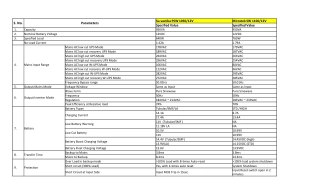
Understanding Transformers in AC Power Distribution
Transformers play a crucial role in transmitting and distributing power in AC systems through mutual induction. They convert high voltage to low voltage and vice versa while maintaining the power balance. Various applications include voltage level adjustments, impedance matching, power system isolation, and more.
- Transformer Basics
- AC Power Distribution
- Mutual Induction
- Voltage Conversion
- Power System Applications
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Lecture on Transformer By D. M. Parshuramkar
Introduction Transformer is the main reason to transmit and distribute power in AC. Transformer is a device which works on the principle of mutual induction.
It is based on principle of MUTUAL According to which an e.m.f. is induced in a coil when current in the neighboring coil changes. INDUCTION.
Transformer is the main reason to transmit and distribute power in AC. Principle of transformer is it convert high voltage (low current) into low voltage (high current). In ideal transformer, input power is equal to out power. In transformer the relation between EMF and current is inversely proportional and EMF and number of turns is directly proportional to each other. The ratio of Es/Ep= Ns/Np is called turns ratio or transformer ratio. Then there are two types of transformer, step-up and step-down transformer.
The ratio is called as turn ratio or transformer ratio. In idea transformer I/P power = O/P Power
Applications There are wide applications of transformers such as, step up (increases) or Step down (Decreases) the level of voltage in other words increases or decreases the level of current, while power almost be same, Welding Machine X-ray tube mobile charging To transform electric current through metallic cables
Applications It can increases or decreases the value of L, C or R in an AC circuit. This can act as impedance transferring device It can isolate two circuit electrically To prevent DC from passing from one circuit to the other Step-down level of voltage at single phase 11KV to 220 V, Three phase 11KV to 440 V
Applications The current transformer Np/Ns and Potential transformer Ns/Np are used in industry and power system It used for impedance matching Impedance transformer ratio=(Ns/Np)2
Power Losses In Transformer Iron losses Copper losses Eddy current losses Hysteresis losses Heat losses I2R
Transformer Transformer Efficiency Efficiency Transformerefficiency is given as: P = 100 % out P in P = out 100 % + P P out loss