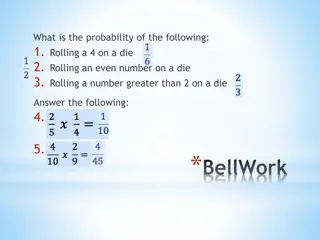Understanding Probability of Simple Events
Explore the concept of probability by learning about simple events, outcomes, and calculating probabilities using favorable outcomes. Discover how to express probability as fractions, decimals, or percentages through real-world examples like coin flips and dice rolls. Enhance your understanding of complementary events and their probabilities in various scenarios. Dive into practical applications of probability in everyday situations, such as Mr. Harada's survey on eye colors in his class.
Uploaded on Jul 22, 2024 | 1 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Unit 5A Probability Probability of Simple Events
Lesson 1: Probability of Simple Events Objective: Swbat find the probability of an event. Do Now:
Lesson 1: Probability of Simple Events Definitions Probability is the chance that some event will occur. A simple event is one outcome or a collection of outcomes. Outcome is a possible result in a probability experiment. Random each outcome is equally likely to occur. Complementary events are two events in which either one or the other must happen.
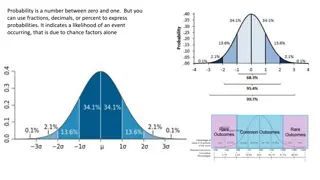
Lesson 1: Probability of Simple Events Probability can be written as a fraction, decimal or percent. Value is between 0 (impossible) and 1 (certain).
Lesson 1: Probability of Simple Events The probability of an event is a ratio that compares the number of favorable outcomes to the number of possible outcomes. P(event) = number of favorable outcomes number of possible outcomes
Lesson 1: Probability of Simple Events Example: Flip of a Coin 2 outcomes (Heads or Tails) P(Heads) = or .5 or 50% P(Tails) = or .5 or 50%
Lesson 1: Probability of Simple Events Example: Roll of a Number Cube 6 outcomes (1,2,3,4,5,6) P(0) = 0/6 0% P(1) = 1/6 or .17 or 17% P(2,3,or 4) = 3/6 or .5 or 50% P(1,2,3,4,5,6) = 6/6 or 100% Complement P(not a 6) = 5/6 or 83%
Lesson 1: Probability of Simple Events Example: Roll of a set of dice 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6
Lesson 1: Probability of Simple Events Real-World Problem Mr. Harada surveyed his class and discovered that 30% of his students have blue eyes. Identify the complement of this event.
Classwork Guided Practice #1 5 Independent Practice #1 5 Problem Solving Practice #1 - 8
Closure Question: What do the possibilities of an event range between? Exit Ticket Homework: Practice # 1 - 18
Exit Ticket There are 3 red marbles, 2 yellow marbles and 3 purple marbles in a bag. What is the probability of picking a purple marble? What is the probability of the complement?