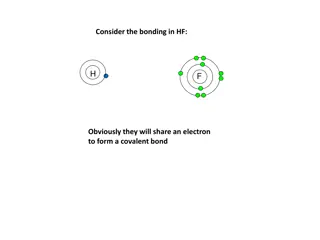
Self-Check Question! The molecule shown here is an example of a(n) ___________ bond. covalent
Types of Bonds to tell what type of bond will form between any two elements, you must know what type of elements you are dealing with: ionic bonds are formed when a metal bonds with a nonmetal.
Part II: Types of Bonds to tell what type of bond will form between any two elements, you must know what type of elements you are dealing with: ionic bonds are formed when a metal bonds with a nonmetal. why? Metals lose electrons to form positive ions (cations), nonmetals gain electrons to form negative ions (anions) to get their desired total of 8 valence electrons. large numbers of cations and anions are electrically attracted to one another, and ionic bonds form! covalent bonds are formed when a nonmetal bonds with another nonmetal, or a metalloid.
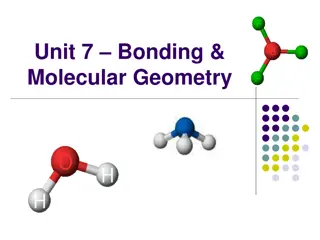
covalent bonds are formed when a nonmetal bonds with another nonmetal, or a metalloid. why? Since nonmetals and metalloids would form similarly-charged negative ions if they tried to make an ionic bond (which would repel each other), they form covalent bonds instead. covalent bonds form when two atoms share their valence electrons (not transfer them). See the water molecule to the right. we will talk about how to tell the difference between a polar and nonpolar covalent bond later on in this unit. let s see if you can tell what type of bond form between the following elements:
lets see if you can tell what type of bond forms between the following elements: C C diatomic oxygen = _____ 2 of the same atom sulfur and hydrogen = _____ diatomic means: _________________________ I oxygen and cesium = _____ magnesium and fluorine = _____ I C sulfur and chlorine = _____ carbon and hydrogen = _____ C I calcium and chlorine = _____ aluminum and nitrogen = _____ I C bromine and chlorine = _____
Self-Check Question! When large #s of cations and anions electrically attract, this forms: an ionic bond
Self-Check Question! Describe what happens to electrons in a covalent bond: they are shared (not transferred) between atoms (no ions form)
Self-Check Question! Nonmetals are found in the _______________________ corner of the periodic table: upper right-hand (or NE)