Understanding VSEPR Theory for Molecule Geometry
Explore the principles of VSEPR theory to predict molecular geometries based on electron pairs, learn about Gillespie Laws, irregular geometries, and examples of different molecular shapes. Discover the impact of lone pairs on bond angles and delve into the 3D model of Ammonia for a comprehensive understanding of molecular structures.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CHRISTIAN EMINENT COLLEGE, INDORE (Academy of Management, Professional Education and Research) An Autonomous Institution Accredited with A Grade by NAAC E-Content On VSEPR Theory 12th June 2020 Prepared By: Prof. Snehlata Hada Department of Chemical Sciences
Objective of the presentation Geometry of the molecule VSEPR - Theory Gillespie Laws
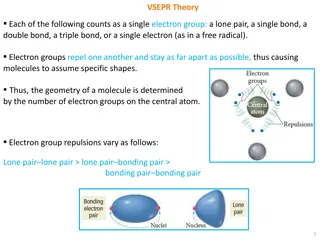
VSEPR THEORY (VALENCE SHELL ELECTRON PAIR REPULSION THEORY) In order to predict the geometry of covalent molecules, valence shell electron pair repulsion theory is given This theory was given by gillespie and nyholm. These arrange themselves in such a way that there is a minimum repulsion between them so that the molecule has minimum energy (i.e. maximum stability Geometry of a molecule depends upon the number of bonding and non- bonding electron pairs in the central atom.
Gillespie Laws If the central atom of the molecule is surrounded by bonded electron pair only, then the geometry will be regular ,according to hybridization .
Table showing geometry of molecules Name of compound BeCl2 BeCl3 CH4 No. of bonding electron pair 2 3 4 Geometry Linear Triangular Planar Regular Tetrahedral Trigonal bipyramidal Octahedral PCl5 5 SF6 6
Irregular geometry When the central atom in a molecule is surrounded by both, bonding electron pairs as well as by lone pairs, then molecule will not have a regular shape. The geometry of the molecule will be disturbed. This alteration or distortion in shape is due to the alteration in bond angles which arises due to the presence of lone pairs on the central atom. :
Irregular geometry No. of Lone pairs on central atom Contraction in bond angle w.r.t. CH4 Molecules Bond Angle CH4 0 109.5 0 0 NH3 1 107.5 0 2 H2O 2 105.5 0 4
Link for further reading https://www.google.com/search?q=vsepr+theory+notes&sx srf=ALeKk01uj_mej1u-qQsE5ynBSsDzH3G- Mg:1627728864179&tbm=isch&source=iu&ictx=1&fir=F- 38NNrRNJQEnM%252CHVYEvExPTS0ZiM%252C_&vet=1&usg= AI4_-kQqPlRp1w7hSvMN- egXGbl_0AWPNA&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwimpfXFko3yAhXgyDgG HcGwDKsQ_h16BAgXEAE#imgrc=Q_trTK65KK-voM