Understanding the Urinary System: Function and Structure
The urinary system, also known as the excretory system, plays a crucial role in regulating water and salt levels in the body, as well as excreting wastes through urine. It consists of organs like the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, each with specific functions in the filtration and elimination process. This system ensures osmoregulation and homeostasis by filtering metabolic wastes and maintaining the body's chemical balance. Explore the components and functions of the urinary system to grasp its importance in bodily functions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Urinary System (Excretory System) SAVANNAH PIRES, MIA MARTINEZ, AND TAYLOR ZACHEY
Definition The system of organs and tissues involved with regulation of water content and salt concentration in the body and with the excretion of wastes and excess water and salt in the form of urine. Osmoregulation- maintaining the body s water/salt levels. (homeostasis)
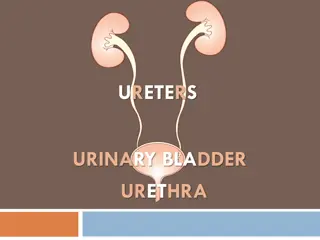
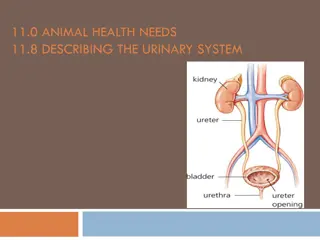
Parts of the Urinary System Kidneys Ureters Urinary Bladder Urethra Penis Vagina
Kidneys Two bean shaped organs Located below the rib cage Involuntary Filter metabolic wastes, excess ions, and chemicals Form urine
Filtration of Urine Blood enters through renal arteries. Enters the glomerulus, pressure releases filtrate to bowman s capsule Flows through proximal convoluted tubule (reabsorbs necessary substances) Enters the Loop on Henle
Filtration of Urine (continued) Concentrated urine enters the Distal Convoluted Tubule Necessary organic molecules reabsorbed. Enters Medulla through channeling ducts.
What is Urine? Watery, yellowish fluid Discharged through urethra Contains water, salt, and urea
Ureters Tubes that carry urine to bladder Composed of fibrous muscle and mucus coat so they can contract
Bladder Holds urine until released Controlled by two sphincter muscles Make urination voluntary Can hold up to 600 ml of urine
Urethra Tube from which urine is released. In males: roughly 8 inches long Females: 1.5 inches long
To Sum it all up: Crash Course Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WtrYotjYvtU
5 Diseases Chronic Kidney Disease Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Urinary Tract Infection Kidney Stones
Chronic Kidney Disease Caused by: Diabetes and High Blood Pressure Immune system conditions Urinary Tract infections Congenital defects Drugs and toxins Symptoms: Less urination, edema, fatigue, loss of appetite, random weight loss, nausea, and headaches Treatment: Diet and exercise Blood pressure medication Overall healthy lifestyle Regular doctors visits
Cystitis Caused by: Bacterial infections (UTI) Reaction to certain drugs Radiation therapy Potential irritants Symptoms: A strong, persistent urge to urinate A burning sensation when urinating Passing frequent, small amounts of urine Blood in the urine (hematuria) Passing cloudy or strong-smelling urine Discomfort in the pelvic area Low-grade fever Treatment: Antibiotics
Interstitial Cystitis Caused by: a defect in the protective lining (epithelium) of the bladder autoimmune reaction Heredity Infection allergy Symptoms: Pain in your pelvis Frequent urination, often of small amounts Pain during sexual intercourse Treatments: physical therapy oral medication
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Caused by: Bacteria entering urinary tract Symptoms: A strong, persistent urge to urinate A burning sensation when urinating Passing frequent, small amounts of urine Urine that appears cloudy Urine that appears red, bright pink or cola-colored a sign of blood in the urine Strong-smelling urine Pelvic pain, in women Rectal pain, in men Treatments: Antibiotics
Kidney Stones Caused by: Urine becomes concentrated Symptoms: Severe pain in the side and back, below the ribs Pain that comes in waves and fluctuates in intensity Pain while urinating Pink, red or brown urine Cloudy or foul-smelling urine Nausea and vomiting Persistent urge to urinate Urinating more often than usual Fever and chills if an infection is present Treatments: Pain medication (to pass kidney stone) Drink plenty of water