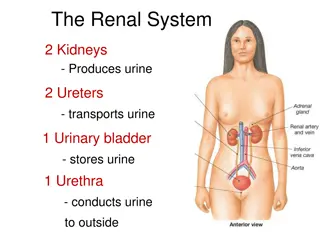
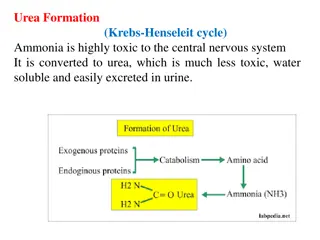
Renal Function Tests (RFTs)
An overview of the functional units of the kidney, including the nephron, and the various functions performed by the kidneys. It also covers laboratory tests used to assess kidney function.
0 views • 17 slides
Laboratory Training
Kidneys play a vital role in the body by filtering waste and maintaining fluid balance. Learn about the structure of kidneys, nephron function, and the importance of blood urea and serum creatinine tests in assessing kidney health. Discover how factors like protein intake and medical conditions affe
1 views • 44 slides
Anatomy of the Kidney: Essential Features and Functions
The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste products, regulating electrolyte balance, maintaining blood pH, producing hormones, and more. This article explores the anatomical features of the kidneys, including their position, extent, internal structure, vascular segments, and coverings. It also
3 views • 16 slides
Regulation of Glomerular Filtration and GFR Physiology Overview
This detailed study delves into the regulation of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in the kidneys. It covers the intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms that control GFR, autoregulation, tubuloglomerular feedback, glomerular filtration membrane, filtration forces, molecular size and filterability of subs
9 views • 20 slides
Urinary Elimination: Anatomy, Physiology, and Function of the Kidneys
The lecture covers the fundamentals of urinary elimination focusing on the kidneys' location, structure, function, and the role of nephrons. It discusses the transport of urine through the ureters to the bladder, highlighting the bladder's muscle layers and the urethra's role in expelling urine. Stu
6 views • 37 slides
An Overview of the Renal System and Nephron Anatomy
The renal system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra, responsible for producing, transporting, storing, and excreting urine. The kidneys are surrounded by three layers, and the nephron is the functional unit responsible for filtering blood and producing urine. Key componen
5 views • 26 slides
Hypokalemia and Potassium Regulation
Hypokalemia is a condition characterized by low potassium levels, crucial for intracellular functions. The Na+/K+ ATPase pump maintains the ICF/ECF gradient. Potassium excretion occurs mainly via the kidneys, with minimal variation in proximal tubule reabsorption. The collecting duct plays a vital r
2 views • 50 slides
Overview of Urinary System Anatomy and General Terminology
This content provides detailed information on the anatomy of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. It explains anatomical terms, Greek term elements related to the system, and general terms for urine and urination. Additionally, it covers urinary dysfunctions such
3 views • 8 slides
Chronic Kidney Disease: Overview and Diagnosis
Explore the essentials of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): its significance, the functioning of kidneys, causes, diagnosis methods, and considerations based on age. Gain insights into CKD stages and learn how to maintain kidney health for a better quality of life.
0 views • 27 slides
Veterinary Anatomy of Urinary System in Different Animals
The urinary system in animals includes kidneys, ureters, and the bladder, all crucial for filtration and urine excretion. The ureters are excretory ducts from the kidneys, while the bladder stores urine before expulsion. Various diagrammatic structures illustrate the urogenital system of animals, pa
0 views • 20 slides
Urea Biosynthesis and the Krebs-Henseleit Cycle in the Liver
Urea is synthesized in the liver through a series of enzymatic steps known as the urea cycle or Krebs-Henseleit cycle. This process involves converting toxic ammonia into urea, a less toxic and water-soluble compound that can be easily excreted in urine. The liver plays a crucial role in urea biosyn
1 views • 20 slides
Acid-Base Balance in the Body: Importance and Regulation
Acid-base balance is crucial for maintaining optimal health, as slight deviations in hydrogen ion concentration can impact enzyme activity and metabolic processes. The body employs various defense mechanisms to regulate pH levels, involving buffers, lungs, and kidneys. Strong acids release more H+ i
3 views • 48 slides
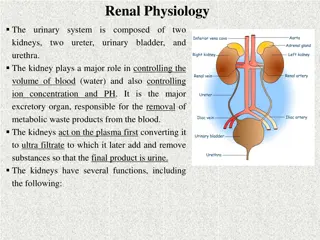
Renal Physiology: The Role of the Kidneys in Maintaining Homeostasis
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra, playing a crucial role in regulating blood volume, ion concentration, and pH. The kidneys, as the major excretory organ, remove metabolic waste products and help maintain water-electrolyte balance, regulate arterial p
1 views • 27 slides
Kidney Function and Laboratory Tests
This article delves into the structure and function of the kidneys, specifically focusing on nephrons and the implications of nephron loss. It also discusses the importance of blood urea and serum creatinine tests in evaluating kidney function, highlighting the differences between the two and their
3 views • 44 slides
Short-Term Effects of Alcohol on the Body
Alcohol consumption has various short-term effects on the body, affecting the brain, liver, blood vessels, heart, kidneys, stomach, and driving abilities. It depresses brain activity, increases heart rate and blood pressure, and influences urine production. Driving under the influence of alcohol has
0 views • 12 slides
Ethical Issues in Organ Transplants
Organ transplantation involves the moving of organs from one body to another to replace damaged or absent organs. The process includes cadaveric and living organ donations, with various transplantable organs like lungs, kidneys, heart, and more. There are ethical issues surrounding organ donation de
0 views • 16 slides
Overview of Acute Pyelonephritis: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Epidemiology
Acute pyelonephritis is a serious bacterial infection of the kidneys, leading to complications such as renal scarring and sepsis. This overview covers key aspects including epidemiology, etiology, clinical presentations, and risk factors. Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies are also disc
0 views • 18 slides
Urinary System: Kidneys, Functions, and Structure
The urinary system, also known as the renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Each kidney contains nephrons, the functional units responsible for filtering waste and regulating blood volume, pressure, electrolytes, and pH balance. The kidneys have an extensive blood sup
0 views • 35 slides
Anomalies of Kidneys and Factors Affecting Renal Function in Veterinary Pathology
An overview of anomalies affecting the kidneys in animals, including ectopic kidney location, renal agenesis, renal aplasia, and renal hypoplasia. The images illustrate anomalies such as fused kidneys and duplication of kidneys, with explanations of occurrence and sequelae. Additionally, factors aff
0 views • 13 slides
Homeostasis in Organisms
Homeostasis is the key to maintaining internal stability in living organisms, ensuring they return to a stable state after fluctuations. This involves various body parts such as the kidneys, skin, liver, and pancreas. Different systems like body temperature regulation, blood pressure control, and os
1 views • 51 slides
Comprehensive Guide to Kidney Transplant: Preparations, Benefits, and Risks
Explore the essential aspects of kidney transplantation, including the significance of kidneys, types of abdominal transplants, fast facts about kidney transplants, benefits, risks, and the kidney transplant waitlist process. Gain insights into the importance of kidney health, the waiting list stati
0 views • 21 slides
Alterations in Genitourinary Function: An Overview
The genitourinary system comprises the urinary and reproductive organs, with the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra playing crucial roles. Maintaining proper function involves factors like renal blood flow, glomerular filtration, tubular function, and urine flow. Nephrons are the functional unit
0 views • 58 slides
Acid-Base Balance and Regulation in the Body
Acid-base balance is crucial for maintaining optimal physiological functions. This content explains the definitions of acids and bases, differentiates between strong and weak varieties, explores the significance of pH control in body fluids, and delves into the roles of buffers, kidneys, and lungs i
0 views • 20 slides
Development of Kidneys and Ureters in Embryology by Dr. Jamila El Medany
This educational material discusses the embryological origin and development of kidneys and ureters. It covers the three systems of kidney development, including the pronephric, mesonephric, and metanephric systems. Detailed descriptions of the formation of the permanent kidney (metanephros), the co
0 views • 17 slides
Embryological Development of Kidneys and Ureters by Prof. Ahmed Fathalla Ibrahim
This lecture by Prof. Ahmed Fathalla Ibrahim discusses the embryological origin of kidneys and ureters, the development of different kidney systems, the formation of the permanent kidney, and common anomalies associated with kidneys and ureters. It covers topics such as the nephrogenic ridge, pronep
0 views • 22 slides
Key Issues and Uncertainties in Tert-Butanol (TBA) Induced Kidney Toxicity
This study discusses the key issues and uncertainties surrounding Tert-Butanol (TBA) induced kidney toxicity. It covers the role of alpha-2u globulin nephropathy, chronic progressive nephropathy (CPN), and the validity of concluding another unknown mode of action. Findings suggest TBA as a weak indu
0 views • 8 slides
Diabetes Insipidus: Types, Causes, and Symptoms
Diabetes insipidus (DI) is a disorder caused by a deficiency of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH), leading to the excessive passage of diluted urine. Central DI results from pituitary or hypothalamus issues, while nephrogenic DI occurs when the kidneys fail to respond to ADH. Common causes include brain t
0 views • 22 slides
Kidney Physiology and Function in the Human Body
Kidneys play a crucial role in regulating arterial blood pressure, erythrocyte production, glucose synthesis, and filtration through nephrons. They cannot regenerate nephrons, leading to a gradual decrease in function with age. Key structures like the hilum, renal artery, and vein, as well as the ne
0 views • 127 slides
The Excretory System and Kidney Functions
The excretory system serves a vital role in removing waste and maintaining internal balance. In humans, the kidneys and bladder are key components of this system, filtering wastes from the blood and producing urine. The kidneys have various functions, including waste elimination, fluid balance regul
0 views • 12 slides
Cardiorenal Syndrome: A Complex Relationship Between the Heart and Kidneys
Cardiorenal Syndrome is a condition where dysfunction in one organ, whether acute or chronic, can lead to dysfunction in the other. This complex relationship involves intricate communication pathways between the heart and kidneys, impacting hemodynamic stability, organ perfusion, and neurohormonal i
0 views • 15 slides
Microvascular Perfusion Loss in Kidneys of Children with Type 1 Diabetes
Dynamic tissue perfusion measurement using PixelFlux reveals microvascular perfusion loss in the kidneys of children with type 1 diabetes. This study examines the impact of diabetes duration, A1C levels, dyslipidemia, and blood pressure on renal microvessel disease. PixelFlux, a color Doppler ultras
0 views • 23 slides
The Essentials of the Urinary System
The urinary system plays vital roles in maintaining internal balance, filtering fluids, regulating blood volume and pressure, and producing essential hormones. Consisting of organs like the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, the system functions through processes like urine formation, tubular r
0 views • 13 slides
Overview of the Urinary System and Kidney Function
The urinary system, also known as the renal system, includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Its main functions are waste elimination, blood volume regulation, electrolyte control, and pH regulation. The kidneys, bean-shaped organs with a complex structure, filter blood to produce urine.
0 views • 35 slides
The Human Urinary System
The human urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter blood to produce urine, which is carried to the bladder through the ureters for storage until excretion. Each kidney is structured with renal pyramids and nephrons for blood filtration and waste remov
0 views • 16 slides
Overview of the Urinary System: Functions, Structure, and Importance
The urinary system plays a crucial role in maintaining water and salt balance, regulating pH levels, and excreting waste products like urea and uric acid. Comprising of organs such as the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra, this system ensures the removal of metabolic waste from the body
0 views • 34 slides
Radiological Anatomy & Investigations of Urinary System by Dr. Husain Alturkistani
This educational resource delves into various imaging modalities used to visualize the urinary system, detailing the anatomy, sizes, and locations of structures like the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. It covers modalities such as plain X-ray, IVU, ultrasound, CT, MRI, and nuclear medicine,
0 views • 90 slides
Foreigners prefer India for Kidney Transplant surgery
Kidney diseases are increasing globally. Once the kidneys fail to function properly, the patients will have severe health complaints. Failed kidneys if not treated in time can be fatal. The two treatments available for failed kidneys are either hemod
0 views • 3 slides
Fatty Liver and Kidney Syndrome (FLKS) in Poultry: Causes and Symptoms
Fatty Liver and Kidney Syndrome (FLKS) is a nutritional deficiency disease in poultry characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver and kidneys. This syndrome can lead to morbidity and mortality in affected chickens, with symptoms like incoordination and abnormal movements. The liver and kid
0 views • 20 slides
Renal Physiology
The renal system, comprising two kidneys and related structures, plays a crucial role in regulating blood volume, ion concentration, and pH. Kidneys function in balancing water, excreting waste products, regulating arterial pressure, maintaining acid-base balance, producing erythrocytes, and more. T
0 views • 27 slides
Fundamentals of Nursing
Kidneys play a vital role in maintaining body fluids by filtering waste and forming urine. Nephrons, the functional units of kidneys, regulate fluid balance through reabsorption and secretion. The urine then travels from kidneys to the bladder through the ureters, where it is stored until eliminatio
0 views • 16 slides