Characteristics and Families of the Periodic Table: A Comprehensive Overview
Explore the characteristics of the periodic table including the alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, lanthanides, actinides, and more. Learn about the properties, valence electrons, and uses of different groups, such as the boron group, carbon group, nitrogen group, oxygen group, halogens, noble gases, and hydrogen. Dive deeper into the classification of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids based on their properties. Discover how elements are categorized in the periodic table and their practical applications.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PERIODIC TABLE
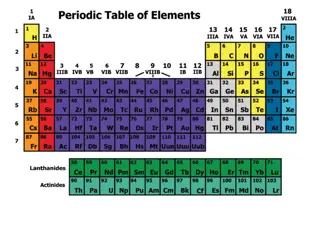
FAMILIES OF THE PERIODIC TABLE
Group # Name Properties Valence Electrons Uses Good or Bad? 1 ALKALI METALS VERY REACTIVE! Shiny, solid, good conductors of heat and electricity Reactive with water and oxygen (water=explosion; oxygen=tarnishing), low densities 1 Na-in salt; help blood pressure Li -in batteries Potassium- our growth (bananas) Can be good or bad depending on use 2 ALKALINE EARTH METALS Somewhat reactive (not as much as group 1), shiny, good conductors of heat and electricity, 2 Ca-bones Airplanes Medical uses 3-12 TRANSITION METALS Shiny, solid (except Mercury), good conductors of electricity and heat, 1-3 Jewelry, electronics, artificial bones (bone replacement) NONE LANTHANIDE Many are radioactive , solid, shiny, soft 1-3 Nuclear power, lenses, cars, S AND ACTINIDES BORON GROUP 13 1 metalloid and rest are metals, solids 3 Dinnerware, foil, airplane and automobile parts (Aluminum is the most abundant element in this group and therefore is used the most)
Group # Name Properties Valence Electrons Uses Good or Bad? 14 CARBON GROUP Solids. (yes, even carbon); there are a mixture of metals, metalloids, and nonmetals 4 Carbon is in all organisms, Ge-computer chips Sn (tin) is used to coat steel cans, and to create bronze objects. Pb (lead) used to be used until it was determined it was poisonous. Can be good or bad depending on use 15 NITROGEN GROUP Solids except for nitrogen, reactivity varies based on the element (Phosphorus is the most reactive) 5 Matches, ammonia, rat poison/pesticides, Nitrogen- in the air, nitrous oxide (laughing gas) 16 OXYGEN GROUP Solid except for oxygen, reactive, flammable 6 -Sulfuric acid (very strong acid), -organisms need oxygen to survive, 17 HALOGENS Reactive, poor conductors of electricity and heat, are not found by themselves in nature, usually are found bonded with another atom of themselves, combine with alkali metals to form salts 7 Toothpaste, disinfectant/antiseptics, water sterilization 18 NOBLE GASES Un-reactive, colorless, odorless, gas form, all are nonmetals, 8 Light bulbs, signs, filling balloons, blimps, H Hydrogen Reactive when combined with oxygen by electricity, colorless, odorless, gas, low density 1 Rocket fuel, found in stars, atmosphere, water
BREAK DOWN PROPERTIES A LITTLE BIT MORE: METALS, NONMETALS, METALLOIDS These are the general properties for each type of classification above These are ways to classify elements based on their properties
METALS (TO THE LEFT AND BOTTOM OF TABLE) Have luster (shininess) Are malleable (easy to make into thin, flat pieces) Are GOODconductors (transferors) of heat and electricity Solid state of matter (except Mercury-he s liquid) Ductile (easy to pull into wire) Few valence electrons (exact amount depends on family) Reactive
NONMETALS (TO THE RIGHT OF THE TABLE) Do not have luster (shininess) Are NOT malleable (easy to make into thin, flat pieces) THEY ARE BRITTLE Are POOR conductors transfers heat and electricity ARE SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, OR GASES at room temperature Are NOT ductile (easy to pull into wire) Many valence electrons (exact amount depends on family) Some are reactive Some are not reactive
METALLOIDS (ON THE ZIGZAG LINE) Physical properties depend on who it is Chemical properties depend on who it is Valence electron number depends on family Are mostly semi-conductors of heat and electricity