Understanding the Periodic Table: Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids
Delve into the characteristics of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids as you explore the layout of the periodic table. Discover how elements are grouped, their properties, and reactivity based on their placement. Uncover the significance of valence electrons, energy levels, and the distinct traits that define each category of elements.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Metals Nonmetals Metalloids The Periodic Table
Characteristic of Metals Found on the LEFT side of the Periodic Table. Malleable can be hammered or rolled into sheets Ductile can be pulled into wires Conductors of heat or electricity Heat and electricity can easily flow through it Shiny
Characteristic of Nonmetals Found on the RIGHT side of the Periodic Table. Brittle Can easily break or shatter Insulators Does not allow heat or electricity to pass through it Dull Not shiny
Characteristic of Metalloids Found along the ZIGZAG line of the Periodic Table. Metalloids share characteristics with both metals and non-metals Semi conductors
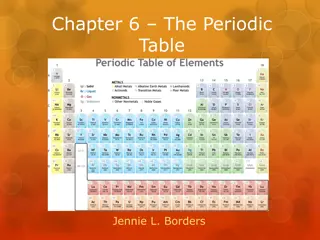
The Periodic Table The columns are called groups or families. Elements in the same group or family have similar properties. The group number also determines the elements valence electrons.
The Periodic Table The rows are called periods. The period determines how many energy levels an element has.
Group 1 Group 1 is called the Alkali Metals These elements have 1 valence electron and are HIGHLY reactive.
Group 2 Group 2 is called the Alkaline Earth Metals These elements have 2 valence electrons and are MODERATELY reactive.
Groups 3 12 Groups 3 12 are called the Transition Metals.
Group 13 Group 13 is called the Boron Group. These elements have 3 valence electrons and are MODERATELY reactive.
Group 14 Group 14 is called the Carbon Group. These elements have 4 valence electrons and are MODERATELY reactive.
Group 15 Group 15 is called the Nitrogen Group. These elements have 5 valence electrons and are MODERATELY reactive.
Group 16 Group 16 is called the Oxygen Group. These elements have 6 valence electrons and are MODERATELY reactive.
Group 17 Group 17 is called the Halogens. These elements have 7 valence electrons and are HIGHLY reactive.
Group 18 Group 18 is called the Nobel Gases. These elements have a FULL OUTER SHELL. These are the most stable or LEAST reactive of all the elements.