Understanding Transformers in Magnetism: Key Concepts and Equations
Explore the fundamental principles of transformers in magnetism, including their structure, equations, and calculations of current and potential difference. Enhance your knowledge with practical examples and challenges for a comprehensive understanding of this topic.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
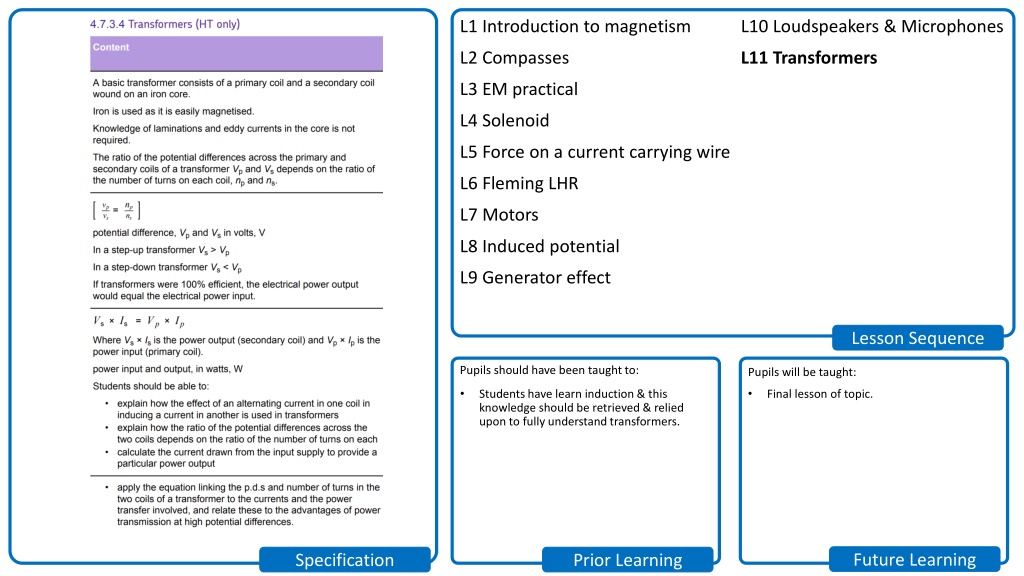
L1 Introduction to magnetism L10 Loudspeakers & Microphones L2 Compasses L11 Transformers L3 EM practical L4 Solenoid L5 Force on a current carrying wire L6 Fleming LHR L7 Motors L8 Induced potential L9 Generator effect Lesson Sequence Pupils should have been taught to: Pupils will be taught: Students have learn induction & this knowledge should be retrieved & relied upon to fully understand transformers. Final lesson of topic. Future Learning Specification Prior Learning
SciDoc Transformers Transformers 29/09/2024 Last Lesson Last Term Last Year Stretch & Challenge I do We do Test I do We do You do Do Now
SciDoc Keywords Learning Objectives Keywords Transformer Primary Secondary Coil Current Potential difference Describe the structure of a transformer. Recall two transformer equations. Calculate current and potential difference using the transformer equations. I do We do Test I do We do You do Do Now
SciDoc Transformers Transformers A basic transformer consists of a primary coil and a secondary coil wound on an iron core. Iron is used as it is easily magnetised. Stretch: What is the equation that relates power, current and potential difference? I do We do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Power conservation Power conservation Vs Is = Vp Ip Where Vsis the potential difference (V) in secondary coil, and Is is the current (A) in secondary coil. Stretch: Vs = 230 V, Is = 13A & Vp = 400,000 V. What is Ip? I do We do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Step Step- -up & step up & step- -down transformers down transformers Vp Vs = Np Ns If there are more turns on the secondary coil (Ns) than the primary coil (Np) then the voltage is stepped up (and vice versa if other way around). Stretch: Is the transformer below step- up or step-down? I do We do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Worksheet Worksheet Complete the worksheet I do We do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Basic answers Basic answers 1. A primary coil and a secondary coil wound on an iron core 2. It is easily magnetisable. 3. It increase the potential difference/reduces the current. This helps to reduce power loss in transmission cables. 4. It decreases the potential difference to a safe level for consumers. I do We do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Medium answers Medium answers 5 0.007 76.7 480 100 800,000 23,000 71.9 I do We do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Hard answers Hard answers 7. Because the p.d. across secondary coil is less than across primary coil. 8. a) 150 turns. b) 66.7 turns. c) 33.3 turns. 9. 18 turns I do We do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Complete the task (6 minutes) I do We do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc Struggle time! Struggle time! Exam question so exam conditions! You have 8 minutes! I do We do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc I do We do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc I do We do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc I do We do Test I do We do You do LO:
SciDoc I do We do Test I do We do You do LO: